Imagine a company that wants to double its bandwidth and ensure redundancy between switches but without causing loops. That’s exactly what EtherChannel does: it combines multiple physical links into a single logical one.
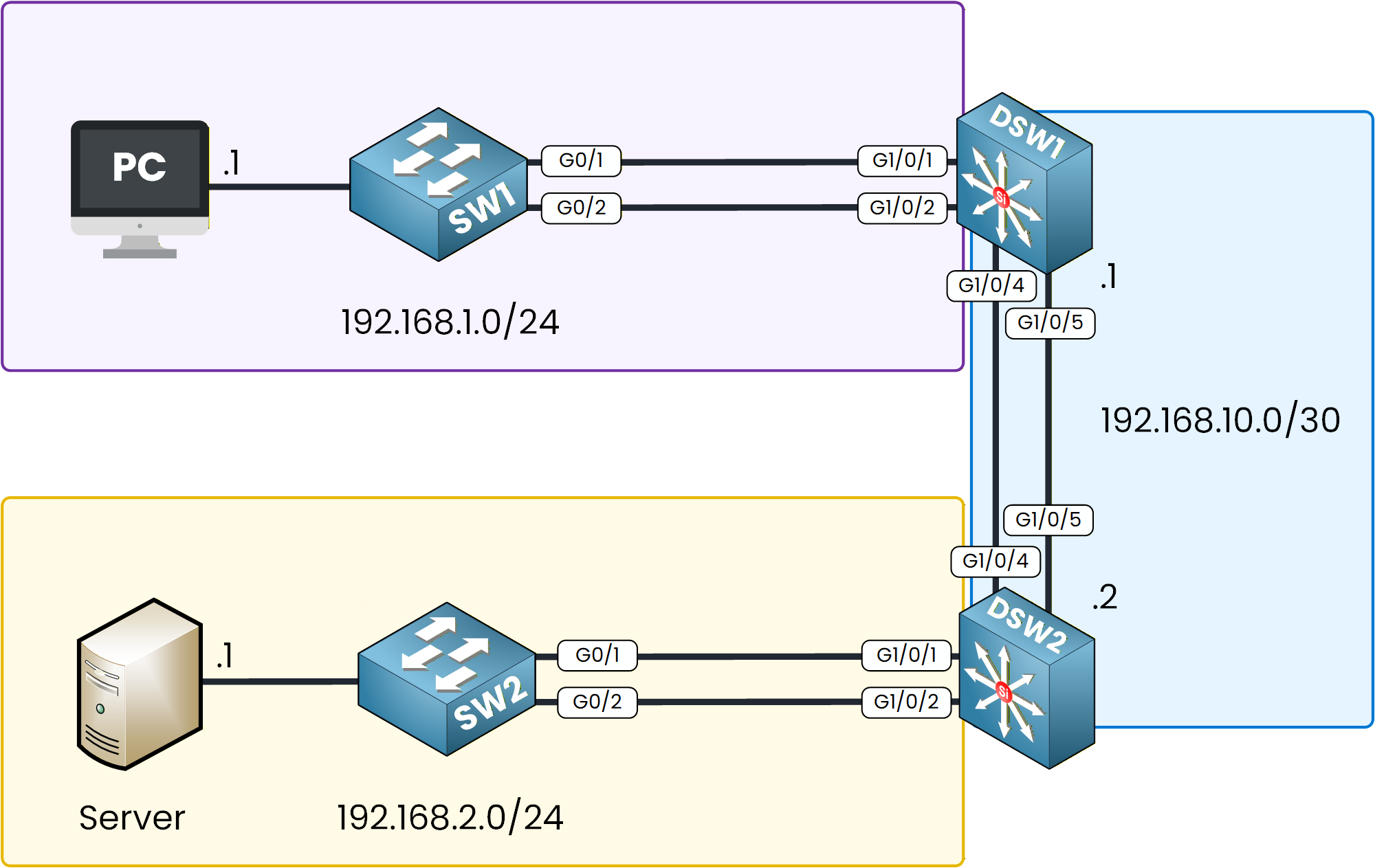
Figure 1 - EtherChannel Configuration Topology
So far in this course, we’ve seen how EtherChannel can be configured using different methods:
In this lab, you’ll put all of that into practice.
