Dynamic ARP Inspection (DAI) is a crucial security feature you need to understand if you want to protect your network from ARP Spoofing and Man-in-the-middle attacks.
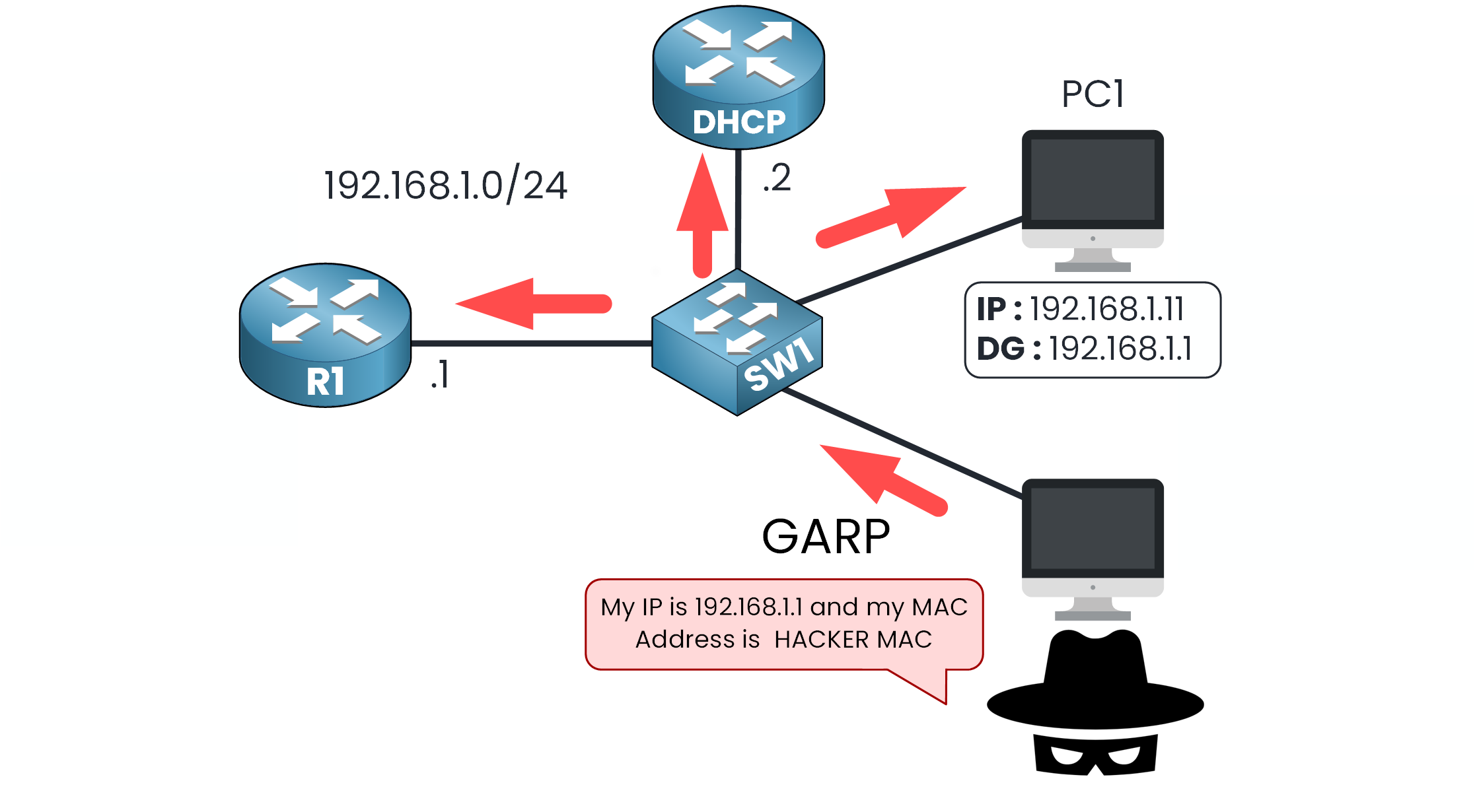
Figure 1 – ARP Spoofing Attack with Forged GARP Message
Imagine a hacker sends a forged Gratuitous ARP (GARP) message claiming that 192.168.1.1 (your gateway) is associated with their own MAC address.
