A LAN (Local Area Network) is a local network.
It is used to connect devices that are physically close to each other.A LAN usually exists in the same location, such as a home, an office, a room, or a single floor of a building.
Example of a Local Area Network
Inside a LAN, devices communicate locally without needing to reach other networks.
As long as devices belong to the same LAN, they can communicate with each other through the switch.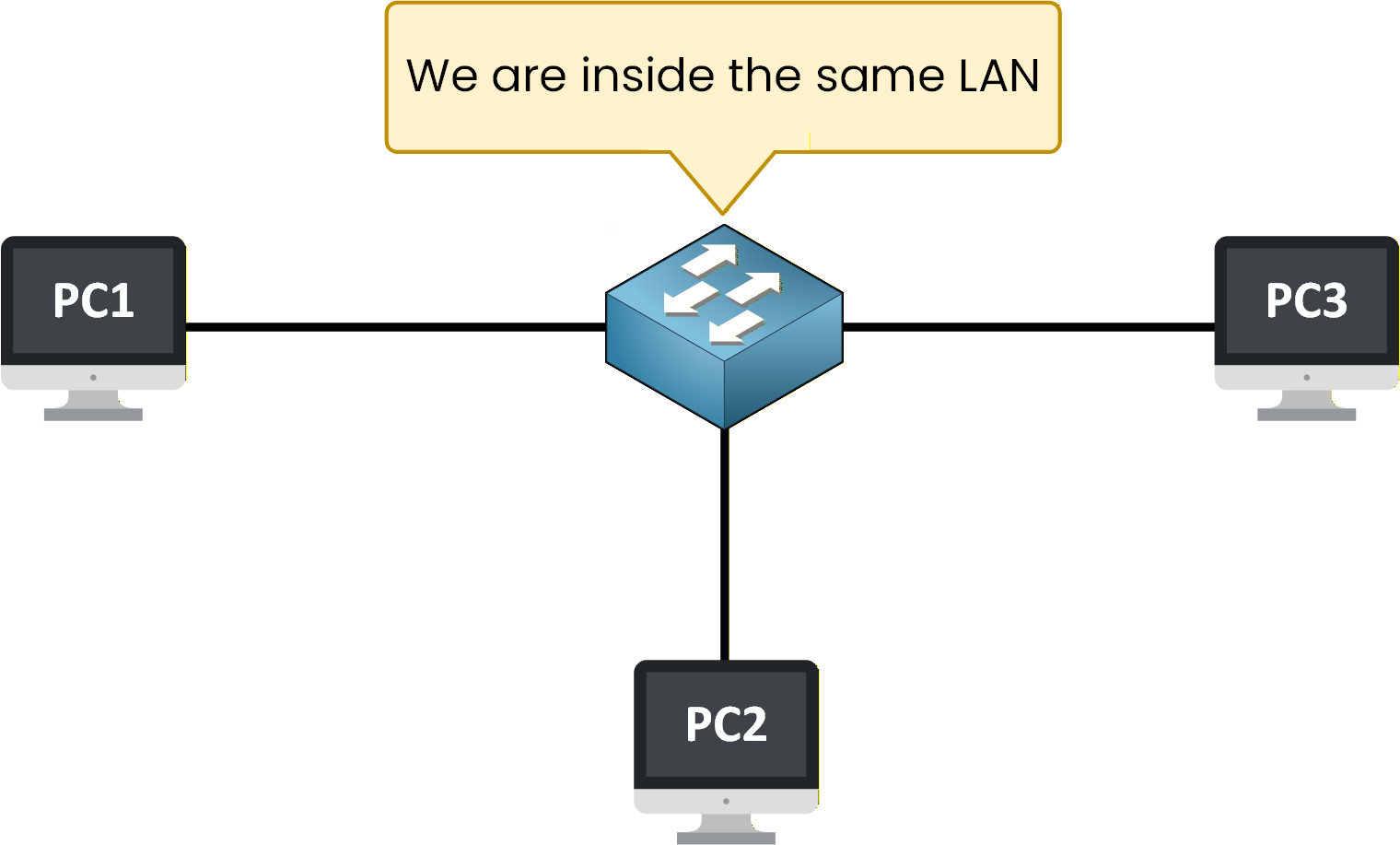
Figure 1 – Devices inside the same Local Area Network (LAN)
Here, you can see an example with three PCs connected to the same network.
