In the previous courses, we learned what a Local Area Network (LAN) is and how devices communicate inside it.
We saw that devices connected to the same LAN exchange data locally through a switch.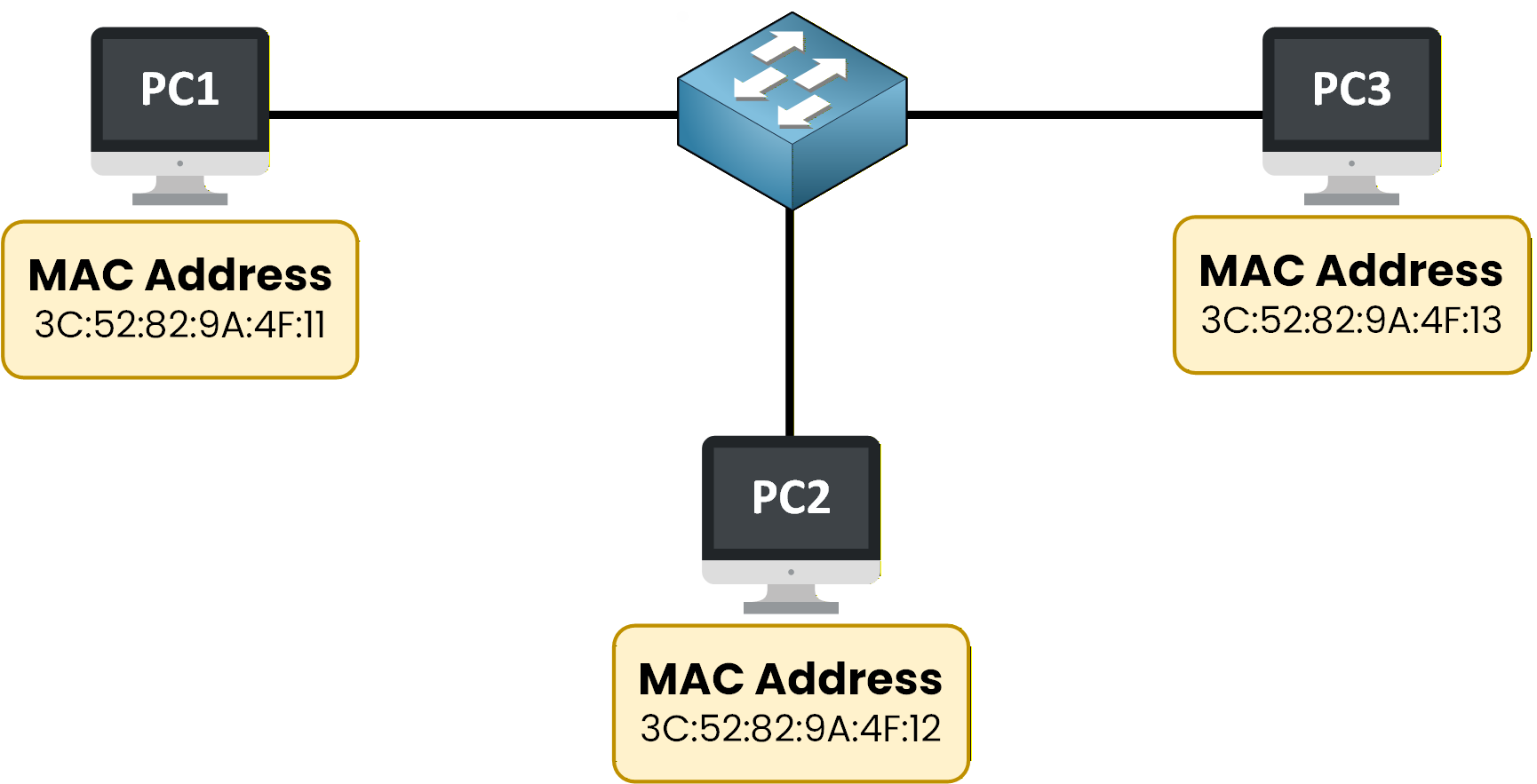
Figure 1 - Local Area Network Example
Inside a LAN, communication does not involve a router.
