In most enterprise networks, only one router is connected to the Internet. This router knows how to reach all external destinations.
Instead of configuring a static default route (0.0.0.0/0) on every internal router, we can define it once on the edge router (R1) and then inject it into the OSPF domain.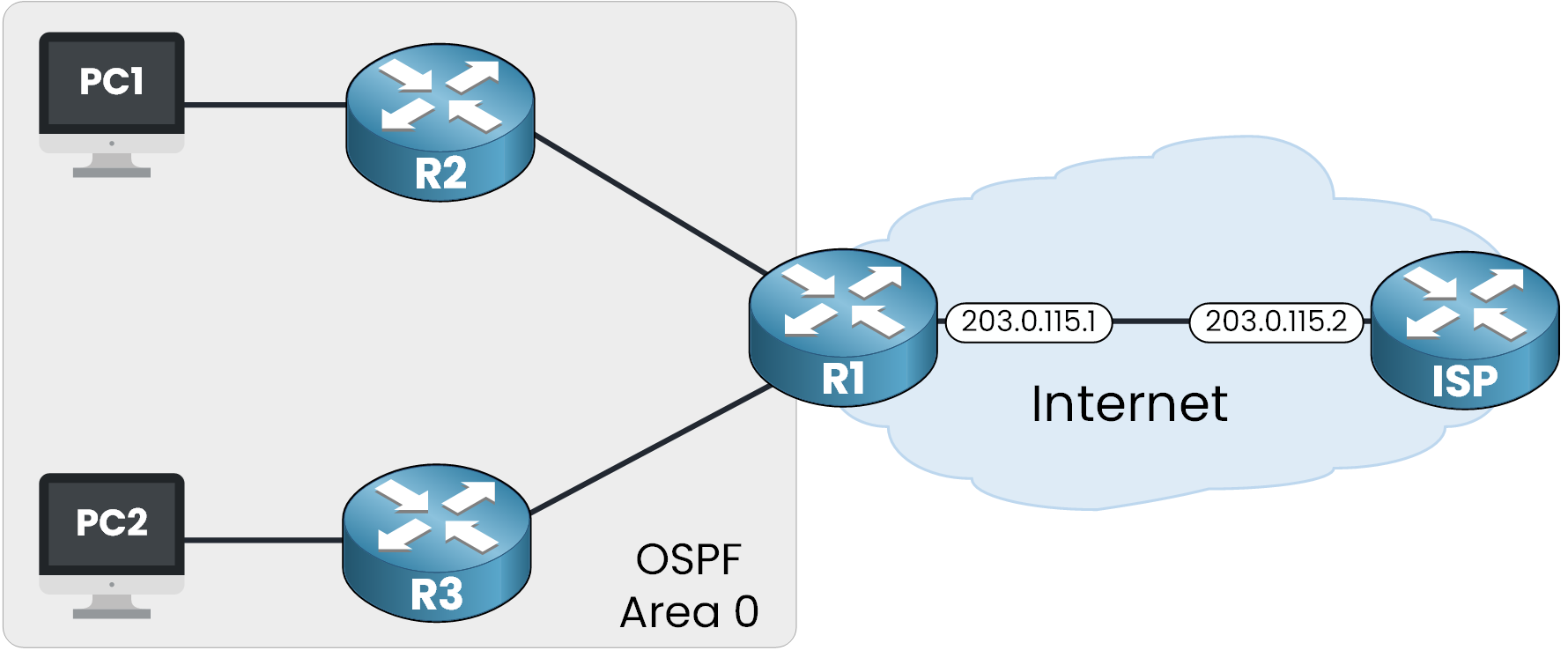
Figure 1 - OSPF used to demonstrate OSPF Default Route
This approach ensures that internal routers like R2 and R3 can dynamically learn the default route via OSPF, and forward any unknown traffic toward R1, which acts as the gateway to the Internet.
Answer the question below
What prefix represents the default route?
First, we need to configure the default route using
ip route 0.0.0.0pointing to the IP of the ISP router.
In our scenario, the next-hop IP address is 203.0.115.2.We assume OSPF neighbor relationships are already established and that networks are being advertised in Area 0.