All these devices are part of the same LAN and can communicate with each other.Answer the question below
What type of network connects devices that are physically close to each other?
Inside a Local Area Network, devices rely on a switch to communicate.
When multiple devices are connected in a LAN, the switch is used to receive data from one device and forward it to the correct destination.The Role of the Switch in Local Communication
When a device sends data, the traffic goes to the switch first.
The switch then forwards the data to another device inside the same LAN.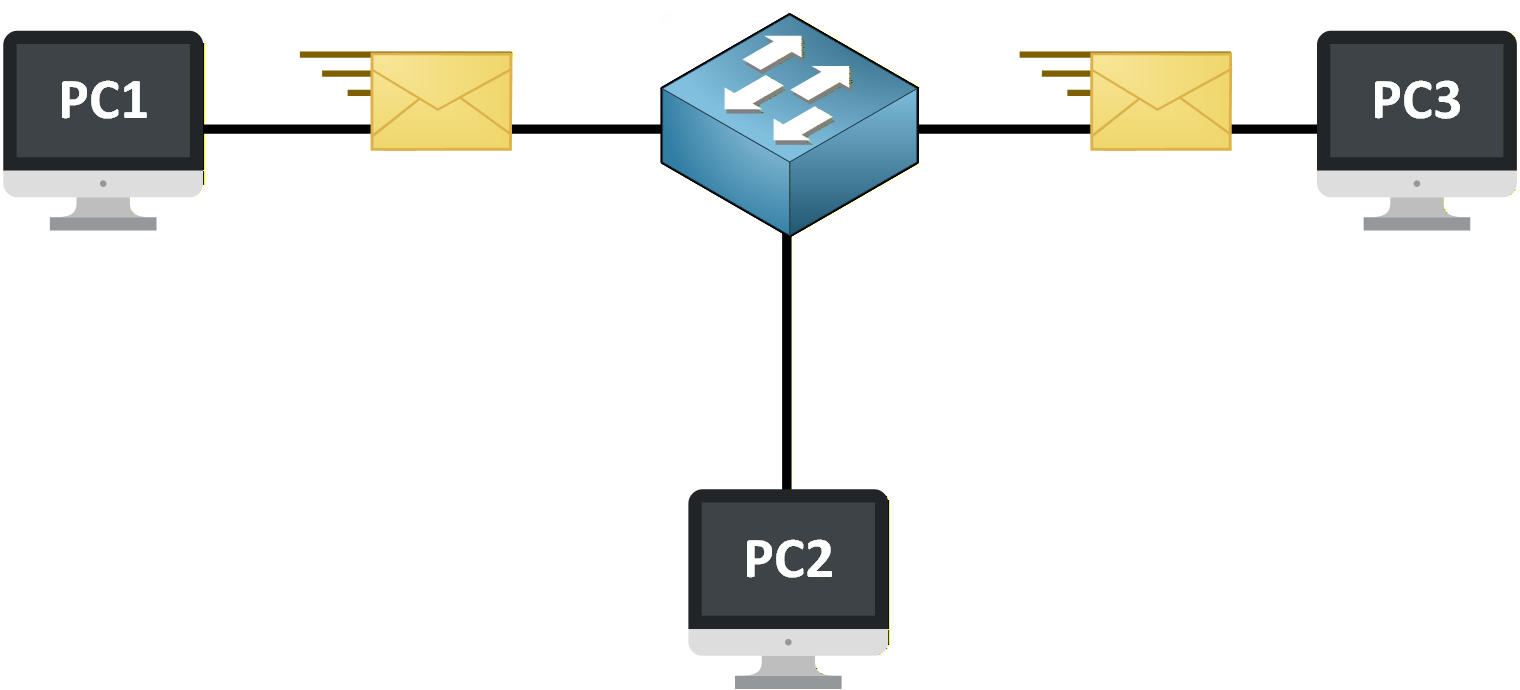
Figure 2 – Devices exchanging data locally through a switch inside the LAN
When a device sends data, the traffic goes to the switch first.
