Voice VLAN on Cisco is a strong feature. It helps you separate and prioritize voice traffic from data traffic. In this guide, we’ll walk you through its purpose, configuration, and how it works step by step.
Let’s take a step back.
Before Cisco introduced the Voice VLAN feature, things were a bit messier. If you had a computer and an IP phone at the same desk, you needed two Ethernet cables and two switch ports.
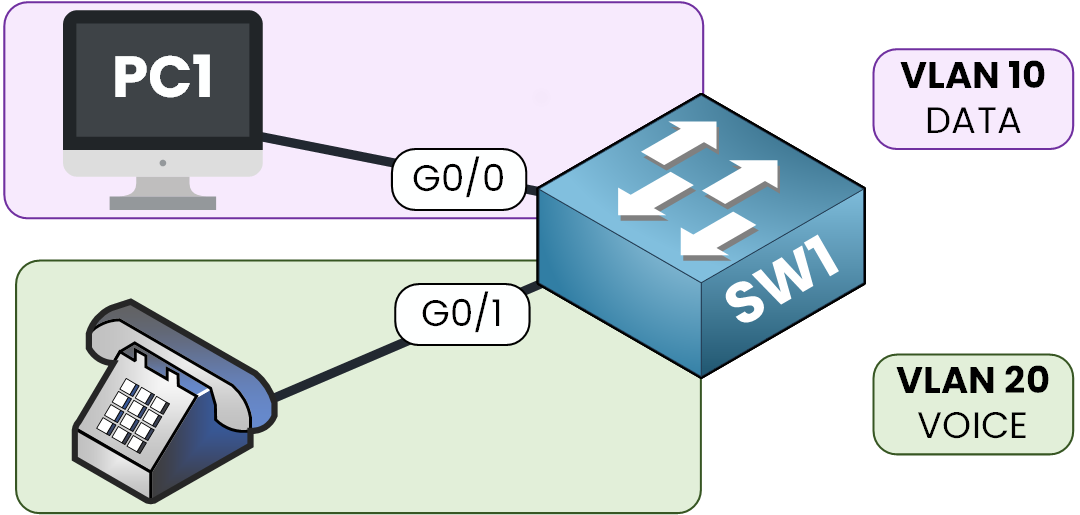
Figure 1 – Before Voice VLAN, each device required a dedicated switch port
Each device had its own port, both configured in access mode:
One port for VLAN 10 (DATA)
One port for VLAN 20 (VOICE)
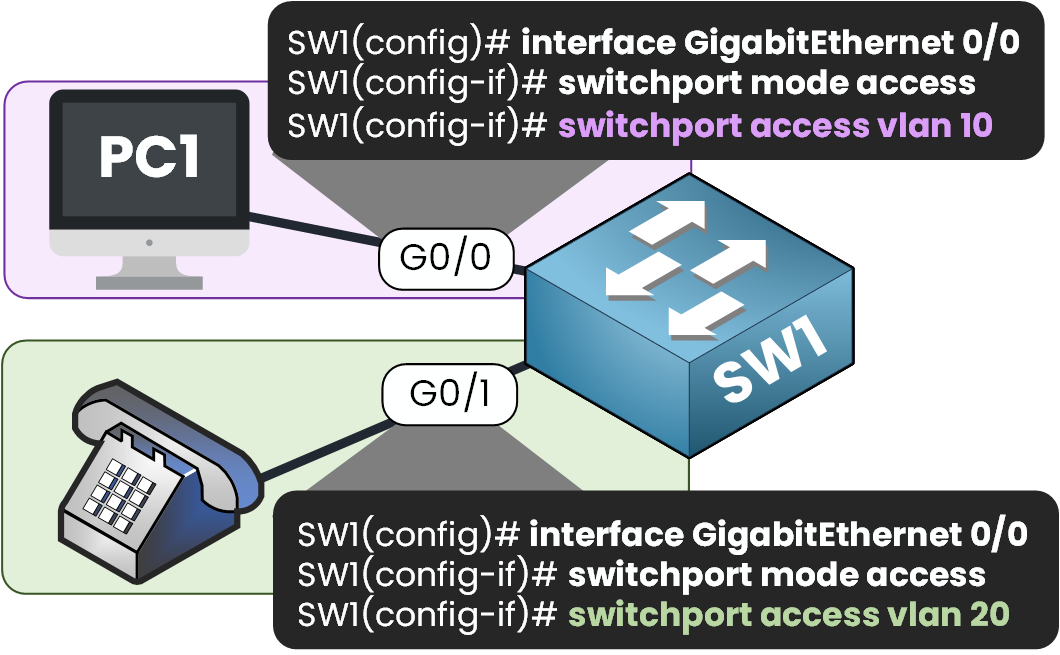
Figure 2 – Each port is manually configured with its own VLAN for data or voice
This setup worked but let’s be honest, it wasn’t efficient:
You were burning two switch ports per user
You had to run more cabling
And you had to configure and maintain twice as many ports
As your network grows, this quickly turns into a scalability nightmare.
