Network traffic types have evolved significantly over the years.
In the early 2000s, two primary types dominated:
Voice Traffic: Predictable bandwidth requirements with consistent packet delivery.
Data Traffic: Non-real-time with varying and unpredictable bandwidth needs.
Today, video traffic has become the largest contributor to global IP traffic, surpassing all others.
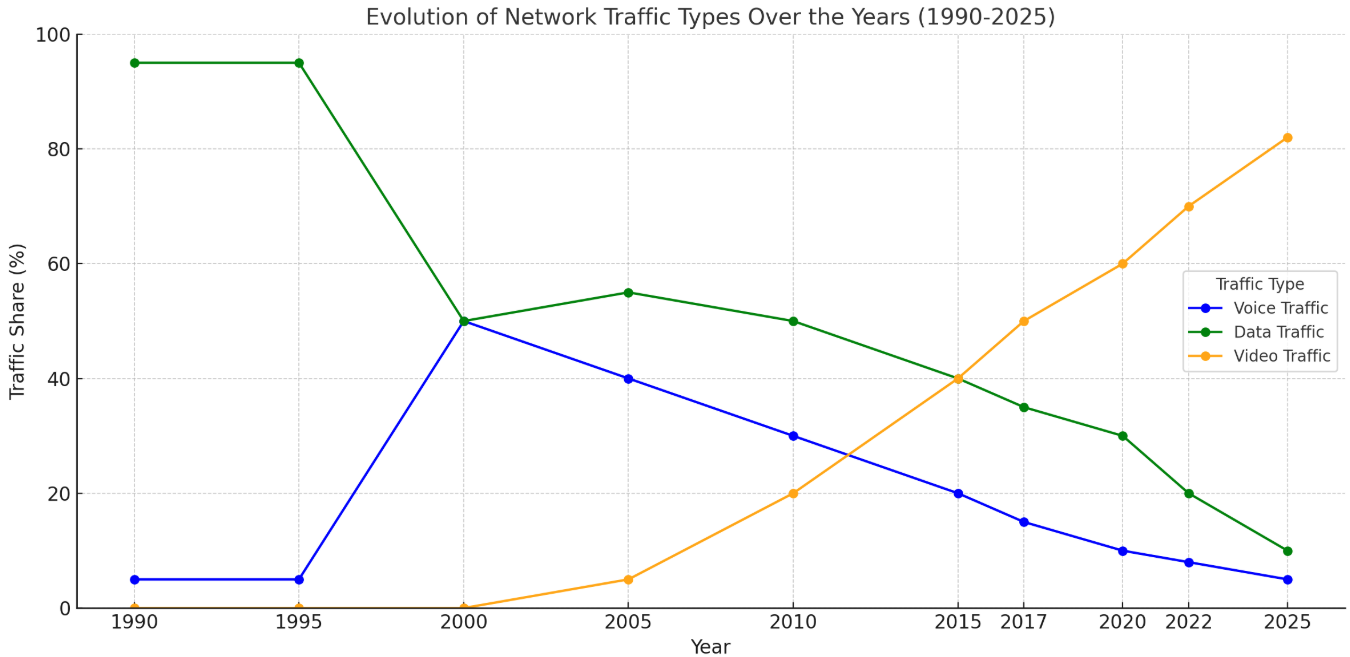
Figure 1 – Evolution of Network Traffic Types Over the Years (1990–2025)
Why is Video Traffic So Dominant?
Streaming Services: Platforms like Netflix and Disney+ are central to this growth.
Video Conferencing: Tools like Zoom and Microsoft Teams have made video communication ubiquitous.
Social Media: Content-heavy platforms like Instagram and Facebook amplify the volume of video traffic.
By 2025, video is projected to make up over 82% of global IP traffic, highlighting the need for Quality of Service (QoS) strategies tailored to video, voice, and data communications.
Answer the question below
Which traffic type is projected to represent over 82% of global IP traffic by 2025?
With the rise of Voice over IP (VoIP), voice communication has shifted to IP networks.
While it is now part of regular data traffic, voice remains highly sensitive to delay, jitter, and packet loss, requiring special attention !