This tricks other devices on the network into updating their ARP tables with false information and that's exactly the kind of attack DAI is designed to prevent.
But before diving deeper into DAI protection, let’s make sure you have a solid understanding of how ARP (Address Resolution Protocol) functions. That foundation will help you fully grasp the value of DAI.
Answer the question below
Which attack does Dynamic ARP Inspection help prevent?
As you may know, ARP (Address Resolution Protocol) maps IP addresses to MAC addresses within a local network. When a device knows only the IP address of another device, it uses ARP to discover the MAC address.
How ARP Works in a Local Network
To better understand ARP, let's look at a simple network with the subnet 192.168.1.0/24.
Here we have a network 192.168.1.0/24:
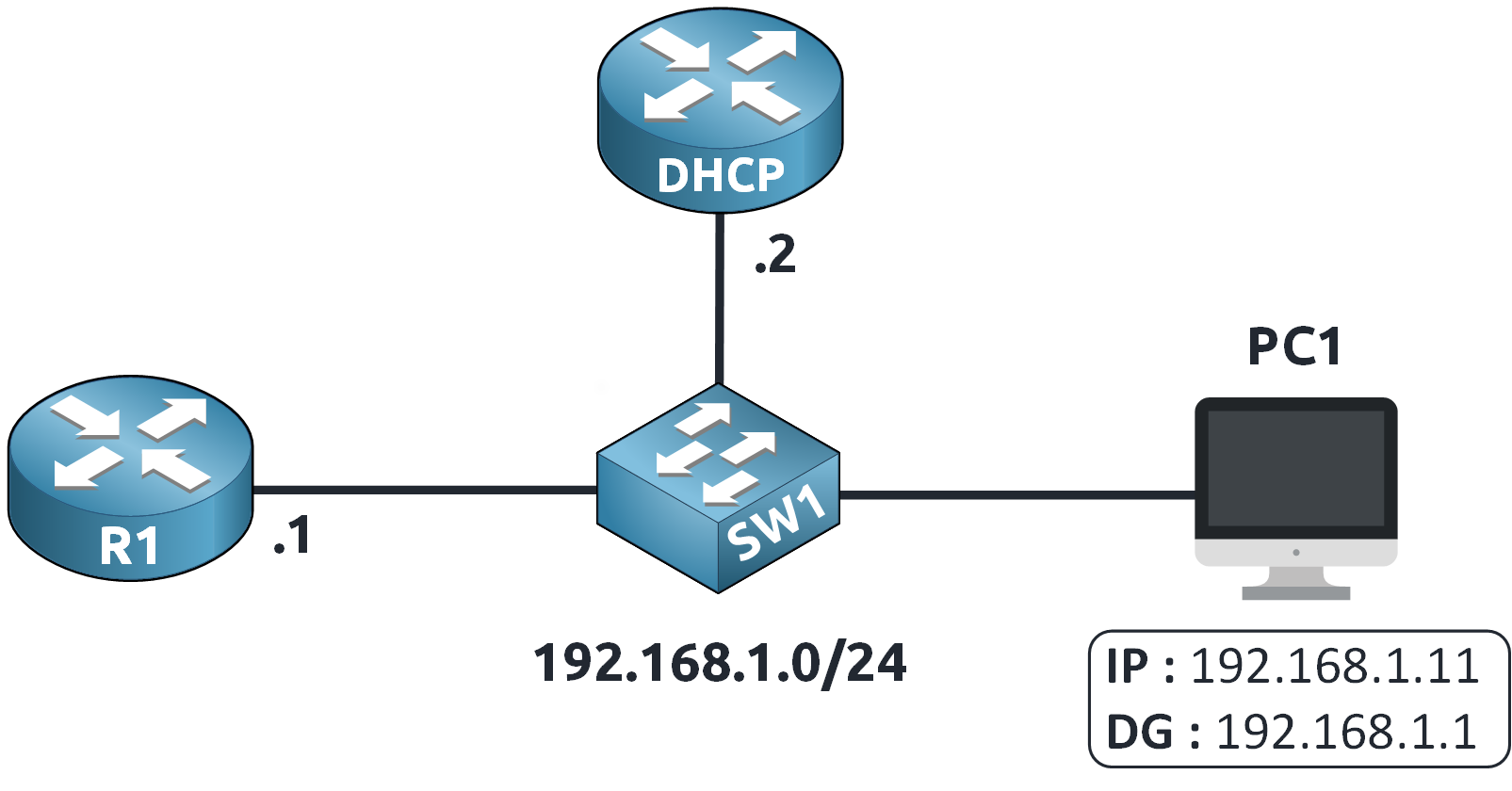
Figure 2 – Network Topology
PC1 is configured using a DHCP server and has an IP address of 192.168.1.11 with a default gateway of 192.168.1.1.