The switch then forwards the data to another device inside the same LAN.As long as devices belong to the same LAN, all communication stays local and does not require a router.
Verifying Local Communication on the Switch
We can verify that devices are connected and communicating by checking the switch interfaces.
SW1# show interfaces status Port Name Status Vlan Duplex Speed Type Gi0/1 connected 1 a-full a-100 10/100/1000BaseTX Gi0/2 connected 1 a-full a-100 10/100/1000BaseTX Gi0/3 connected 1 a-full a-100 10/100/1000BaseTX Gi0/4 notconnect 1 auto auto 10/100/1000BaseTXThis output shows that:
The devices are physically connected to the switch.
All devices belong to the same VLAN (VLAN 1 by default).
Because the devices are connected to the same switch and VLAN, their communication remains inside the LAN.
No router is required for this local exchange.Answer the question below
Inside a LAN, which device is responsible for receiving data from one device and forwarding it to the correct destination?
Now that you understand how devices communicate inside a LAN, let’s look at where this communication happens in the OSI model.
In networking, different tasks are handled at different layers.
For LAN communication, only a specific part of the OSI model is involved.Layer 2 Handles Local Communication
Communication inside a LAN happens at Layer 2, also called the Data Link layer.
This is the layer where the switch operates.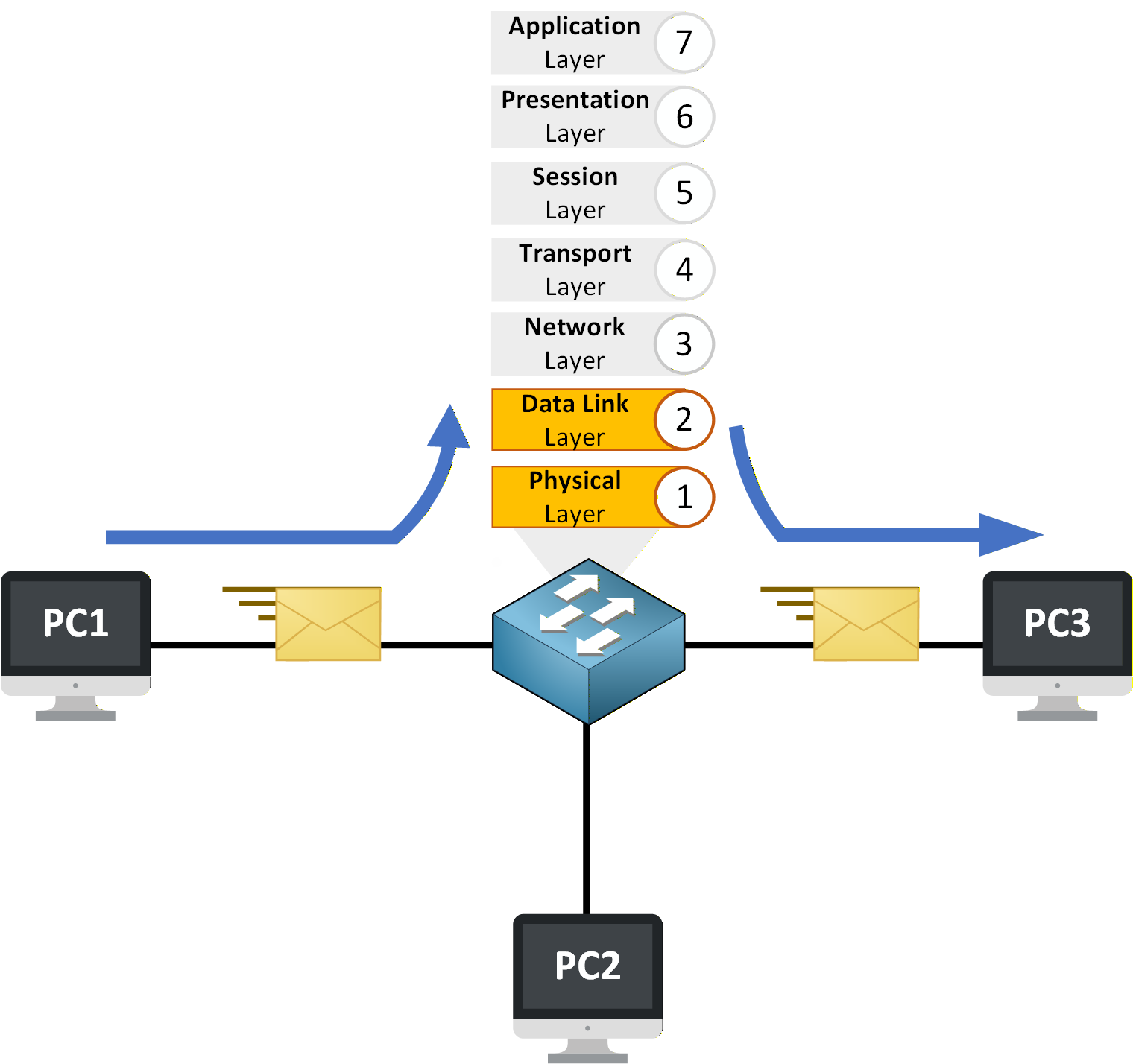
