Imagine you’re working in a network with devices from multiple vendors, and you need to identify the topology but don’t have a detailed diagram. This is where LLDP (Link Layer Discovery Protocol) becomes your best ally!
Unlike CDP (Cisco Discovery Protocol) which is proprietary to Cisco, LLDP is an open-standard protocol that allows devices from different manufacturers to exchange neighbor information together.
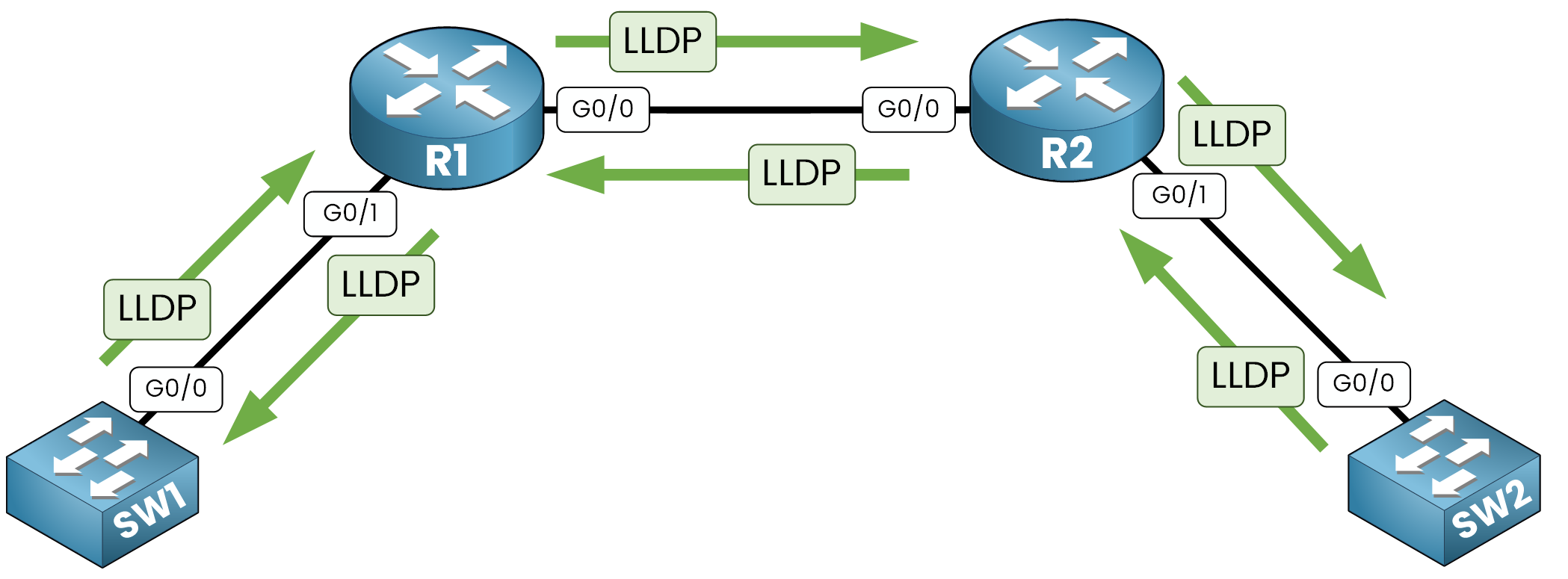
Figure 1 – LLDP exchanges neighbor information between devices
LLDP operates at Layer 2 (Data Link Layer) of the OSI model. It helps network devices share details about their identity, capabilities, and connectivity to theirs neighbors.
For example, using LLDP on a Cisco router allows you to discover neighboring devices like an HP switch or an Avaya IP phone. This interoperability makes LLDP ideal for multi-vendor environments.
Answer the question below
You might wonder, how does LLDP share so much useful information?
LLDP relies on LLDP Data Units (LLDPDUs) frame which are sent periodically over LLDP active interfaces. These LLDPDUs contain multiple details, including:
Device ID: The hostname of the device.
Port ID: The interface sending the LLDPDU.