Answer the question below
Before Cisco introduced Voice VLAN, how many switch ports were required per user?
To solve this inefficiency, Cisco introduced the Voice VLAN feature.
Modern IP phones, like the Cisco 79xx series, have a built-in mini switch with two ports:
One that connects directly to the switch
One that connects to your PC
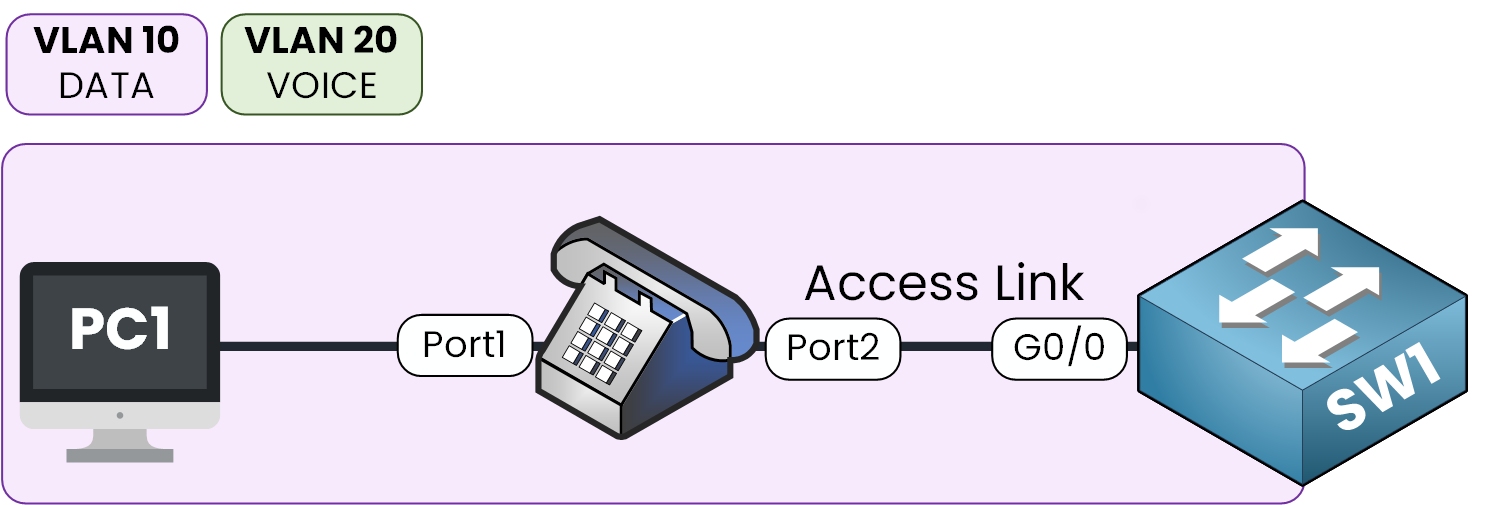
Figure 3 – PC and phone share one port using Voice VLAN and the phone’s mini switch
This setup allows both the PC and the phone to share the same Ethernet link on the switch.
Answer the question below
With the Voice VLAN feature, how many switch ports are needed to connect both a PC and an IP phone at the same desk?
Alright, so how does all this actually work?
Let's say you configured your switch port like this:
Access VLAN: 10 (for Data)
Voice VLAN: 20 (for Voice)
Now imagine traffic coming from the PC and the IP phone:
The PC sends untagged frames → the switch associates them with VLAN 10 (DATA)
The IP phone tags its voice traffic using 802.1Q marking it as VLAN 20 (VOICE)
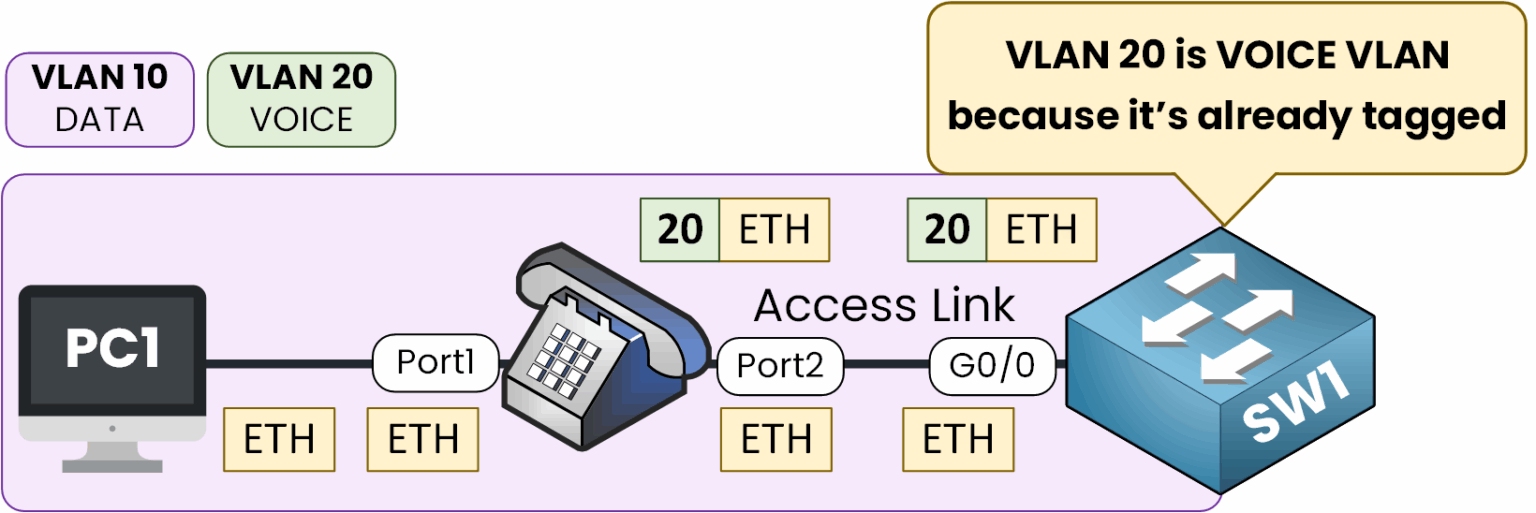
Figure 4 – Voice VLAN uses 802.1Q tagging while data remains untagged
Your switch port GigabitEthernet 0/0 is still configured in access mode but it now understands two types of traffic:
Untagged = Data VLAN
Tagged = Voice VLAN
Voice Traffic is Prioritized
What's is also very cool is that voice traffic is prioritized to ensure a good Quality of Service.
