VRF (Virtual Routing and Forwarding) is a network virtualization technology that allows a router to have multiple independent routing tables.
Just like VLANs isolate traffic at Layer 2 by creating virtual switches, VRFs isolate routing domains at Layer 3 by creating virtual routers on a single physical device.
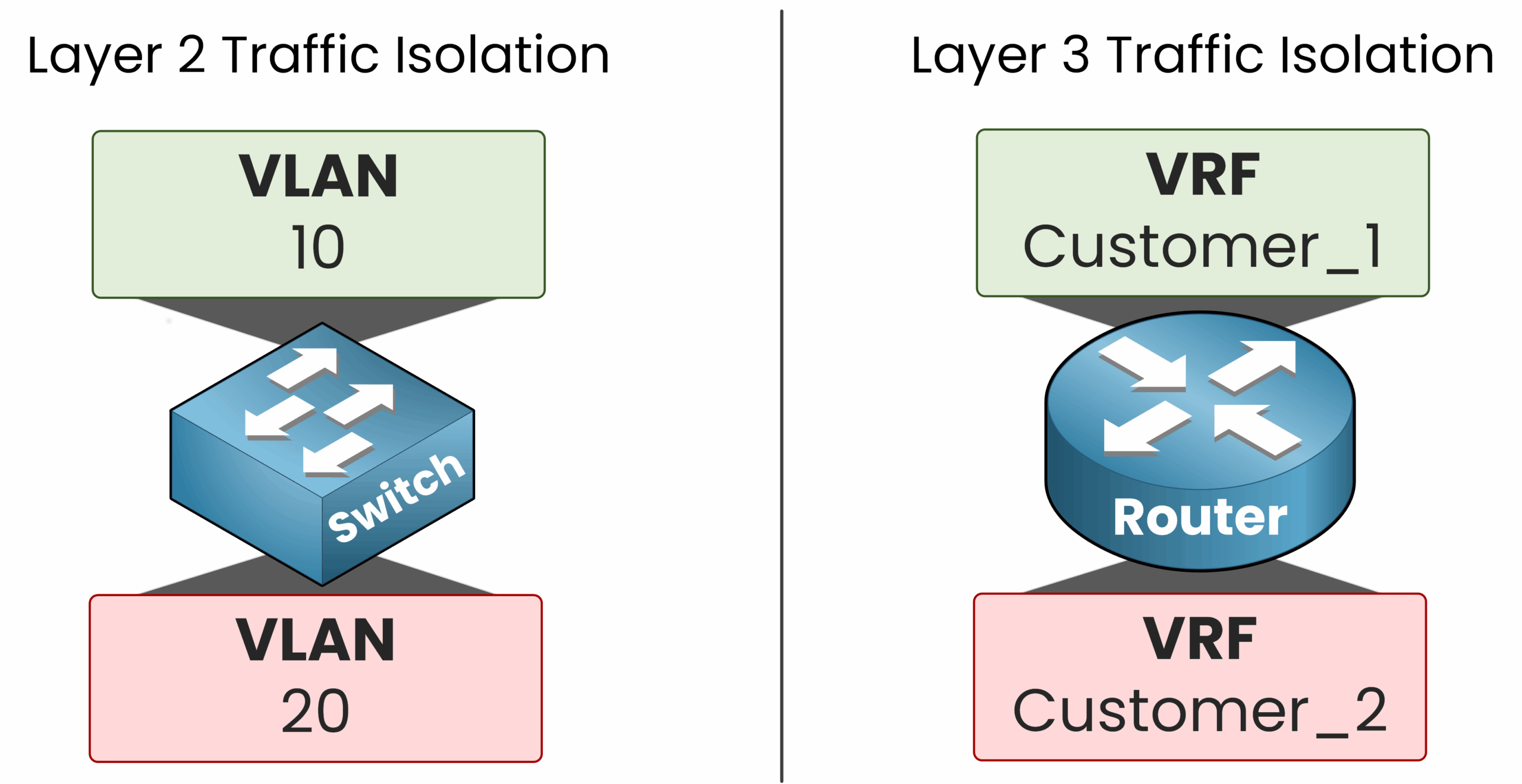
Figure 1 –VLANs isolate Layer 2 traffic and VRFs isolate Layer 3 routing
In this course, we’ll focus on VRF-Lite, a simplified version of VRF that does not use MP-BGP (Multiprotocol BGP) or MPLS (Multiprotocol Label Switching). This is the type of VRF you need to understand for the CCNA exam. To help you grasp its value, let’s walk through a real-world example.