Figure 3 – Data flows through the switch at Layer 2 inside the LAN
When devices exchange data inside the same LAN, the switch processes and forwards Ethernet frames based on MAC addresses, not IP addresses.
To see how the switch makes forwarding decisions, we can check its MAC address table:
SW1# show mac address-table Vlan Mac Address Type Ports ---- ----------- -------- ----- 1 0011.2233.4455 DYNAMIC Gi0/1 1 00aa.bbcc.ddee DYNAMIC Gi0/2 1 00ff.1122.3344 DYNAMIC Gi0/3This output shows that the switch has learned the MAC addresses of the connected devices.
Each MAC address is associated with a specific port.When a frame arrives, the switch checks the destination MAC address and forwards the frame to the correct port.
At this stage:
No IP routing occurs
No router is involved
All forwarding decisions are made at Layer 2
Inside a LAN, communication is handled entirely at the Data Link layer.
Answer the question below
At which OSI layer does communication inside a LAN occur?
At this point, you know that devices communicate locally through a switch and that this communication happens at Layer 2. Now let’s clearly define what the switch does and where its role stops.
Local Communication vs External Networks
Inside a LAN, the switch is responsible for local communication.
It connects devices together and forwards data only within the same network.As long as traffic stays inside the LAN, the switch is all that is needed.