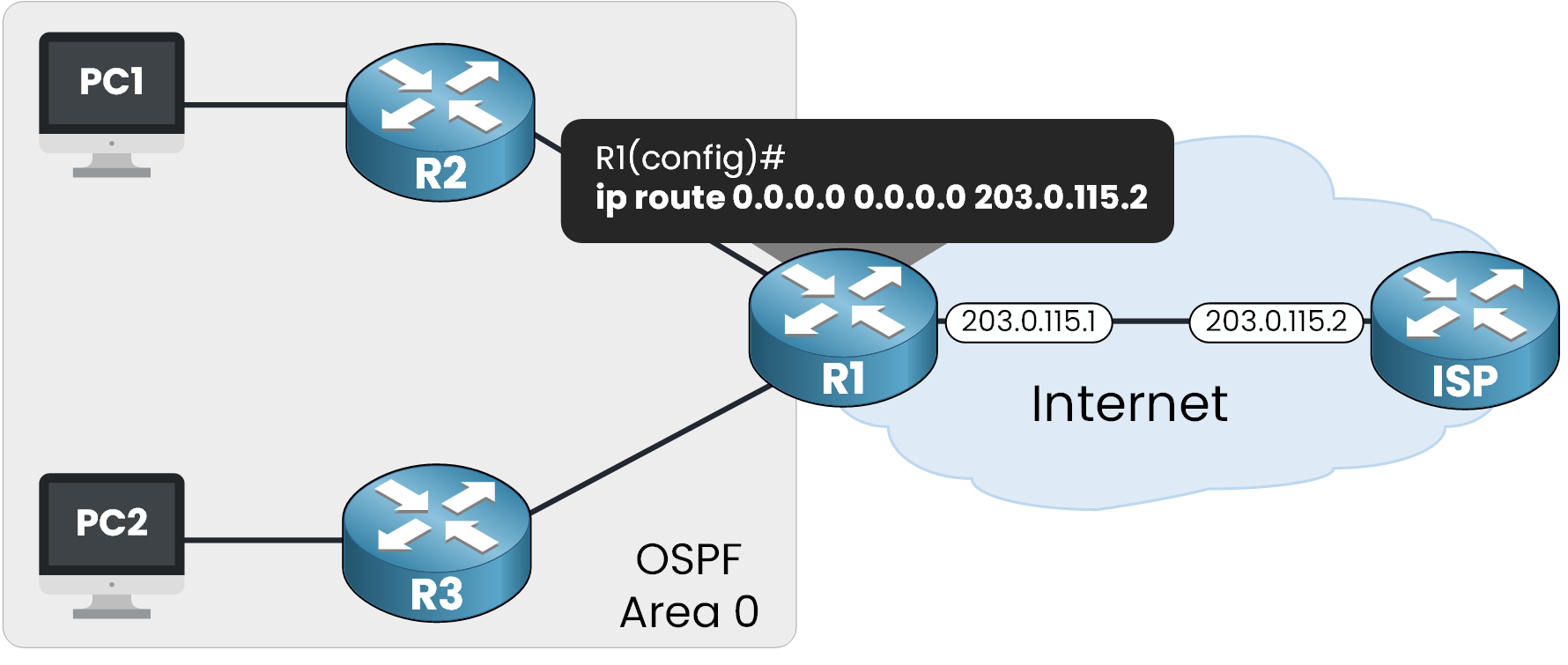
Figure 2 - Configuration of default static route on R1
We now configure the static default route on R1:
R1# conf t Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z. R1(config)# ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 203.0.115.2 R1(config)# endThis instructs R1 to send all unknown destination traffic to the ISP router at 203.0.115.2.
To verify that the route has been installed correctly, you can inspect the routing table:
R1# show ip route Codes: L - local, C - connected, S - static, R - RIP, M - mobile, B - BGP D - EIGRP, EX - EIGRP external, O - OSPF, IA - OSPF inter area N1 - OSPF NSSA external type 1, N2 - OSPF NSSA external type 2 E1 - OSPF external type 1, E2 - OSPF external type 2, E - EGP i - IS-IS, L1 - IS-IS level-1, L2 - IS-IS level-2, ia - IS-IS inter area * - candidate default, U - per-user static route, o - ODR P - periodic downloaded static route Gateway of last resort is 203.0.115.2 to network 0.0.0.0 192.168.1.0/24 is variably subnetted, 2 subnets, 2 masks C 192.168.1.0/24 is directly connected, GigabitEthernet0/1 L 192.168.1.1/32 is directly connected, GigabitEthernet0/1 192.168.2.0/24 is variably subnetted, 2 subnets, 2 masks C 192.168.2.0/24 is directly connected, GigabitEthernet0/0 L 192.168.2.1/32 is directly connected, GigabitEthernet0/0 203.0.115.0/24 is variably subnetted, 2 subnets, 2 masks C 203.0.115.0/24 is directly connected, GigabitEthernet0/2 L 203.0.115.1/32 is directly connected, GigabitEthernet0/2 S* 0.0.0.0/0 [1/0] via 203.0.115.2In this output:
The letter
Sindicates a static routeThe asterisk
*indicates that this route is the candidate default routeThe line Gateway of last resort... confirms that R1 is now set to forward unknown traffic via the ISP
Answer the question below
Which next-hop does R1 use in the static default route?
Now that the default route exists on R1, we need to advertise it into OSPF so that other routers can learn it dynamically.