We’ll recap everything step by step, so you can configure and verify each EtherChannel type directly in Packet Tracer.How to Begin
Before starting, download the lab file using the button at the top of the page.
You’ll find a ready-made topology with all IP addresses and VLANs pre-configured, so you can focus entirely on the EtherChannel setup.Lab Overview
Here’s the structure we’ll follow throughout this lab:
Step 1 – Configure a Layer 2 EtherChannel between SW1 and DSW1 using PAgP and set the interfaces as trunk ports.
Step 2 – Configure a Layer 2 EtherChannel between SW2 and DSW2 using LACP and set the interfaces as trunk ports.
Step 3 – Configure a static Layer 3 EtherChannel between DSW1 and DSW2 and assign IP addresses.
Step 4 – Configure static routing on DSW1 and DSW2 to allow communication between the PC and the server.
Step 5 – Verify connectivity by pinging the server from the PC.
Let’s Get Started
Open the Packet Tracer file and try to configure the first EtherChannel on your own.
This way, you’ll actively apply what you’ve learned before checking the guided solution that follows.In the next sections, we’ll walk through each configuration step together, explain the commands, and verify that everything works correctly.
Answer the question below
In this first step, we’ll configure an EtherChannel between SW1 and DSW1 using the PAgP protocol.
This will allow both switches to dynamically negotiate the bundle and act as a single logical trunk.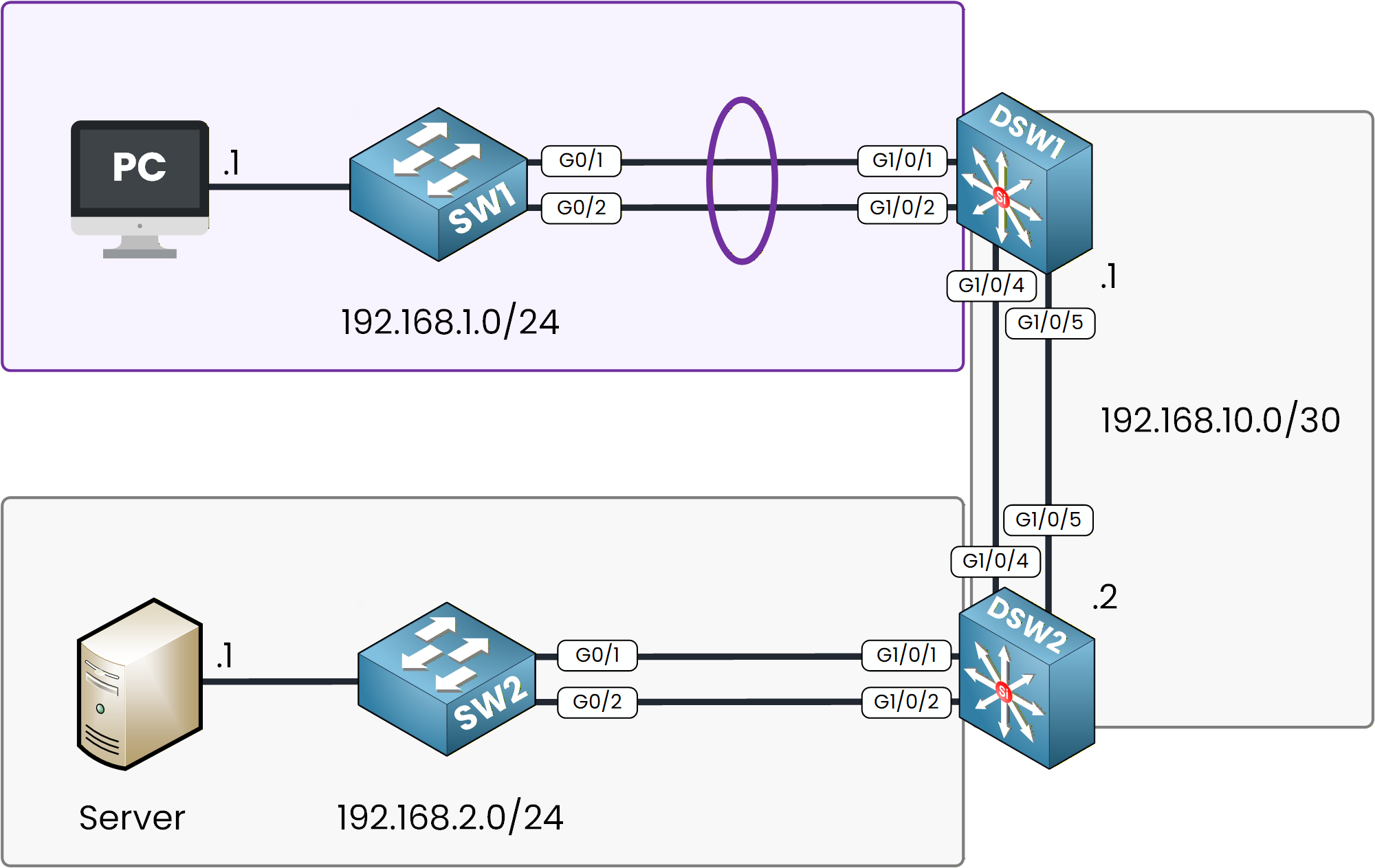
Figure 2 - PAgP EtherChannel Configuration Topology
Configuring SW1
Let’s start by connecting to SW1 and grouping interfaces GigabitEthernet 0/1 and 0/2 into a single EtherChannel.
SW1# configure terminal Enter configuration commands, one per line. SW1(config)# interface range gigabitEthernet 0/1-2 SW1(config-if-range)# channel-group 1 mode ? active Enable LACP unconditionally auto Enable PAgP only if a PAgP device is detected desirable Enable PAgP unconditionally on Enable Etherchannel only passive Enable LACP only if a LACP device is detectedAmong the available modes, desirable and auto belong to PAgP.