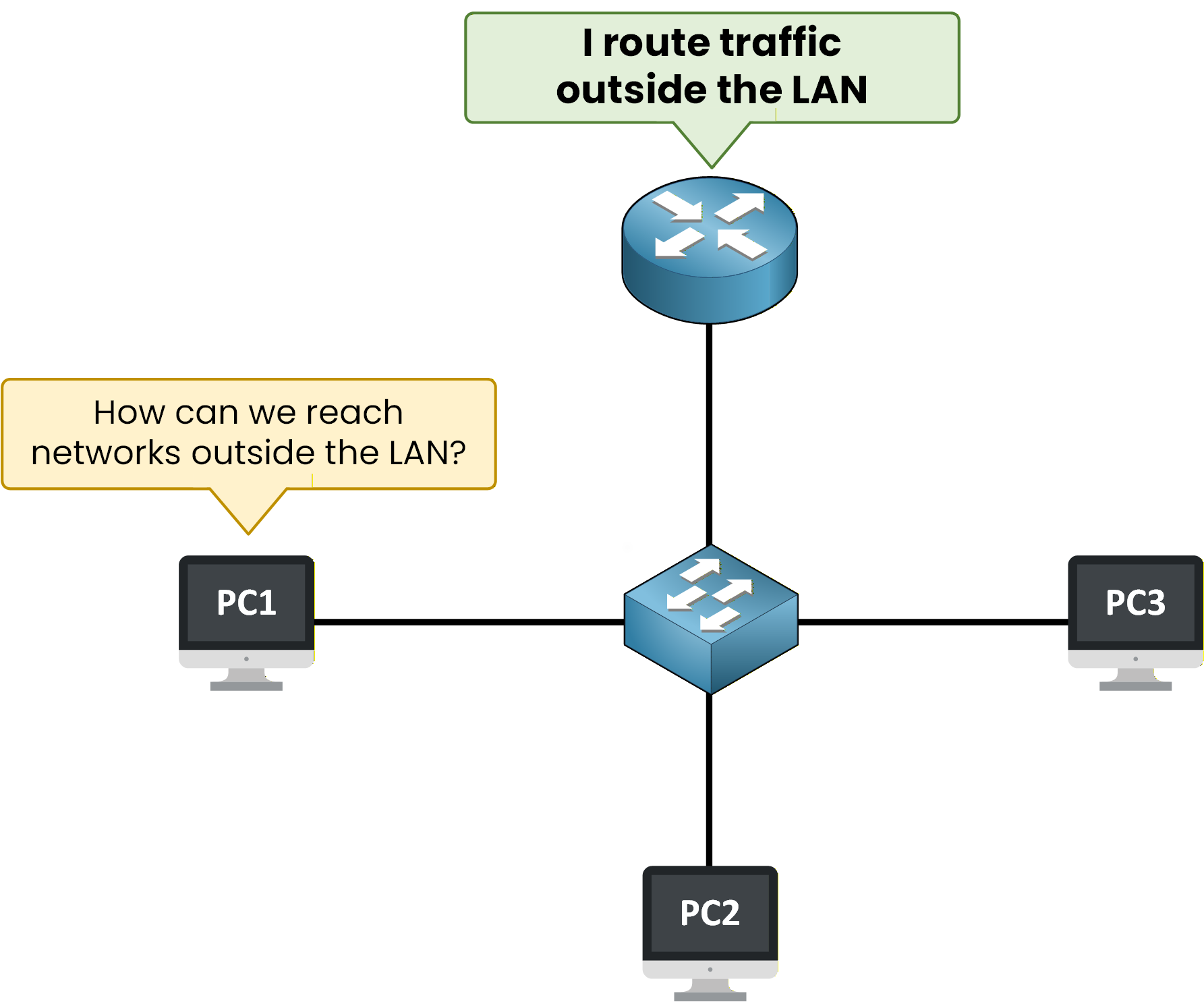
Figure 4 – A router is required to reach networks outside the LAN
However, the switch cannot send traffic to other networks.
When a device needs to reach a destination outside the LAN, local communication is no longer enough.At this point, traffic must be sent to a router.
Verifying the Router’s Role
Let’s look at the router configuration:
R1# show ip interface brief Interface IP-Address OK? Method Status Protocol GigabitEthernet0/0 192.168.1.1 YES manual up up GigabitEthernet0/1 10.0.0.1 YES manual up upThis output shows that:
GigabitEthernet0/0 is connected to the LAN network (192.168.1.0/24).
GigabitEthernet0/1 connects to another network
When a device inside the LAN wants to reach an external destination, it sends traffic to the router’s LAN interface (192.168.1.1).