Imagine PC1 wants to send a ping to 8.8.8.8!
Since the destination is outside the 192.168.1.0/24 subnet, PC1 must send the traffic through its default gateway (R1).
Visualizing ARP Step-by-Step
When the ping to 8.8.8.8 is initiated, PC1 first checks its MAC address table.
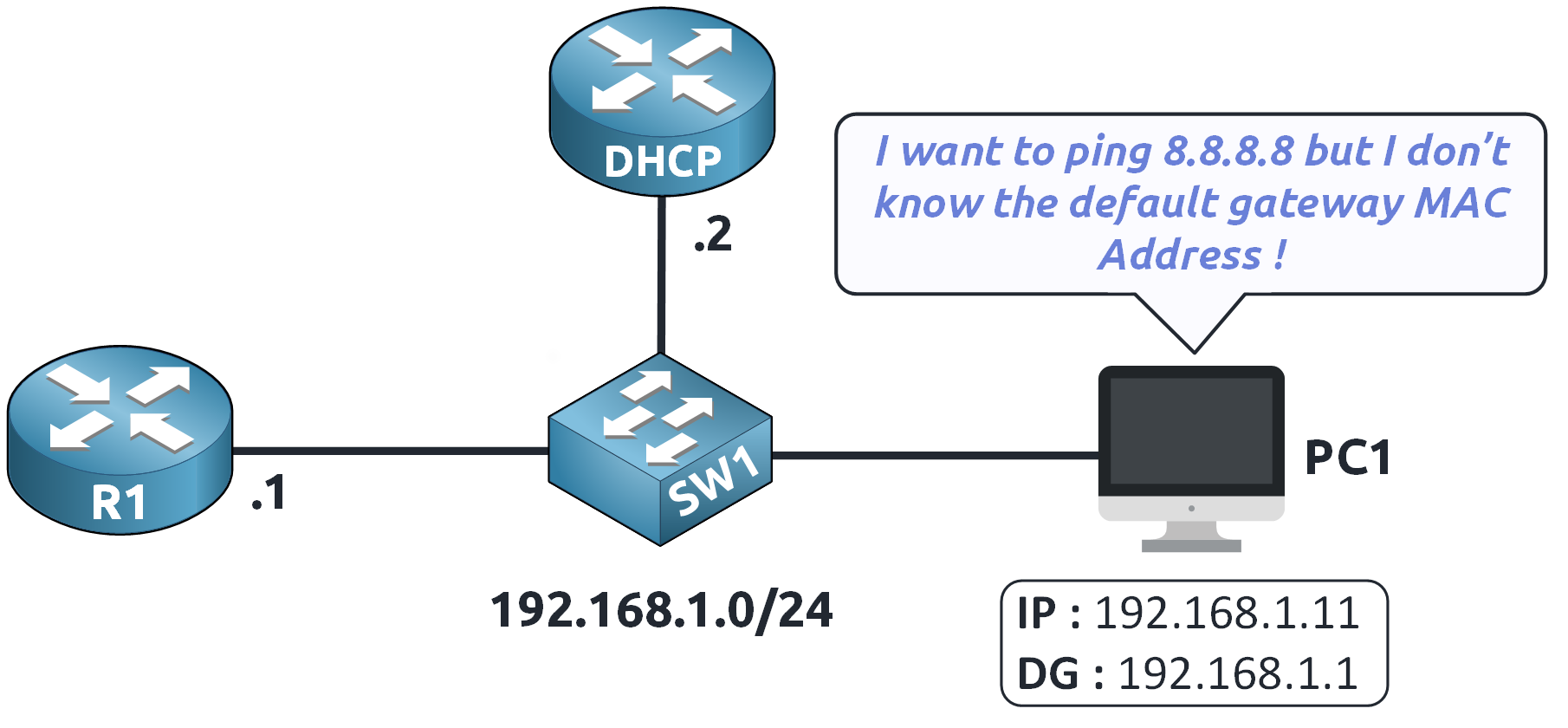