We’ll choose desirable so the switch actively forms the EtherChannel.SW1(config-if-range)# channel-group 1 mode desirable Creating a port-channel interface Port-channel 1 %LINEPROTO-5-UPDOWN: Line protocol on Interface GigabitEthernet0/1, changed state to up %LINEPROTO-5-UPDOWN: Line protocol on Interface GigabitEthernet0/2, changed state to up SW1(config-if-range)# exitAt this stage, the logical interface Port-channel 1 has been created, and both links are now bundled.
However, the EtherChannel is still inactive since the opposite switch is not yet configured.Let’s now enable trunking on this new Port-Channel.
Set Port-Channel as Trunk
To enable trunking, we apply the
switchport mode trunkcommand under the Port-Channel interface.SW1(config)# interface po1 SW1(config-if)# switchport mode trunk SW1(config-if)# endThat’s it. The logical interface is now acting as a trunk.
Let’s check the EtherChannel status to confirm the configuration.Check EtherChannel Status
The
show etherchannel summarycommand displays all EtherChannels configured on the device.
Here, Po1 is flagged as SD, which means the EtherChannel is Layer 2 (S) but currently Down (D).SW1# show etherchannel summary Flags: D - down P - in port-channel I - stand-alone s - suspended H - Hot-standby (LACP only) R - Layer3 S - Layer2 U - in use f - failed to allocate aggregator u - unsuitable for bundling w - waiting to be aggregated d - default port Number of channel-groups in use: 1 Number of aggregators: 1 Group Port-channel Protocol Ports ------+-------------+-----------+---------------------------------------------- 1 Po1(SD) PAgP Gig0/1(I) Gig0/2(I)This is perfectly normal for now, the opposite switch hasn’t been configured yet.