System Capabilities: The role of the device (router, switch, IP phone, etc.).
Management IP Address: If configured, this provides a management access point.
Neighboring devices collect and store this information in their LLDP tables.
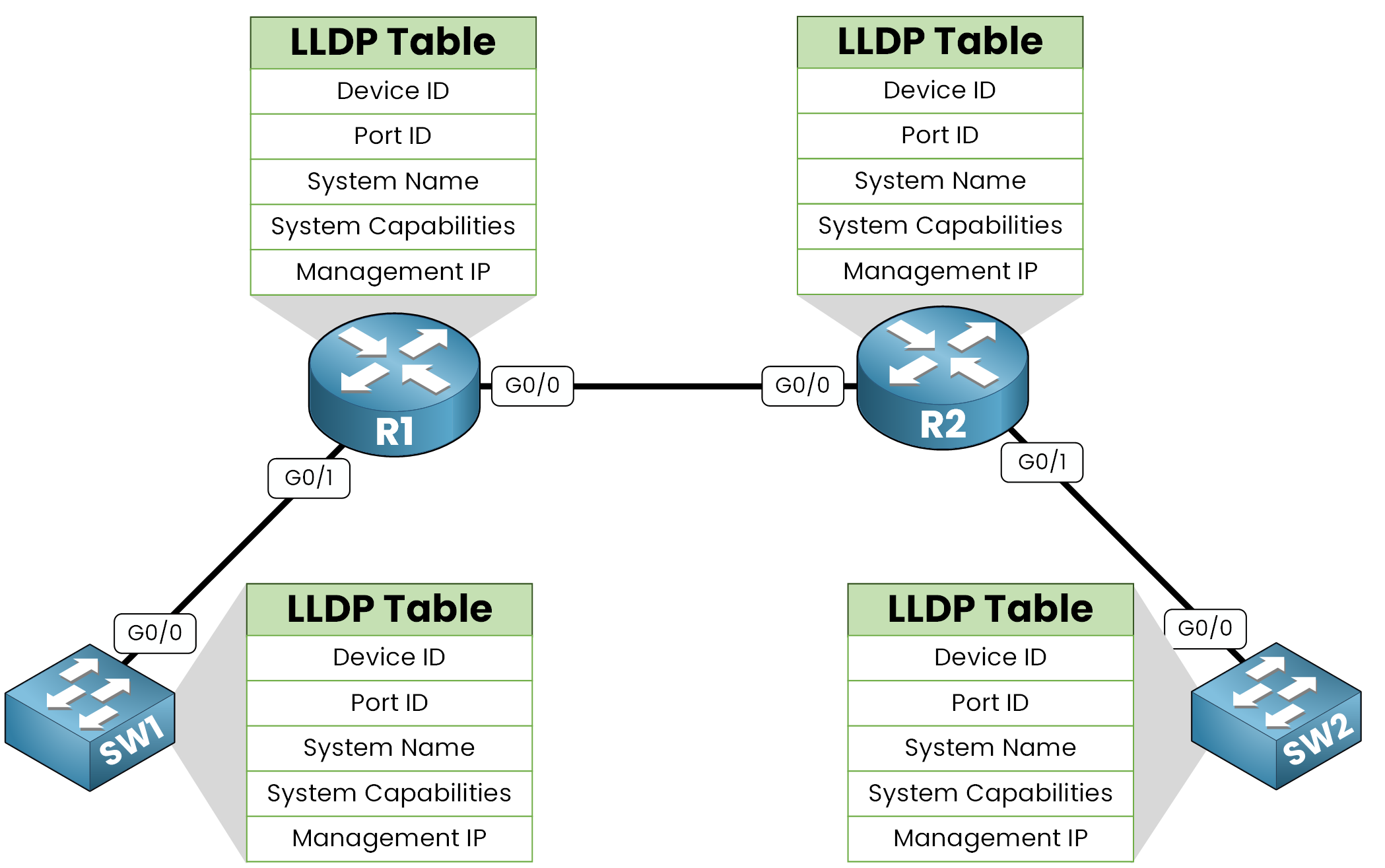
Figure 2 – LLDP store neighbors devices details using LLDP tables
This allows administrators to easily verify and understand network connections.