Figure 3 – ARP Process Begins: MAC Address Unknown
Since the MAC address of 192.168.1.1 is unknown…
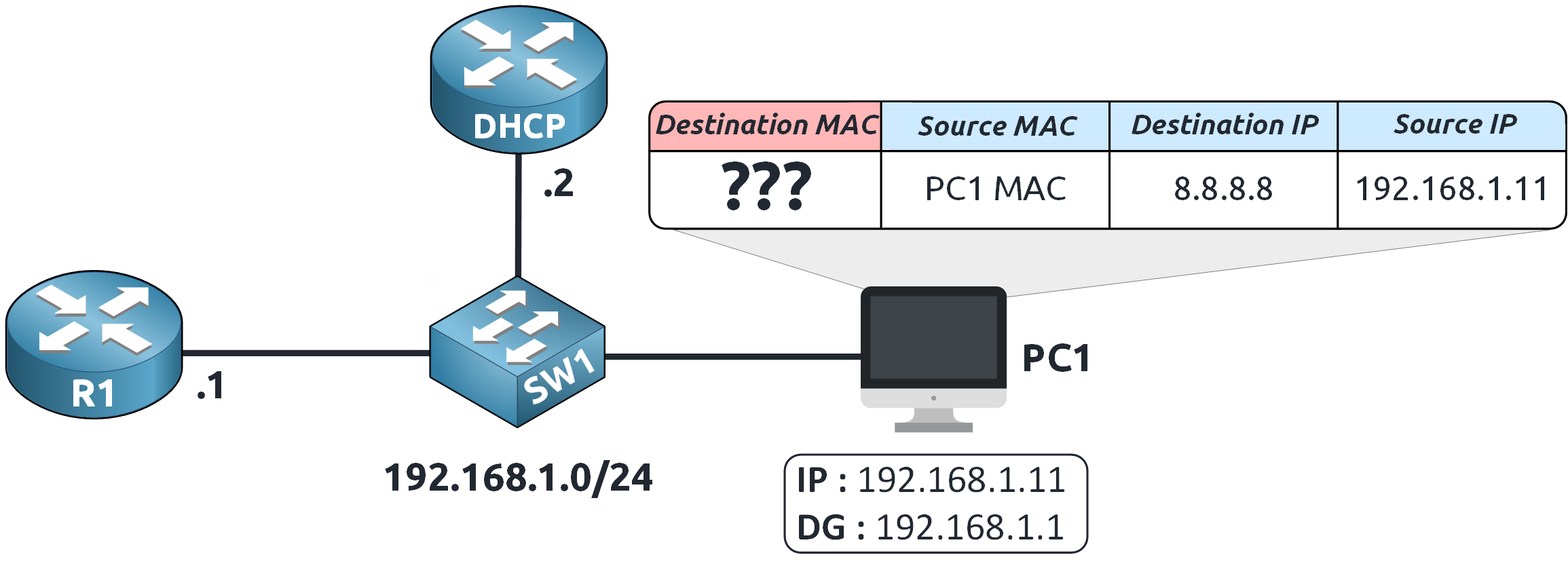
Figure 4 – PC1 Sends ARP Request for Default Gateway MAC
PC1 sends an ARP Request to the local network:
"Who has 192.168.1.1? Tell me your MAC address!"