Answer the question below
What does a VRF isolate at Layer 3?
Imagine a Service Provider needs to connect two customers to the same ISP router.
As the diagram shows, both Customer 1 and Customer 2 need to access the internet through the ISP. But the network engineer is facing a key question: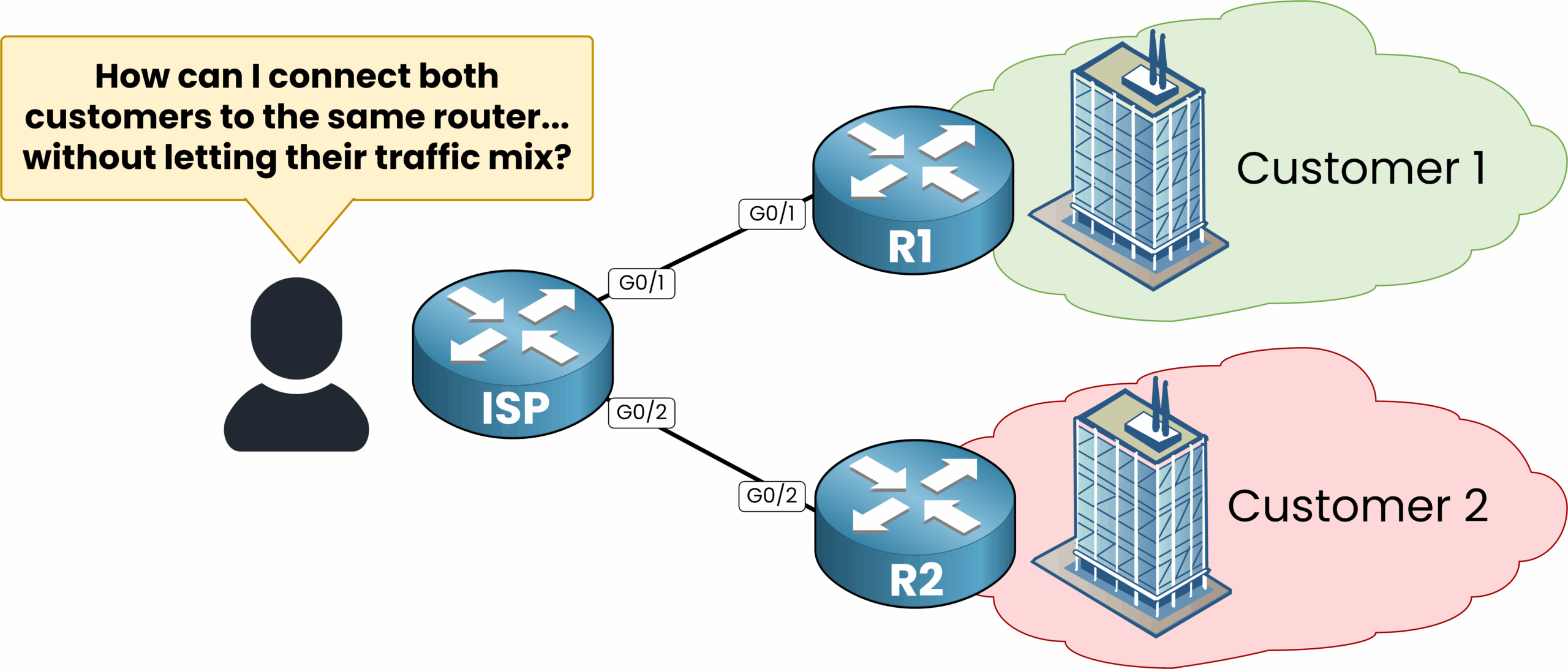
Figure 2 – Connecting two customers to the same ISP router without isolating their traffic
This is exactly the kind of question I want to guide you toward with this example to show you why VRFs are so valuable and how we can use them to our advantage.
By default, the ISP router uses a single global routing table.