LLDP Timers
LLDP manages advertisements and neighbor information using specific timers:
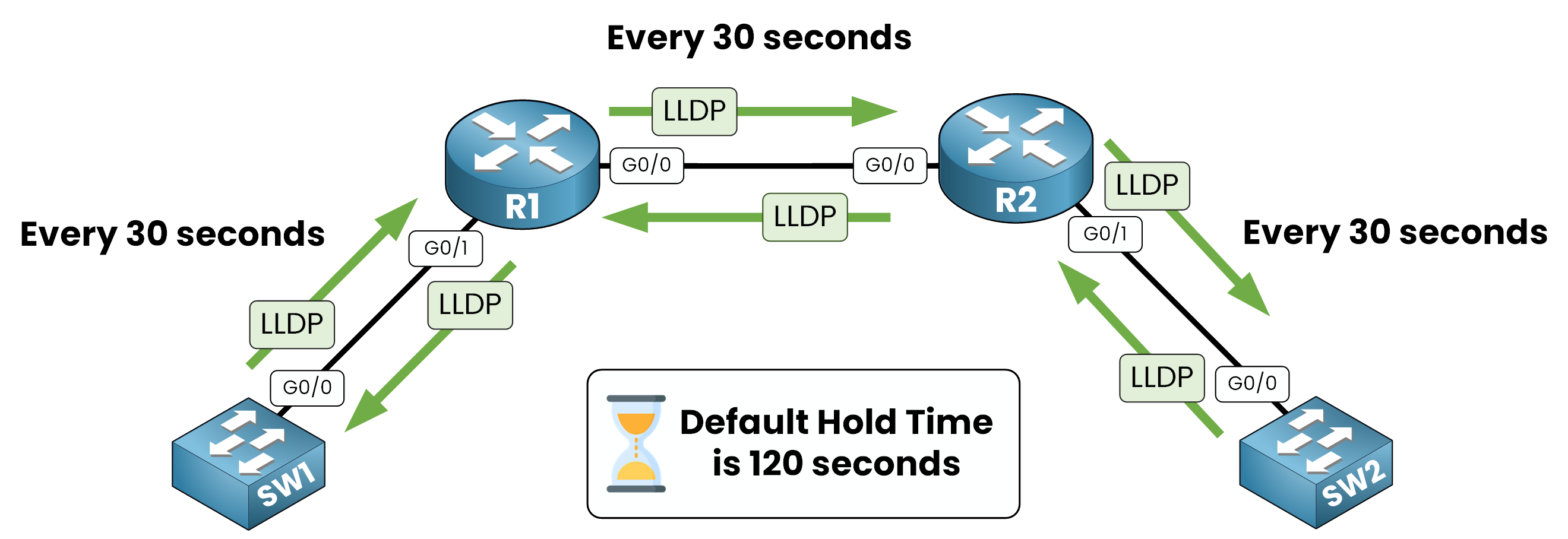
Figure 3 – LLDP sends updates every 30 seconds and holds info for 120 seconds
Timers in LLDP:
Transmission Timer: Defines how often LLDPDUs are sent. The default value is 30 seconds.
Hold Timer: Specifies how long neighbor information is retained after the last received update. The default is 120 seconds.
These timers help maintain an up-to-date view of network devices while minimizing unnecessary traffic.
Answer the question below
What is the default LLDP hold time in seconds?
Enabling LLDP Globally
By default, LLDP may be disabled on your Cisco devices. To enable it globally, use the following command in configuration mode:
R1(config)# lldp runWhat this does:
Activates LLDP on all active interfaces.
Allows the device to send and receive LLDP information.
Once enabled, your device will start discovering directly connected neighbors.