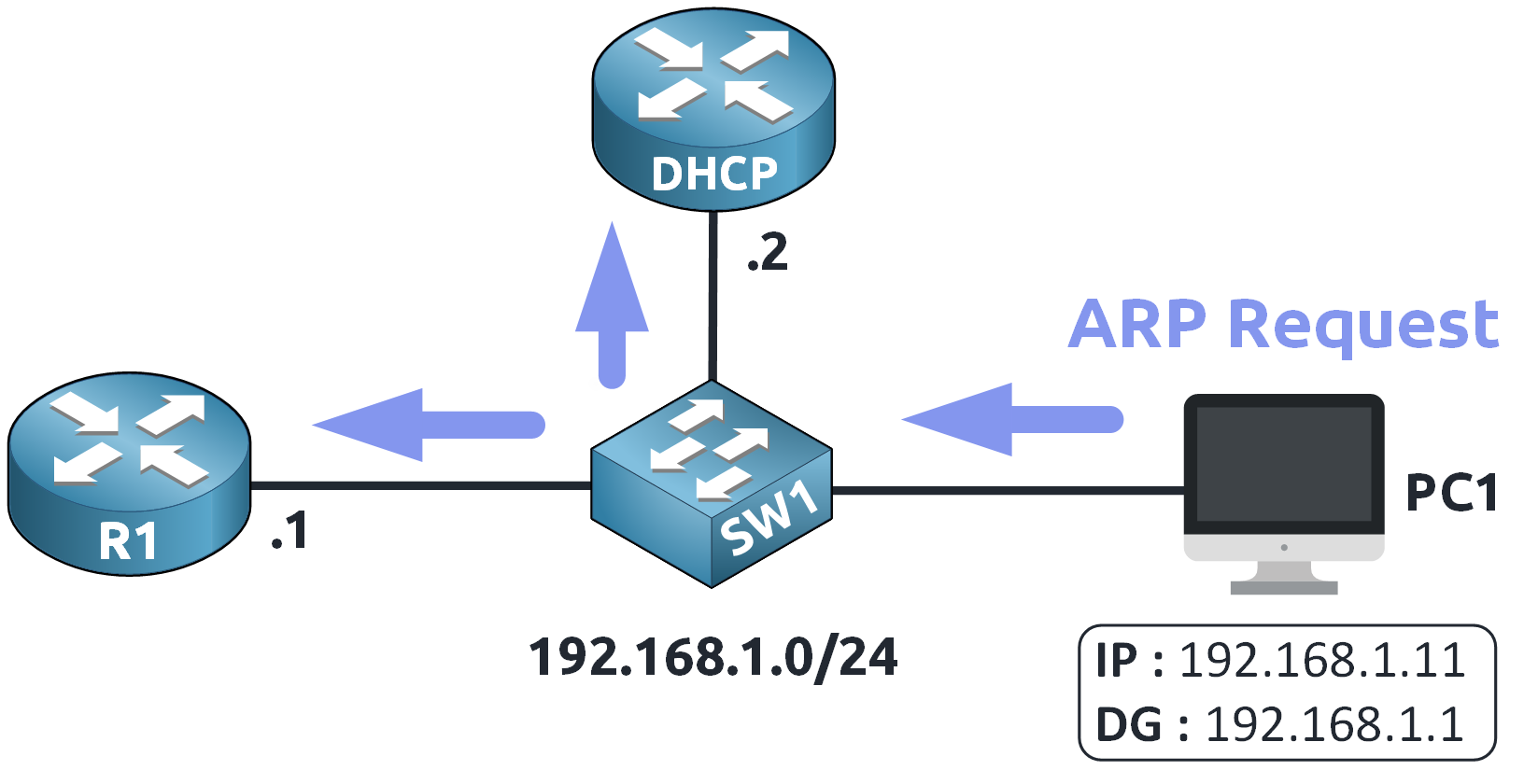
Figure 5 – ARP Request Broadcasted on the Network
The router (R1) receives the request and responds with an ARP Reply providing its MAC address.