Configuring DSW1
Now, let’s move to DSW1 and configure the same EtherChannel.
We’ll bundle GigabitEthernet 1/0/1 and 1/0/2 into Port-Channel 1 using desirable mode.
We could have used auto, but using desirable on both sides ensures negotiation succeeds immediately.DSW1# configure terminal Enter configuration commands, one per line. DSW1(config)# interface range g1/0/1-2 DSW1(config-if-range)# channel-group 1 mode desirable Creating a port-channel interface Port-channel 1The logical interface Po1 has now been created.
Next, let’s enable trunking on it.Set Port-Channel as Trunk
We’ll apply the same principle: enable trunking directly under the Port-Channel interface.
DSW1(config)# interface po1 DSW1(config-if)# switchport mode trunk DSW1(config-if)# endLet’s now verify if the EtherChannel is up and operational.
Check EtherChannel Status
The
show etherchannel summaryoutput now shows SU, indicating that the EtherChannel is Layer 2 (S) and Up (U) which means it’s working properly.DSW1# show etherchannel summary Flags: D - down P - in port-channel I - stand-alone s - suspended H - Hot-standby (LACP only) R - Layer3 S - Layer2 U - in use f - failed to allocate aggregator u - unsuitable for bundling w - waiting to be aggregated d - default port Number of channel-groups in use: 1 Number of aggregators: 1 Group Port-channel Protocol Ports ------+-------------+-----------+---------------------------------------------- 1 Po1(SU) PAgP Gig1/0/1(P) Gig1/0/2(P)Each physical interface now shows (P), confirming it’s actively participating in the bundle.
Verify Trunk Configuration
We can also confirm that the trunk is correctly operational using the
show interfaces trunkcommand.DSW1# show interfaces trunk Port Mode Encapsulation Status Native vlan Po1 on 802.1q trunking 1 Port Vlans allowed on trunk Po1 1-1005 Port Vlans allowed and active in management domain Po1 1 Port Vlans in spanning tree forwarding state and not pruned Po1 nonePerfect, the EtherChannel is now up, trunking, and fully operational.