As long as devices are part of the same local network, the switch is responsible for forwarding traffic between them.This local communication relies on MAC addresses.
Each device has a MAC address, and the switch uses these MAC addresses to decide how data should move inside the LAN.Communication Inside a LAN Happens at Layer 2
To better understand how this communication works, we need to look at the OSI model.
Communication inside a LAN happens at Layer 2, also known as the Data Link layer.
This is the layer where the switch operates.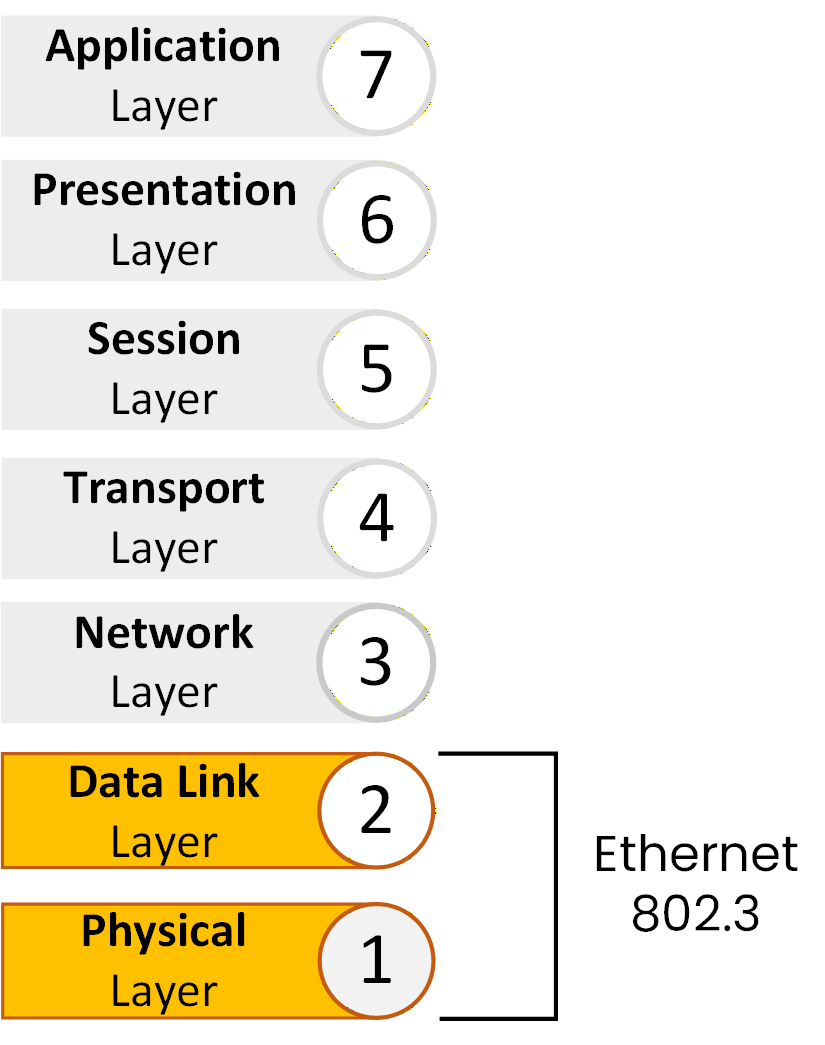
Figure 2 – Ethernet operates at the Data Link layer (Layer 2)
Ethernet is the technology used at Layer 2 to enable local communication.
It defines how data is formatted, addressed, and transmitted between devices inside the LAN.At this point, we know two important things:
Switches operate at Layer 2
Switches use MAC addresses to forward traffic inside the LAN
But this raises an important question:
How are MAC addresses actually carried from one device to another?
MAC addresses do not travel alone.
They are transported inside a Layer 2 structure defined by Ethernet.This structure is called the Ethernet frame.
Answer the question below
At which OSI layer does communication inside a LAN occur?
Inside a Local Area Network, devices need a simple and common way to communicate with each other.
They cannot just send data randomly.