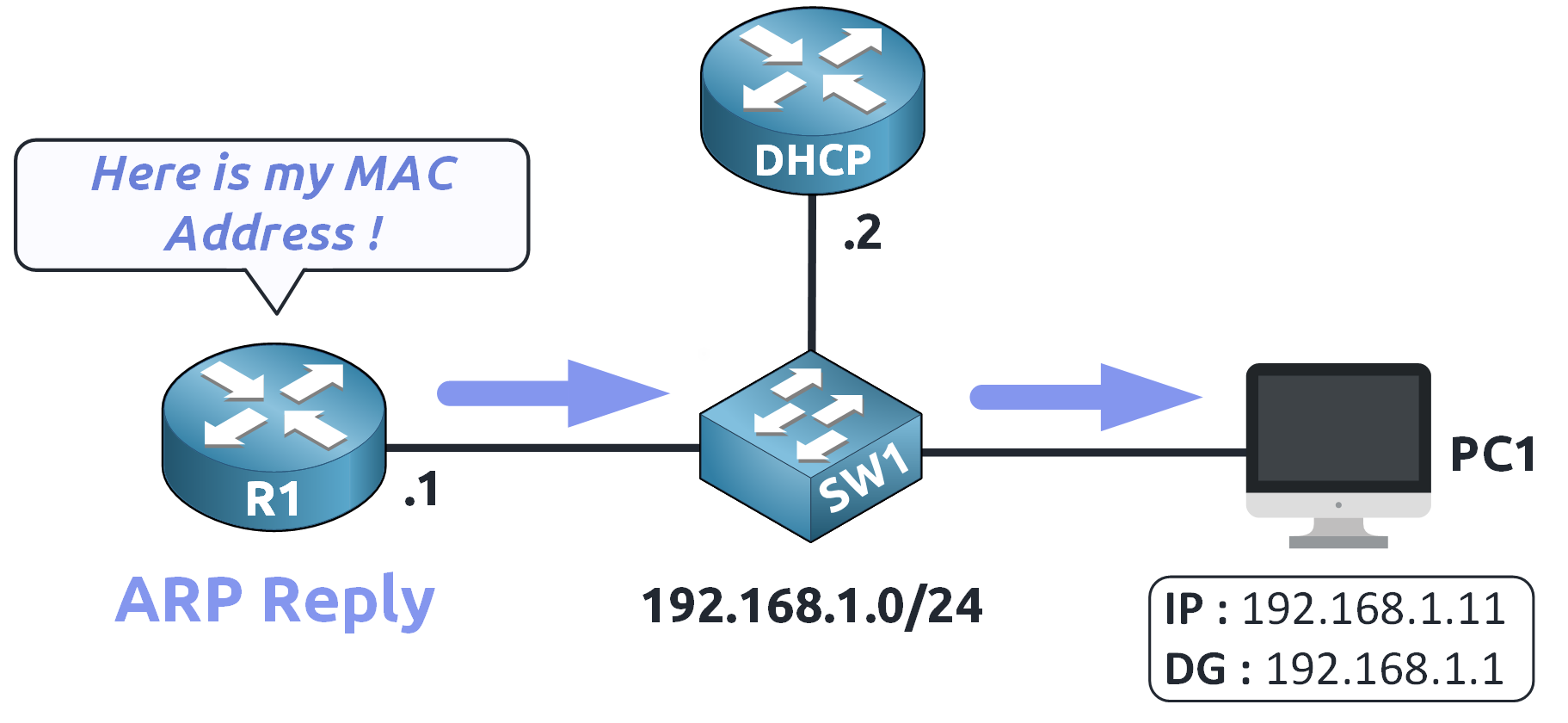
Figure 6 – ARP Reply Received: MAC Address Learned
Now that PC1 knows the MAC address of 192.168.1.1…