You’ve successfully configured a Layer 2 EtherChannel using PAgP.Answer the question below
Which PAgP mode actively tries to form an EtherChannel on its own?
In this step, you will configure an EtherChannel between SW2 and DSW2 using LACP.
Unlike PAgP, LACP follows the IEEE 802.3ad standard, which means it can work across devices from different vendors.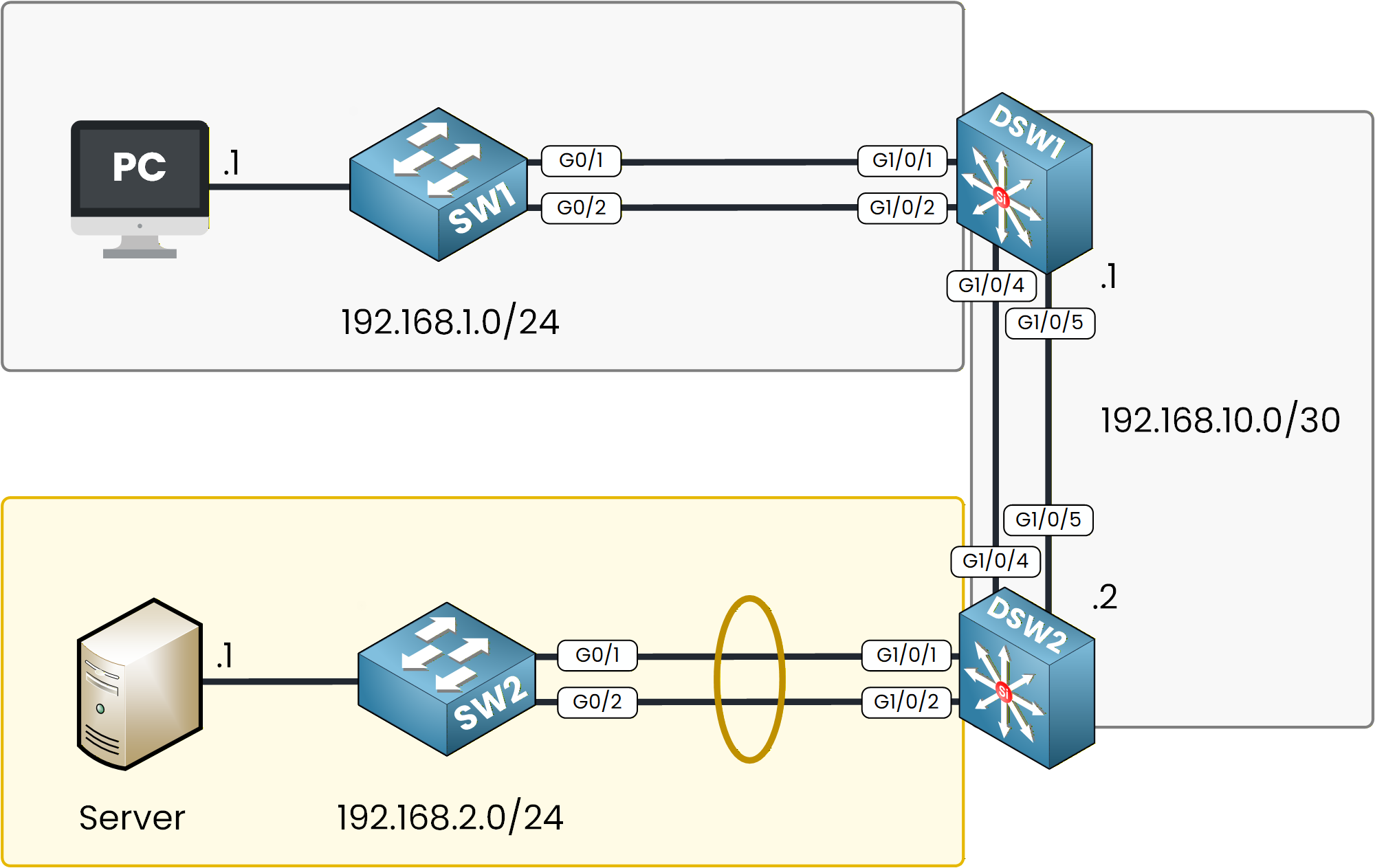
Figure 3 - LACP EtherChannel Configuration Topology
Configuring SW2
Let’s start by connecting to SW2.
You will group GigabitEthernet 0/1 and 0/2 into a single logical interface called Port-Channel 2.SW2# configure terminal Enter configuration commands, one per line. SW2(config)# int range g0/1-2 SW2(config-if-range)# channel-group 2 mode ? active Enable LACP unconditionally auto Enable PAgP only if a PAgP device is detected desirable Enable PAgP unconditionally on Enable Etherchannel only passive Enable LACP only if a LACP device is detectedYou probably remember the PAgP modes from the previous step.
This time, the available LACP modes are active and passive.
Choose active mode so the switch initiates the negotiation process.SW2(config-if-range)# channel-group 2 mode active Creating a port-channel interface Port-channel 2 %LINEPROTO-5-UPDOWN: Line protocol on Interface GigabitEthernet0/1, changed state to up %LINEPROTO-5-UPDOWN: Line protocol on Interface GigabitEthernet0/2, changed state to up SW2(config-if-range)# exitThe Port-Channel interface has now been created.
Both links are bundled, but the EtherChannel is not operational yet because the other side is not configured.40 % Complete: you’re making great progress
Unlock the rest of this lesson
If you’d like to continue your CCNA journey, simply create your free account.
Access all CCNA lessons
Practice with hands-on labs
Train with Practice exams and Quizzes
Progress tracking in your dashboard
Made by network engineers - CCNP certified
learners globally