In this course, we’ll explore Dynamic ARP Inspection configuration through a simple and realistic scenario.
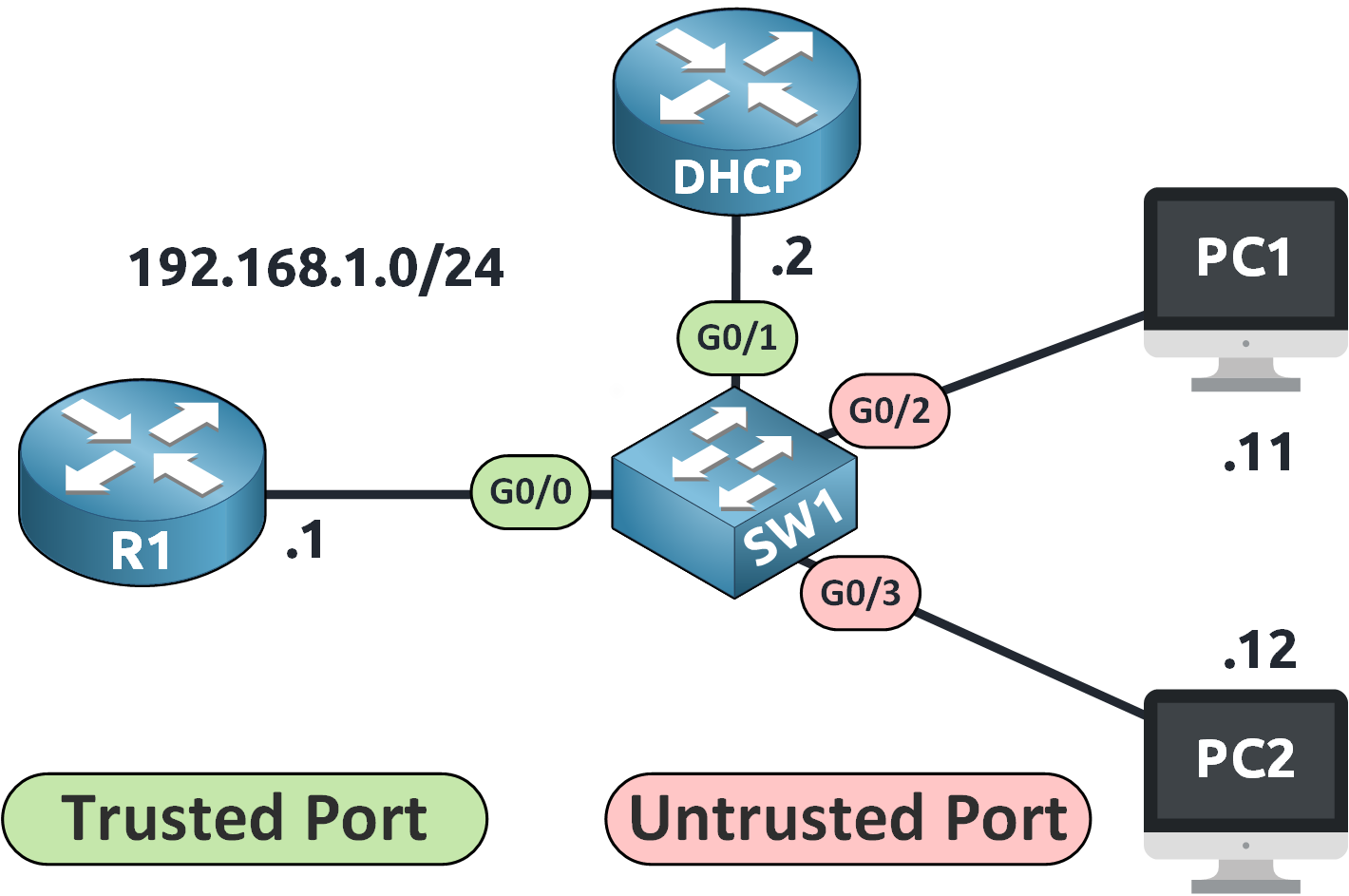
Figure 1 – Network Topology for DAI Configuration
We are working on switch SW1 with the following network:
DHCP Server connected to G0/1
Router (R1) connected to G0/0
PC1 connected to G0/2
PC2 connected to G0/3
All devices are on VLAN 1 in the 192.168.1.0/24 subnet.
Step 1: Configure DHCP on the Router
Before anything else, the router must assign IP addresses.