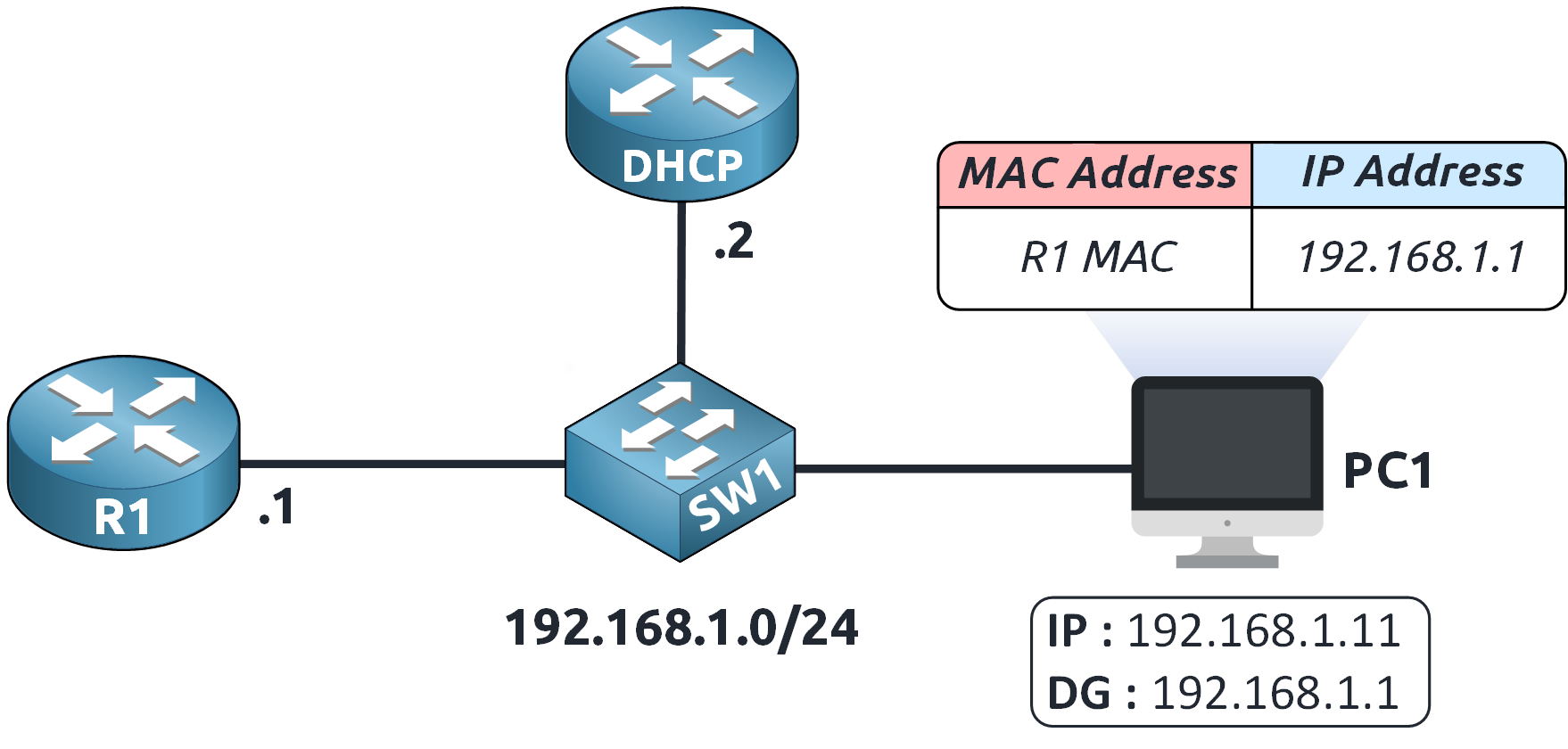
Figure 7 – PC1 Updates ARP Table with Gateway MAC Address
It can send the ping to 8.8.8.8 through the default gateway !