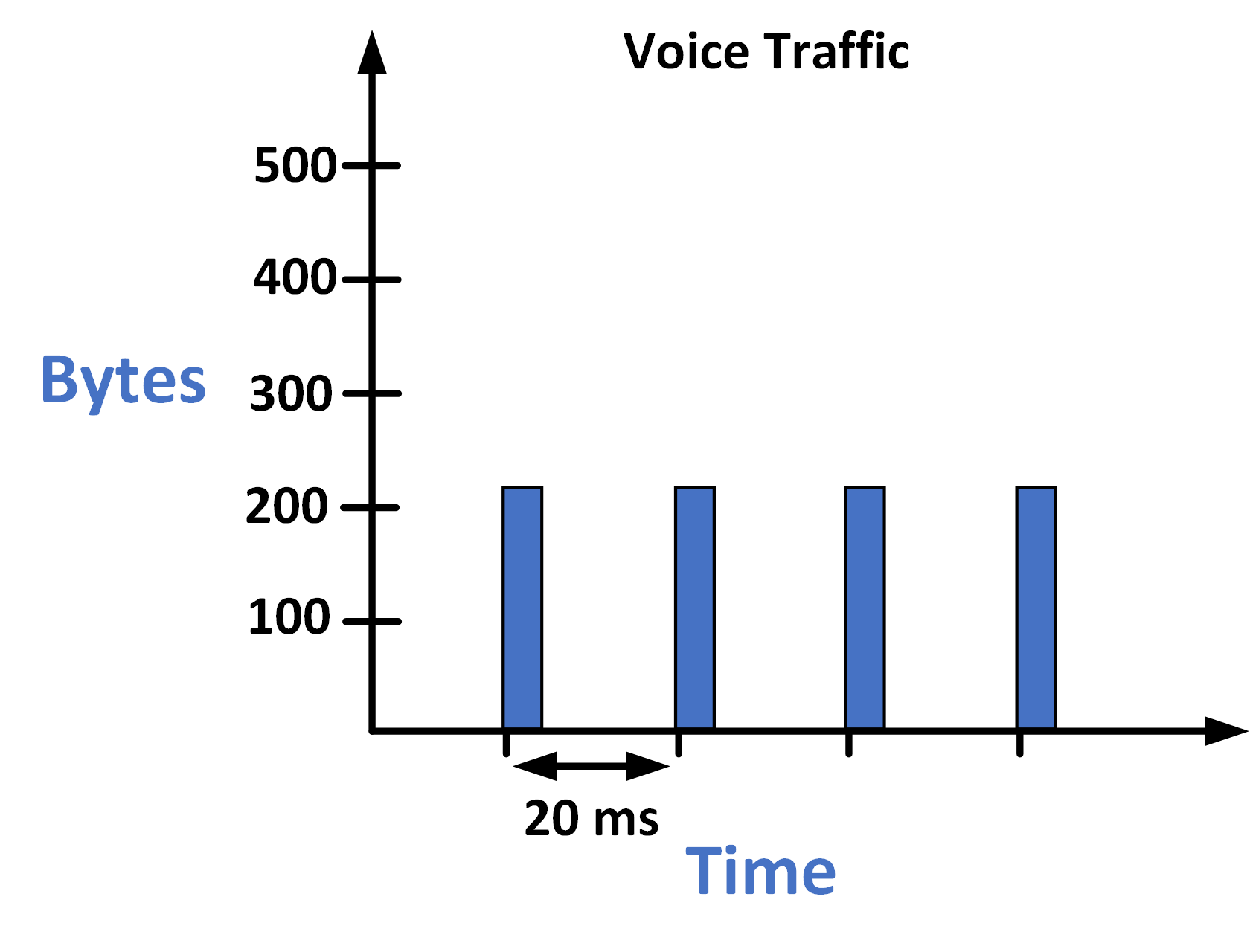
Figure 2 – Characteristics of Voice Traffic Transmission
40 % Complete: you’re making great progress
Unlock the rest of this lesson
If you’d like to continue your CCNA journey, simply create your free account.
Access all CCNA lessons
Practice with hands-on labs
Train with Practice exams and Quizzes
Progress tracking in your dashboard
Made by network engineers - CCNP certified
learners globally
Traffic Types
Network traffic types are a core CCNA concept that explains how voice, video, and data behave differently across real networks. If you do not understand these differences, QoS can fail and performance suffers, but this lesson will make everything clear and practical.