DCHP# show run | s dhcp ip dhcp excluded-address 192.168.1.1 192.168.1.10 ip dhcp pool VLAN1 network 192.168.1.0 255.255.255.0 default-router 192.168.1.1 dns-server 8.8.8.8This setup:
Reserves addresses .1 to .10 for static assignment
Assigns dynamic IPs from .11 upward
Sets R1 as the default gateway
Uses Google DNS
Step 2: Enable DHCP Snooping
DAI needs the DHCP Snooping Binding Table, so we must activate DHCP Snooping first.
We enable DHCP Snooping globally and activate it on VLAN 1 (the default VLAN):
SW1# conf t Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z. SW1(config)# ip dhcp snooping SW1(config)# ip dhcp snooping vlan 1 SW1(config)# no ip dhcp snooping information optionThe information option is used when a DHCP relay agent is involved, which is not the case here, so we disable it.
Next, we trust the interface connected to the DHCP server:
SW1(config)# int g0/1 SW1(config-if)# ip dhcp snooping trust SW1(config-if)# endAnswer the question below
What feature creates the IP-to-MAC entries used by DAI?
Step 3: Verify the DHCP Snooping Binding Table
Use this command to confirm that IP/MAC mappings have been recorded:
SW1# show ip dhcp snooping binding MacAddress IpAddress Lease(sec) Type VLAN Interface ------------------ --------------- ---------- ------------- ---- ------------ 00:50:79:66:68:8C 192.168.1.11 86304 dhcp-snooping 1 G0/2 00:50:79:66:68:8F 192.168.1.12 86366 dhcp-snooping 1 G0/3 Total number of bindings: 2PC1 and PC2 are now recognized as legitimate DHCP clients. Their IP/MAC pairs will be used for ARP validation.