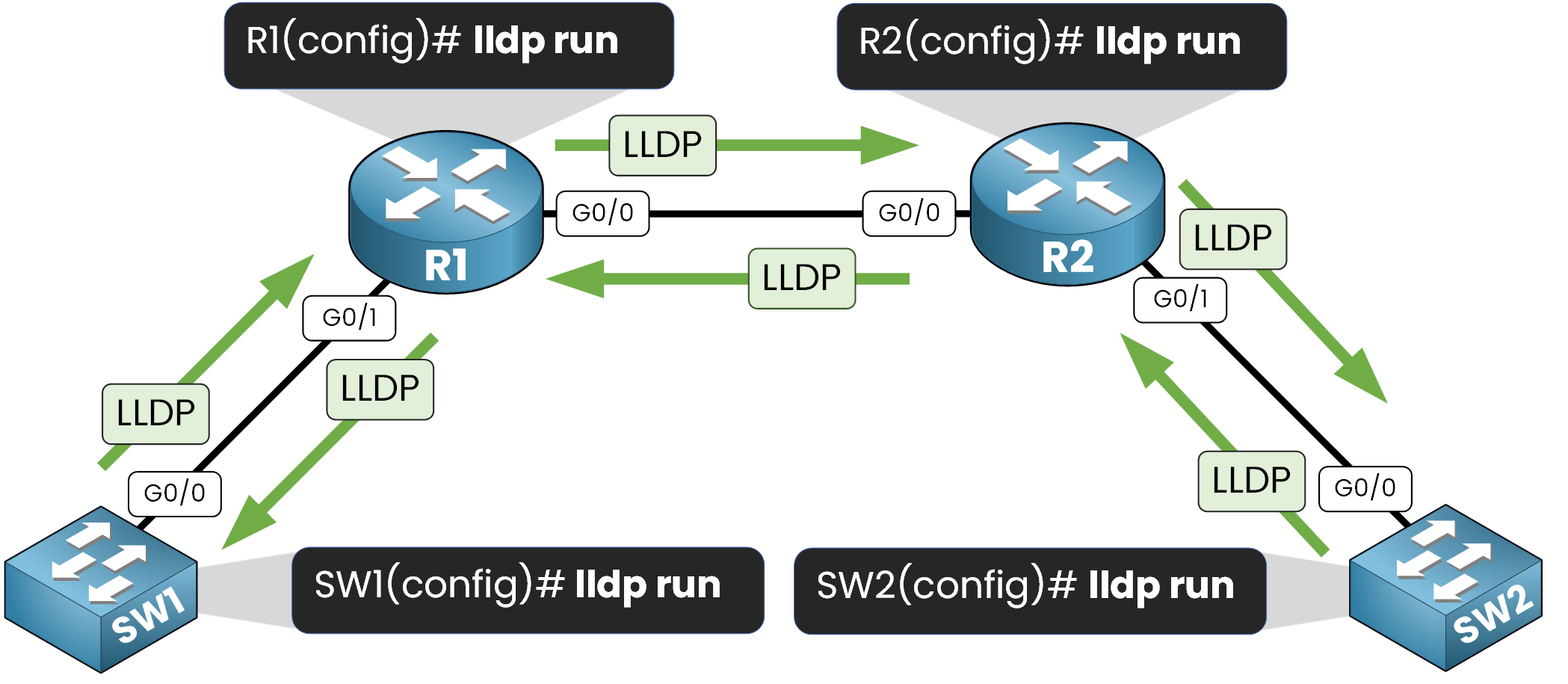
Figure 4 – The lldp run command enables LLDP on all active interfaces
40 % Complete: you’re making great progress
Unlock the rest of this lesson
If you’d like to continue your CCNA journey, simply create your free account.
Access all CCNA lessons
Practice with hands-on labs
Train with Practice exams and Quizzes
Progress tracking in your dashboard
Made by network engineers - CCNP certified
learners globally
Link Layer Discovery Protocol (LLDP)
LLDP (Link Layer Discovery Protocol) is an open-standard protocol that lets network devices from different vendors exchange neighbor information. In this lesson, you’ll learn how LLDP works, how to configure it on Cisco devices, and how it helps in multi-vendor troubleshooting.