The router then forwards the traffic to the appropriate external network.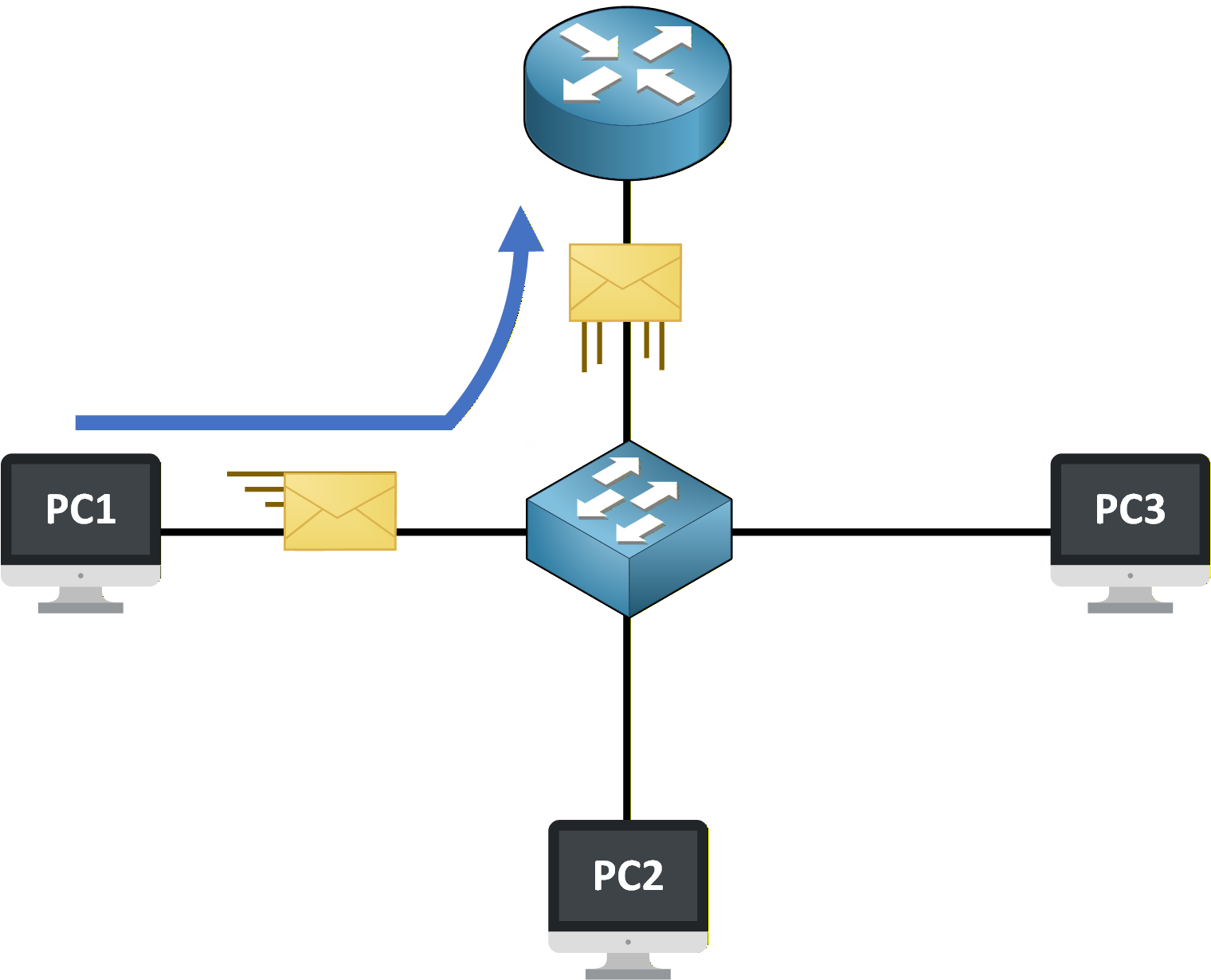
Figure 5 – Traffic leaving the LAN through the router
The router is the device that handles communication between different networks.
The switch forwards the traffic to the router, and the router takes over to reach external destinations.Keep this simple rule in mind:
The switch is used for communication inside the LAN
The router is used to reach networks outside the LAN
Answer the question below
Which device is used to reach networks outside the LAN?