To communicate correctly, all devices must follow the same rules.These rules define how data is packaged and exchanged inside the LAN.
This is why Ethernet frames exist.Ethernet Frames: The Common Language of a LAN
As shown in the figure, when PC1 wants to communicate with another device in the LAN, it does not send data directly.
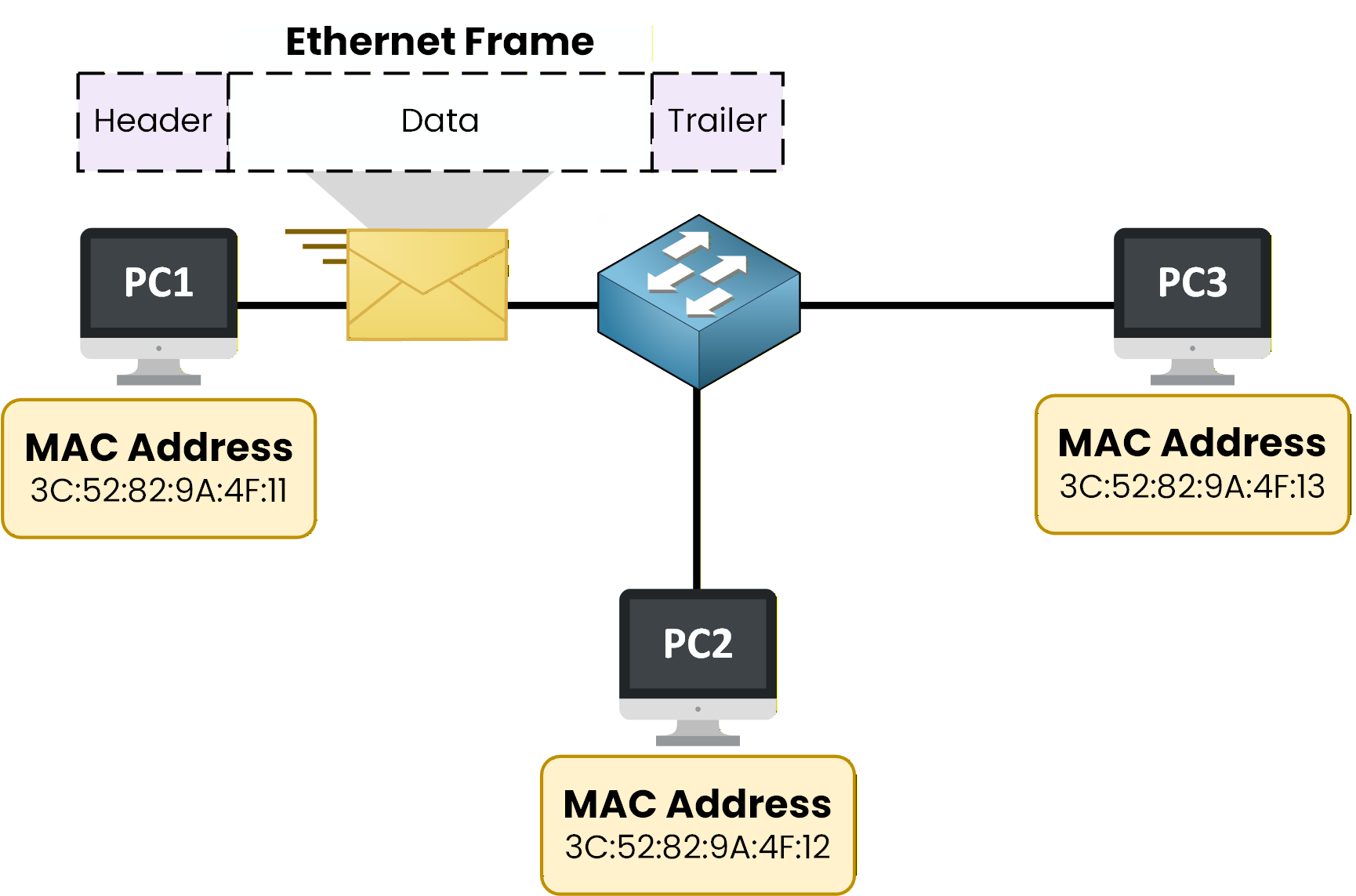
Figure 3 – Devices in a LAN communicate using Ethernet frames
Instead, the data is placed inside an Ethernet frame.