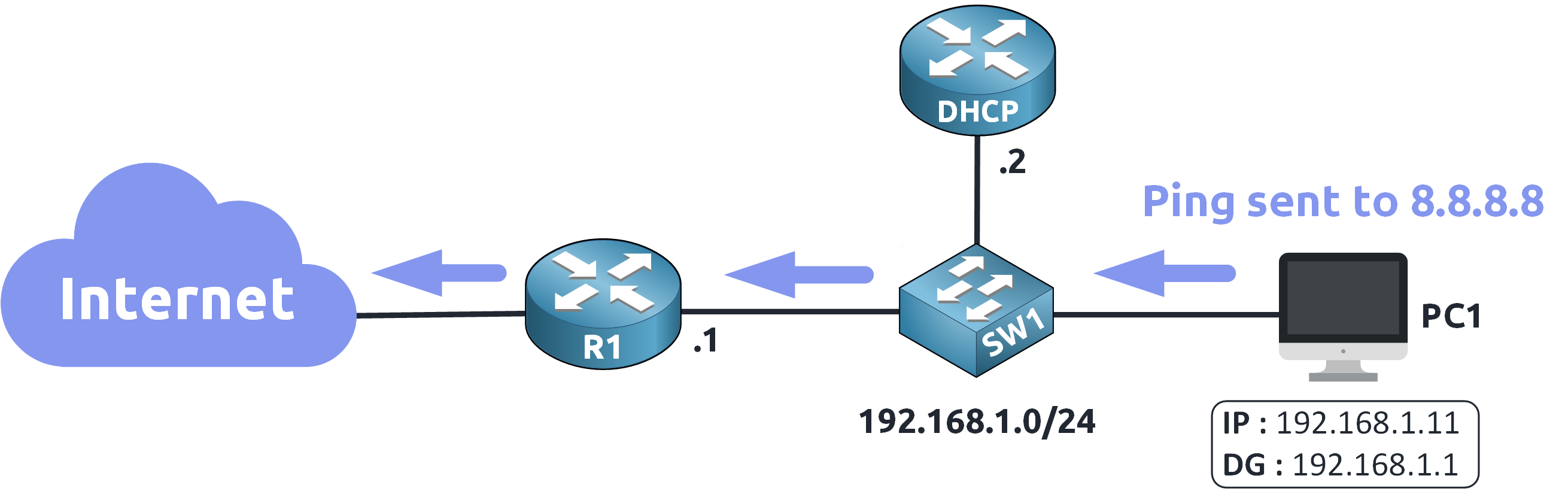
Figure 8 – Successful Communication via Default Gateway
It’s a simple and efficient mechanism but unfortunately, it's also vulnerable to attacks, as we’ll see in the next section.
Answer the question below
What does ARP map an IP address to?
While ARP is fundamental to network communication, it was never designed with security in mind. That makes it an easy target for attackers who want to intercept or manipulate traffic.
One of the most common threats is the Man-in-the-Middle (MitM) attack using ARP spoofing.
Understanding Gratuitous ARP (GARP)
BBefore we explore how the attack works, let’s take a moment to understand Gratuitous ARP.
40 % Complete: you’re making great progress
Unlock the rest of this lesson
If you’d like to continue your CCNA journey, simply create your free account.
Access all CCNA lessons
Practice with hands-on labs
Train with Practice exams and Quizzes
Progress tracking in your dashboard
Made by network engineers - CCNP certified
learners globally