This is done using thedefault-information originatecommand under the OSPF process: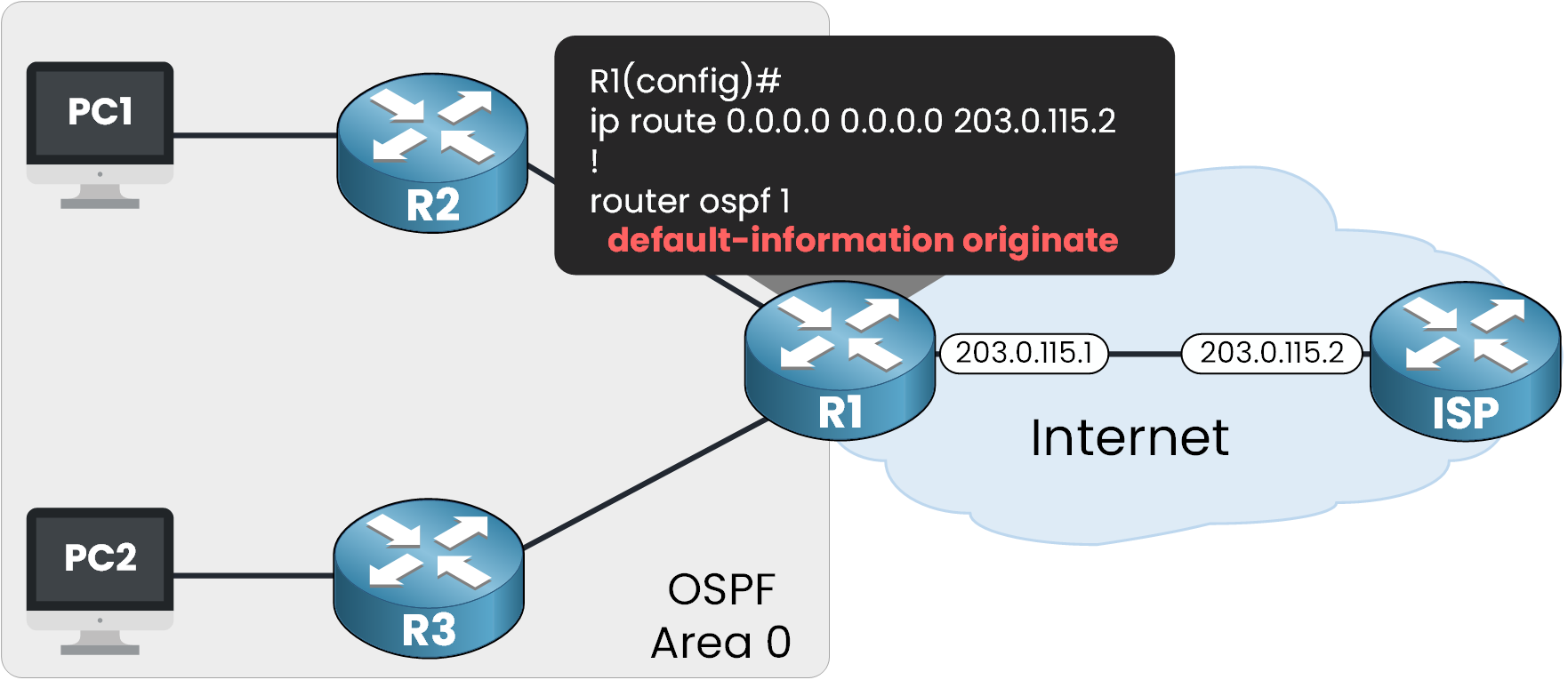
Figure 3 - Advertising the default static route in OSPF
In R1 we applied this command:
R1# conf t Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z. R1(config)# router ospf 1 R1(config-router)# default-information originate R1(config-router)# endThis tells R1 to inject the default route into OSPF but only if the route exists in the routing table.
We can verify OSPF status with:
R1# show ip protocols Routing Protocol is "ospf 1" Outgoing update filter list for all interfaces is not set Incoming update filter list for all interfaces is not set Router ID 203.0.115.1 It is an autonomous system boundary router Redistributing External Routes from, Number of areas in this router is 1. 1 normal 0 stub 0 nssa Maximum path: 4 Routing for Networks: 192.168.1.0 0.0.0.255 area 0 192.168.2.0 0.0.0.255 area 0 Routing Information Sources: Gateway Distance Last Update 203.0.115.1 110 00:00:03 Distance: (default is 110)This confirms:
40 % Complete: you’re making great progress
Unlock the rest of this lesson
If you’d like to continue your CCNA journey, simply create your free account.
Access all CCNA lessons
Practice with hands-on labs
Train with Practice exams and Quizzes
Progress tracking in your dashboard
Made by network engineers - CCNP certified
learners globally
OSPF Default Route
An OSPF default route lets the edge router advertise a single 0.0.0.0/0 path into the OSPF area. This lesson shows how to configure and verify its distribution across internal routers.