As soon as both customers are connected to the Service Provider, the ISP router will learn the connected networks and will be inserted in the routing table.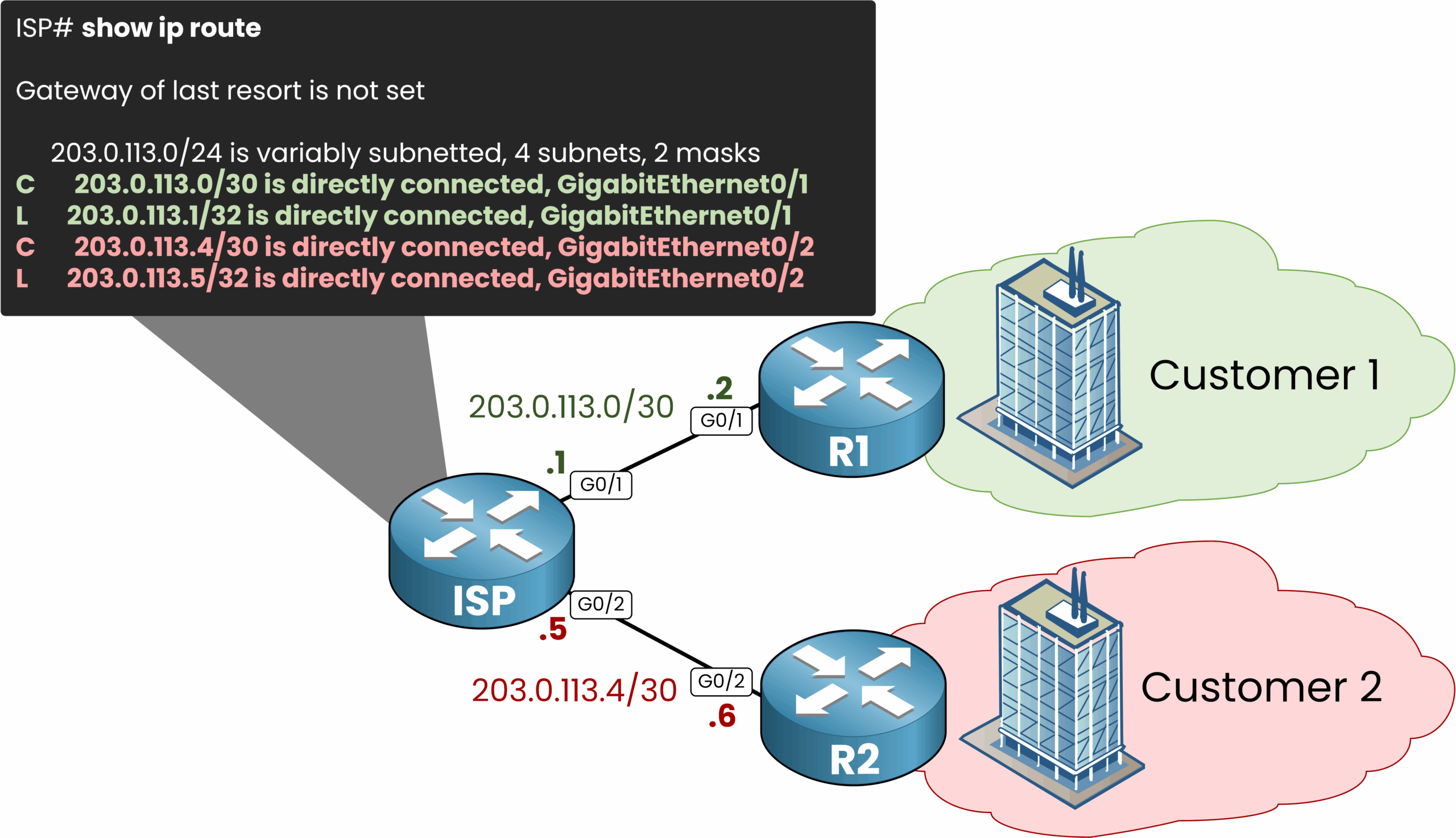
Figure 3 – Without VRF: all routes in one routing table.
This leads to a serious risk of traffic leakage between customers, since the ISP router doesn’t distinguish between Customer 1 and Customer 2’s routes.
This means Customer 1 could potentially reach Customer 2’s network if we’re not careful, a serious security risk.What we really need in this situation is a way to completely separate the routes used to reach Customer 1 from the routes used to reach Customer 2.
That way, each customer is fully isolated from the other. This is exactly what Virtual Routing and Forwarding (VRF) allows us to achieve.
Answer the question below
What problem occurs when an ISP router uses a single global routing table for multiple customers?
With VRF, we can turn a single physical router into multiple virtual routers. In our example, we'll create two virtual routing instances:
One VRF named
CUSTOMER_1with its own routing tableOne VRF named
CUSTOMER_2with its own routing table
Then, we assign the appropriate physical interfaces to each VRF.