Answer the question below
What table stores the legitimate IP and MAC bindings?
Step 4: Enable DAI on VLAN 1
DAI only requires one command per VLAN to be activated.
SW1# conf t Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z. SW1(config)# ip arp inspection vlan 1DAI is now monitoring ARP traffic on VLAN 1. If you have multiple VLANs, repeat this command for each one.
Step 5: Define Trusted Interfaces
By default, all switch ports are untrusted.
We must manually trust ports connected to infrastructure devices:
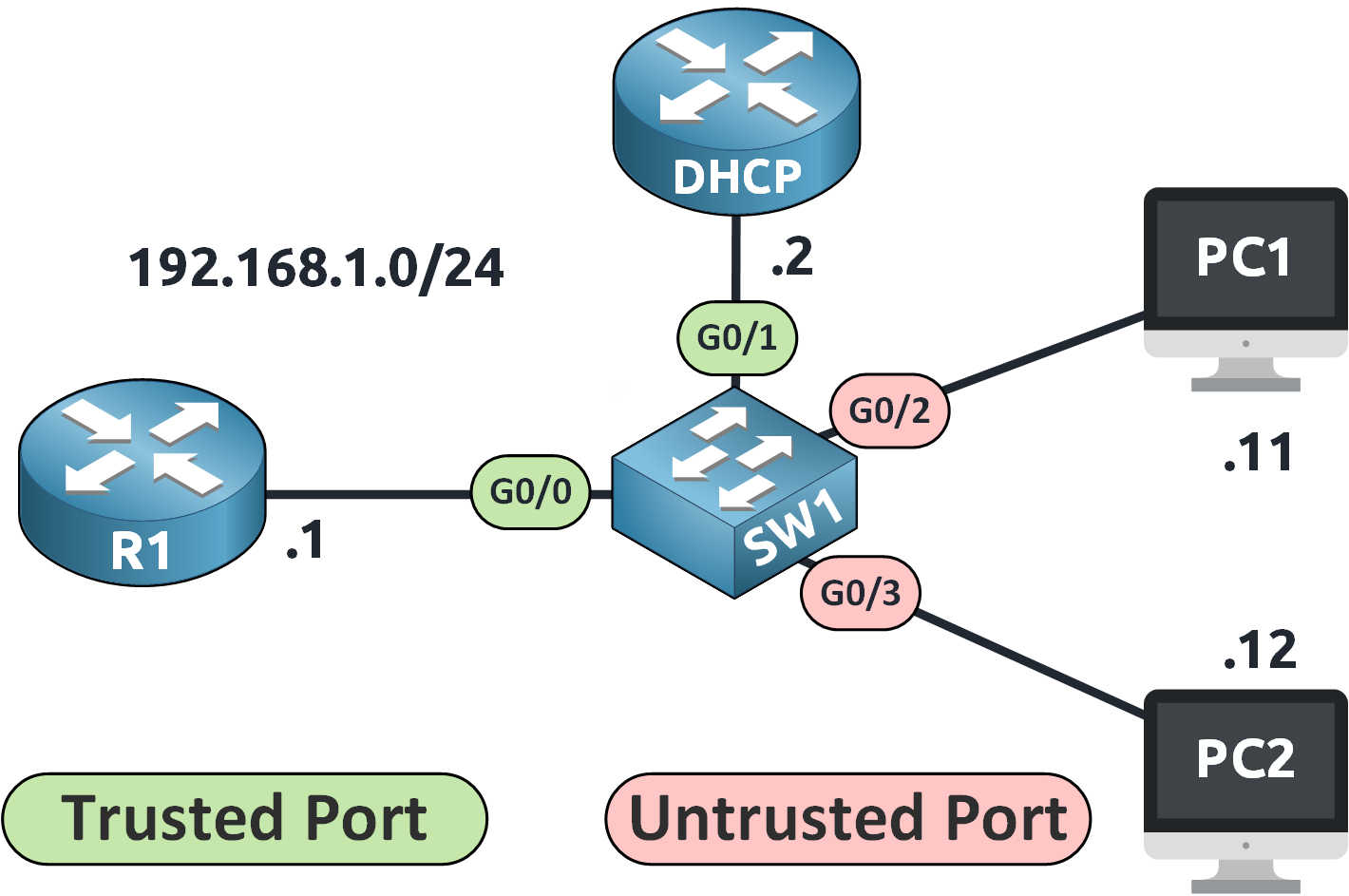
Figure 2 – Network Topology for DAI Configuration
SW1(config)# int g0/0 SW1(config-if)# ip arp inspection trust SW1(config-if)# exit SW1(config)# int g0/1 SW1(config-if)# ip arp inspection trust SW1(config-if)# endNow, ARP packets on these interfaces will not be inspected.
Answer the question below
Are user-facing switch ports trusted or untrusted for DAI?
Step 6: Verify DAI Status
We can verify that DAI is working correctly using the following command:
SW1# show ip arp inspection interfaces Interface Trust State Rate (pps) Burst Interval --------------- ----------- ---------- -------------- Gi0/0 Trusted None N/A Gi0/1 Trusted None N/A Gi0/2 Untrusted 15 1 Gi0/3 Untrusted 15 1 Gi1/0 Untrusted 15 1 Gi1/1 Untrusted 15 1 Gi1/2 Untrusted 15 1 Gi1/3 Untrusted 15 1This confirms:
G0/0 and G0/1 are trusted (router and DHCP server)
G0/2 and G0/3 are untrusted (user-facing ports)
Simulating an ARP Spoofing Attack
Let’s now test the effectiveness of DAI by simulating an attack.
In this scenario, PC2 (attacker) tries to impersonate the default gateway 192.168.1.1.
It does so by sending a Gratuitous ARP (GARP) message, falsely claiming that its own MAC address is associated with the IP address of the router.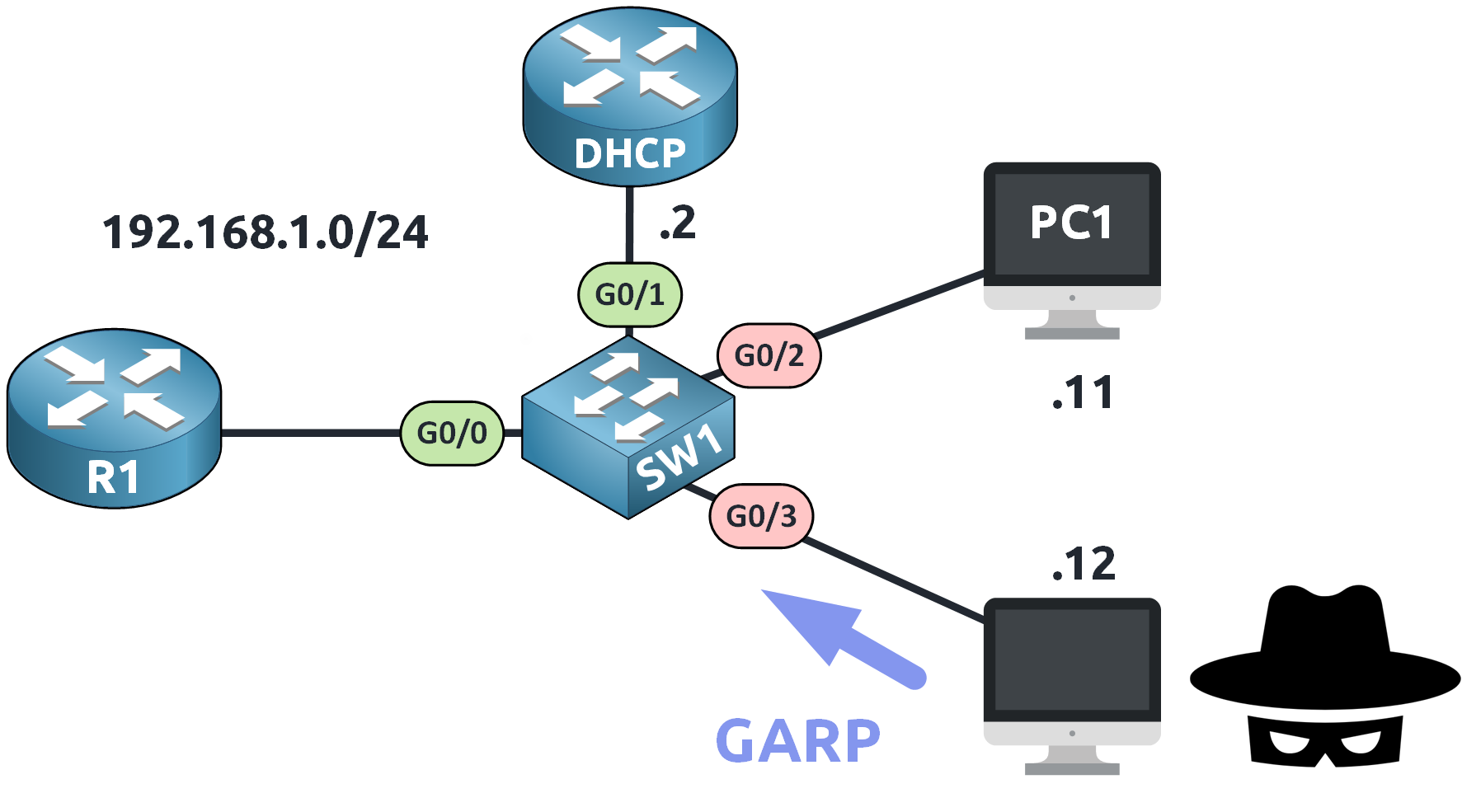
Figure 3 – Simulating an ARP Spoofing Attack
A Gratuitous ARP is an unsolicited ARP reply used to announce a device’s IP-to-MAC mapping. While legitimate in some contexts (like for IP changes), it can be exploited for spoofing.
On an untrusted port like G0/3, this GARP is intercepted by the switch and analyzed.
Wireshark Capture
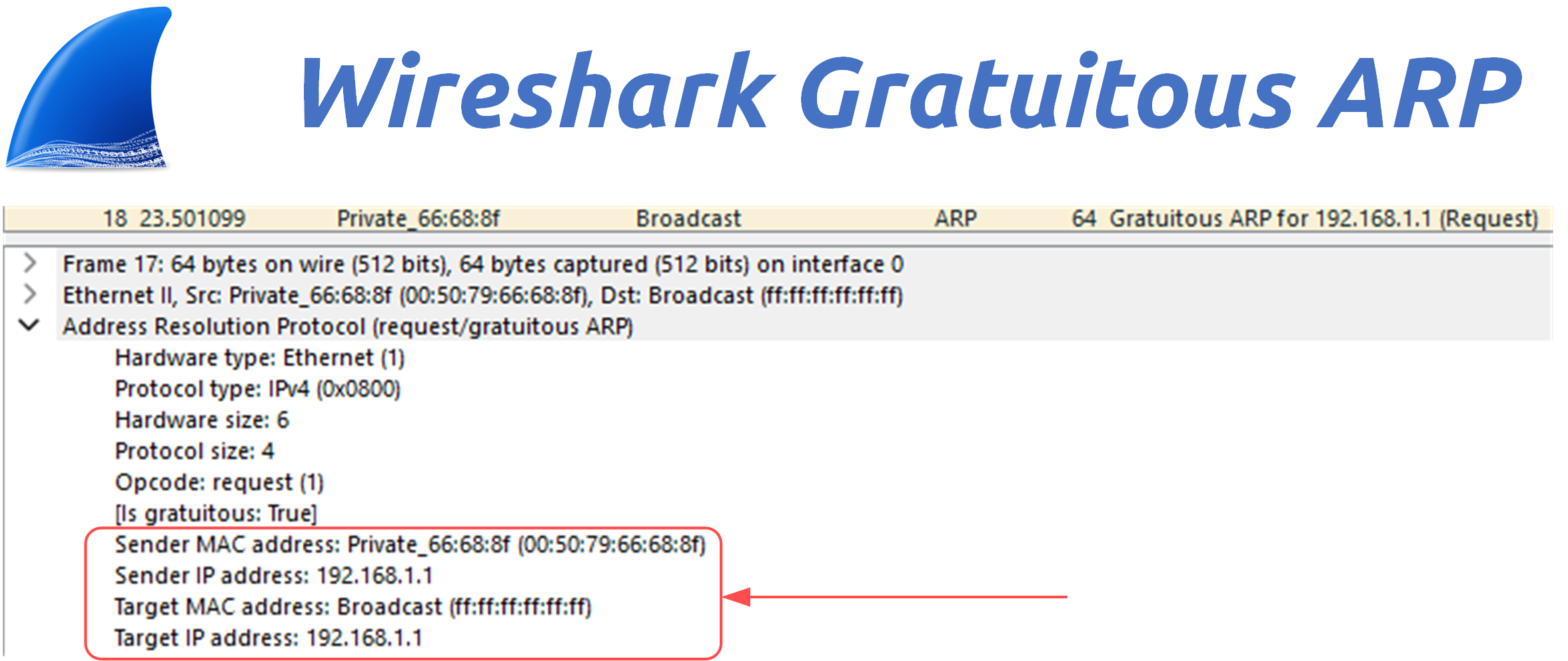
Figure 4 – Wireshark Capture of a Gratuitous ARP (GARP)
A packet capture reveals that the ARP message sent from PC2 claims:
Sender MAC: Attacker's MAC address
Sender IP: 192.168.1.1
Target MAC: Broadcast (ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff)
Target IP: 192.168.1.1
This is a clear attempt to poison the ARP tables of other hosts.
DAI Blocks the Attack
Because the DHCP Snooping Binding Table does not contain any entry mapping 192.168.1.1 to the attacker's MAC address, the switch considers this ARP packet invalid.
Here’s what appears in the logs:
*Jan 31 16:18:51.531: %SW_DAI-4-DHCP_SNOOPING_DENY: 1 Invalid ARPs (Req) on Gi0/3, vlan 1.([0050.7966.688f/192.168.1.1/ffff.ffff.ffff/192.168.1.1/ 16:18:50 UTC Fri Jan 31 2025]) *Jan 31 16:18:52.531: %SW_DAI-4-DHCP_SNOOPING_DENY: 1 Invalid ARPs (Req) on Gi0/3, vlan 1.([0050.7966.688f/192.168.1.1/ffff.ffff.ffff/192.168.1.1/ 16:18:51 UTC Fri Jan 31 2025]) *Jan 31 16:18:53.590: %SW_DAI-4-DHCP_SNOOPING_DENY: 1 Invalid ARPs (Req) on Gi0/3, vlan 1.([0050.7966.688f/192.168.1.1/ffff.ffff.ffff/192.168.1.1/ 16:18:52 UTC Fri Jan 31 2025])These messages confirm that the Dynamic ARP Inspection feature is actively monitoring and rejecting invalid ARP packets.
Thanks to DAI, the attacker is blocked from poisoning the ARP table, and the spoofing attempt fails silently, without impacting network users preventing the man-in-the-middle attack.
40 % Complete: you’re making great progress
Unlock the rest of this lesson
If you’d like to continue your CCNA journey, simply create your free account.
Access all CCNA lessons
Practice with hands-on labs
Train with Practice exams and Quizzes
Progress tracking in your dashboard
Made by network engineers - CCNP certified
learners globally
Dynamic ARP Inspection Configuration
DAI configuration protects your LAN by validating ARP against the DHCP Snooping binding table and inspecting only untrusted ports. You will trust uplinks, set rate limits, and enable IP and MAC checks to block spoofing without interrupting legitimate traffic.