As you can see here, the IP phone tags voice traffic by default with 802.1q Class of Service (CoS) = 5
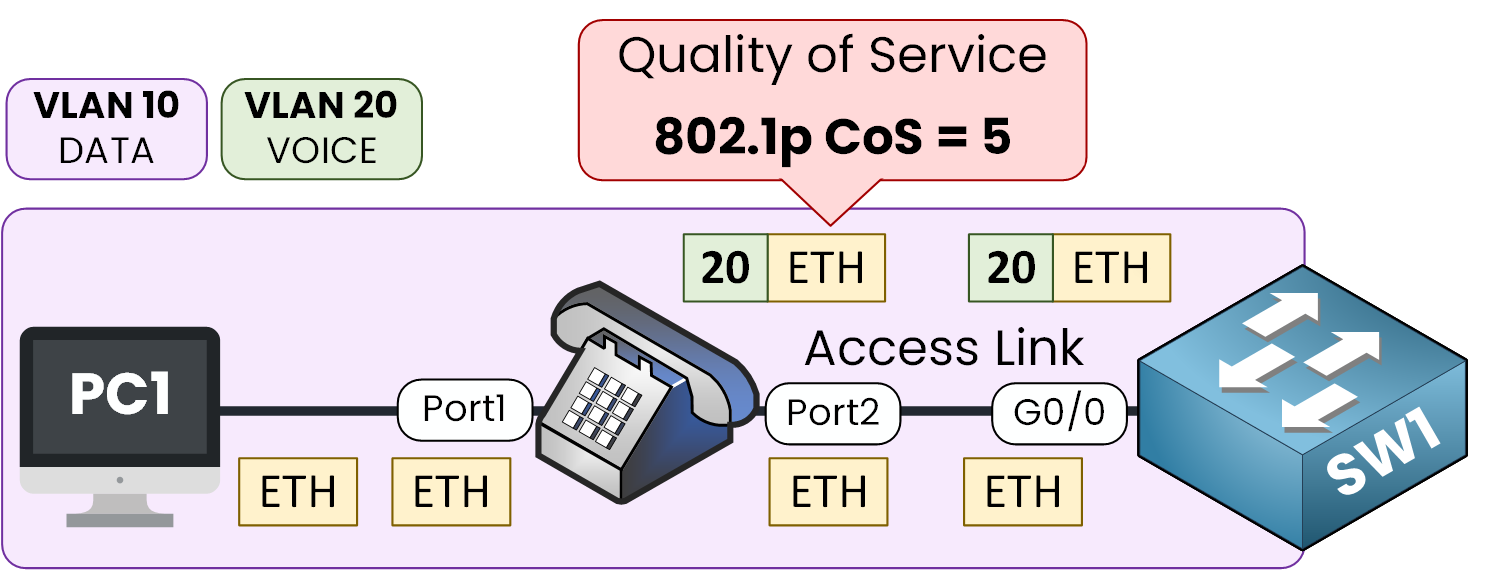
Figure 5 – Voice traffic is tagged with CoS 5 to ensure quality of service.
40 % Complete: you’re making great progress
Unlock the rest of this lesson
If you’d like to continue your CCNA journey, simply create your free account.
Access all CCNA lessons
Practice with hands-on labs
Train with Practice exams and Quizzes
Progress tracking in your dashboard
Made by network engineers - CCNP certified
learners globally
Voice VLAN
In the past, every desk with a PC and a phone required two ports and two cables. In this lesson, you’ll learn how Cisco’s Voice VLAN solved this problem by separating and prioritizing voice traffic on the same port.