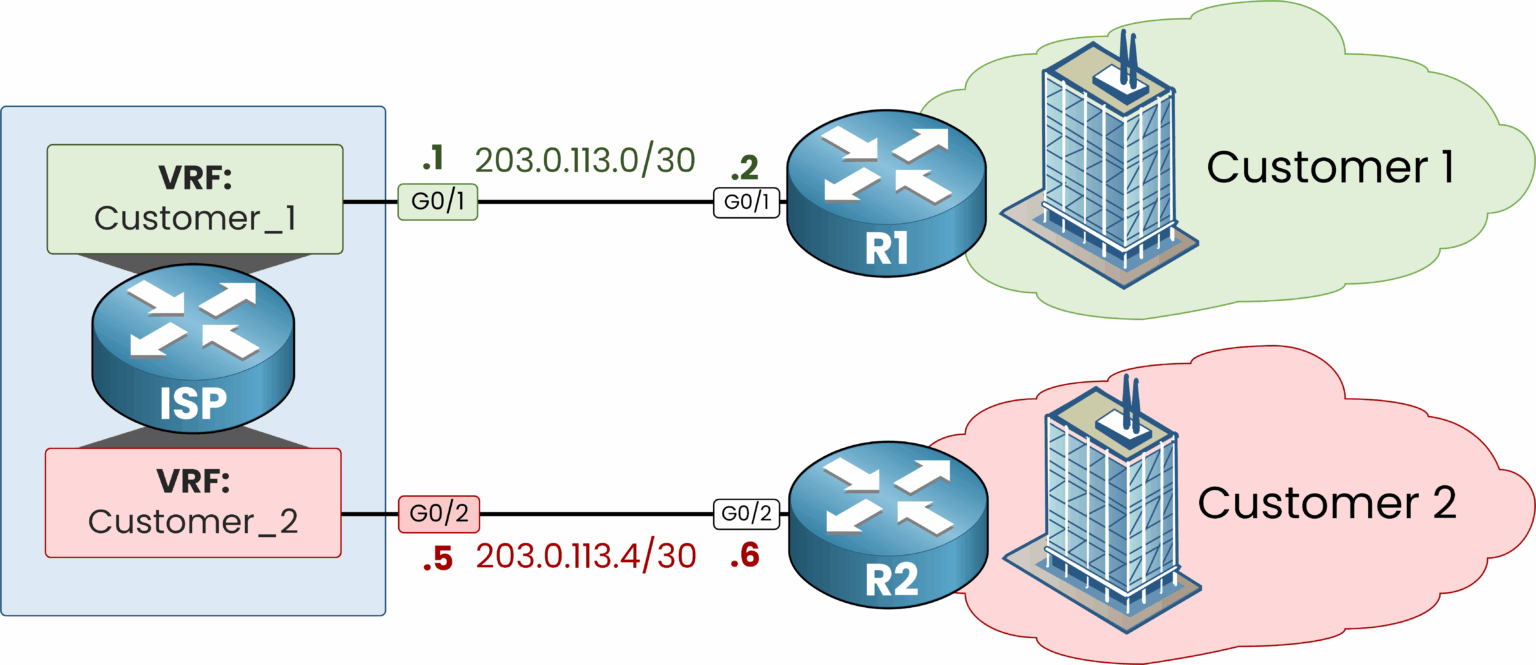
Figure 4 – VRFs create separate routing instances per customer.
At this point, the ISP router hosts two independent routing environments:
Each VRF has its own set of interfaces
Each VRF has its own routing table
And there is complete separation between the two
That’s all it takes. As shown above, each customer is now isolated within its own VRF.
This means Customer 1 and Customer 2 cannot see or reach each other, even though they’re using the same physical ISP router.Answer the question below
What does each VRF have to keep customer traffic separated?
Virtual Routing and Forwarding comes with a lot of benefits that you should be aware especially for your CCNA study.
First, it's the Independent Routing Tables.
Independent Routing Tables
Each VRF maintains its own routing table that is completely separated from others.
By default:
Traffic from one VRF can’t reach another
Routing entries and interfaces are fully isolated
We can look at the content of our 2 VRF by using the show ip route vrf vrf-name command:
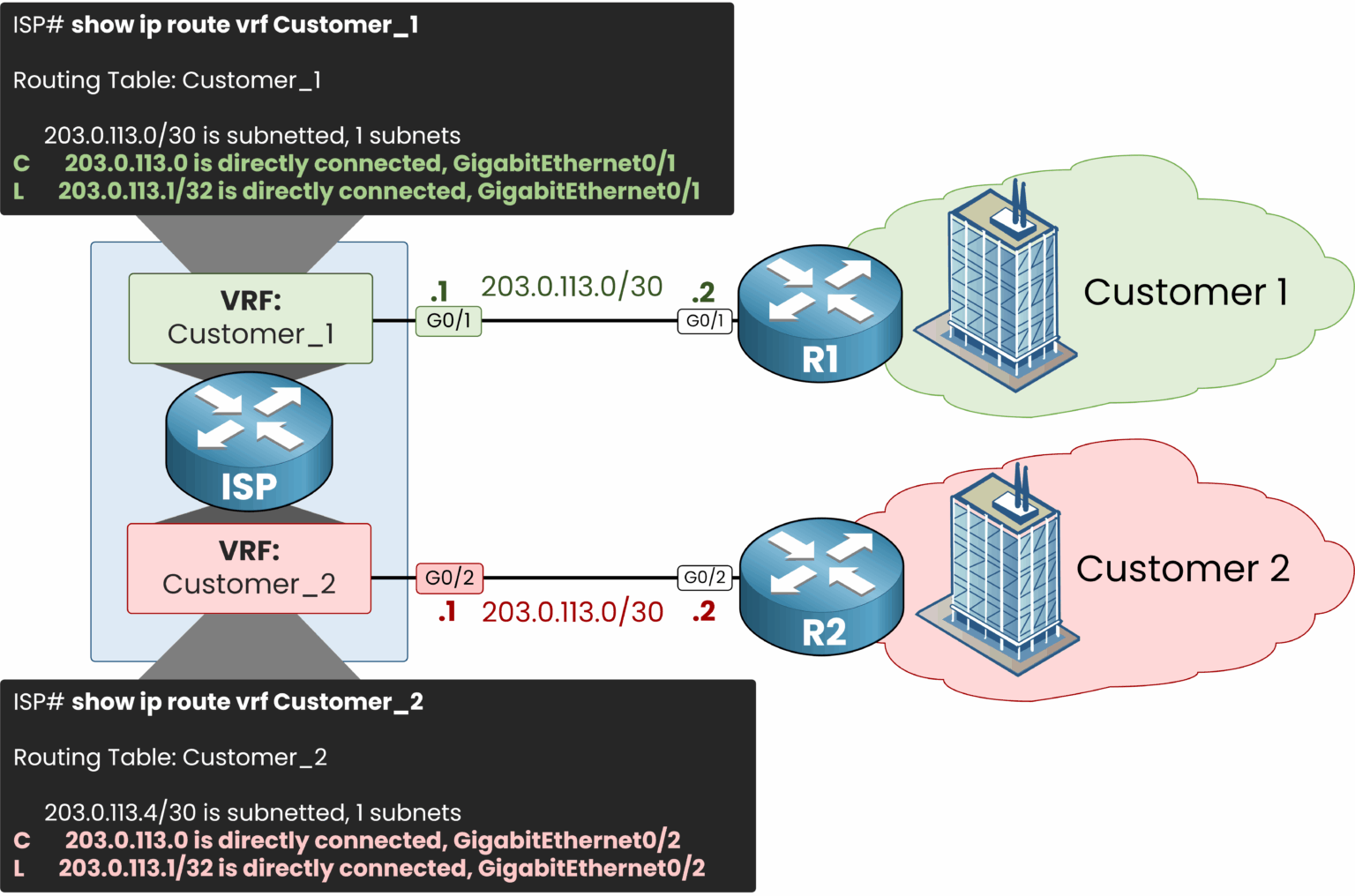
Figure 5 – Each VRF has its own routing table.
40 % Complete: you’re making great progress
Unlock the rest of this lesson
If you’d like to continue your CCNA journey, simply create your free account.
Access all CCNA lessons
Practice with hands-on labs
Train with Practice exams and Quizzes
Progress tracking in your dashboard
Made by network engineers - CCNP certified
learners globally
Virtual Routing and Forwarding (VRF)
Virtual Routing and Forwarding (VRF) allows a single Cisco router to host multiple independent routing tables, creating isolated routing domains on the same device. In this lesson, you’ll learn why VRF matters, how it prevents traffic leakage, and how VRF-Lite is applied in real networks.