You can think of an Ethernet frame as an envelope:
the envelope carries the data
it travels across the LAN
it is understood by the switch and other devices
Ethernet Frames Are Used for Every LAN Communication
Every device in the LAN uses the same Ethernet frame format.
This common format allows all devices to communicate using the same rules.Every time devices communicate inside a LAN, an Ethernet frame is created.
There is no local communication without Ethernet frames.At this stage, remember this simple idea:
Inside a LAN, devices communicate using Ethernet frames.
Ethernet frames provide the structure that makes local communication possible.Answer the question below
What structure is used by devices to communicate inside a LAN?
Let’s start by looking at an Ethernet frame.
As shown in the figure below, an Ethernet frame is divided into three main parts:
Header
Data
Trailer

Figure 4 – Ethernet frame structure
Each part of the Ethernet frame has a specific role in local communication.
Let’s look at them one by one.The Ethernet Frame Header
The header is the most important part of the Ethernet frame for the switch.
It contains the information needed to:
identify the sender
identify the receiver
understand what type of data is being carried
This is the part of the frame that the switch analyzes to make decisions.
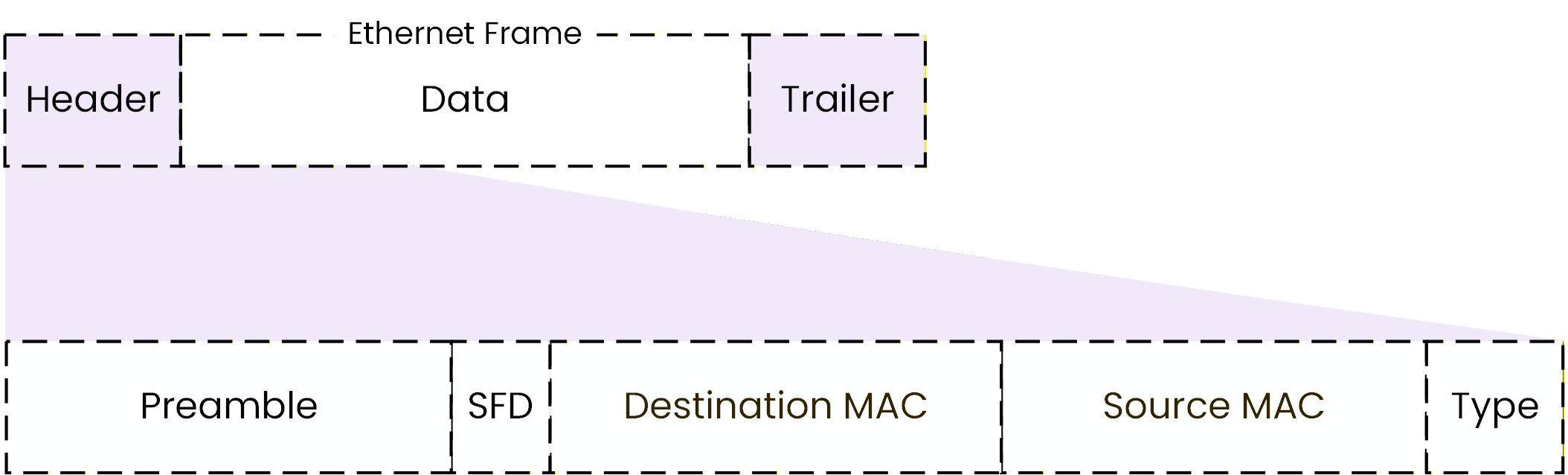
Figure 5 – Ethernet Header Field
Before the actual header fields, Ethernet includes synchronization information.
Preamble and Start Frame Delimiter (SFD)
At the very beginning of an Ethernet frame, you will find the Preamble and the Start Frame Delimiter (SFD).
These fields are used to prepare the receiving device before the actual frame arrives.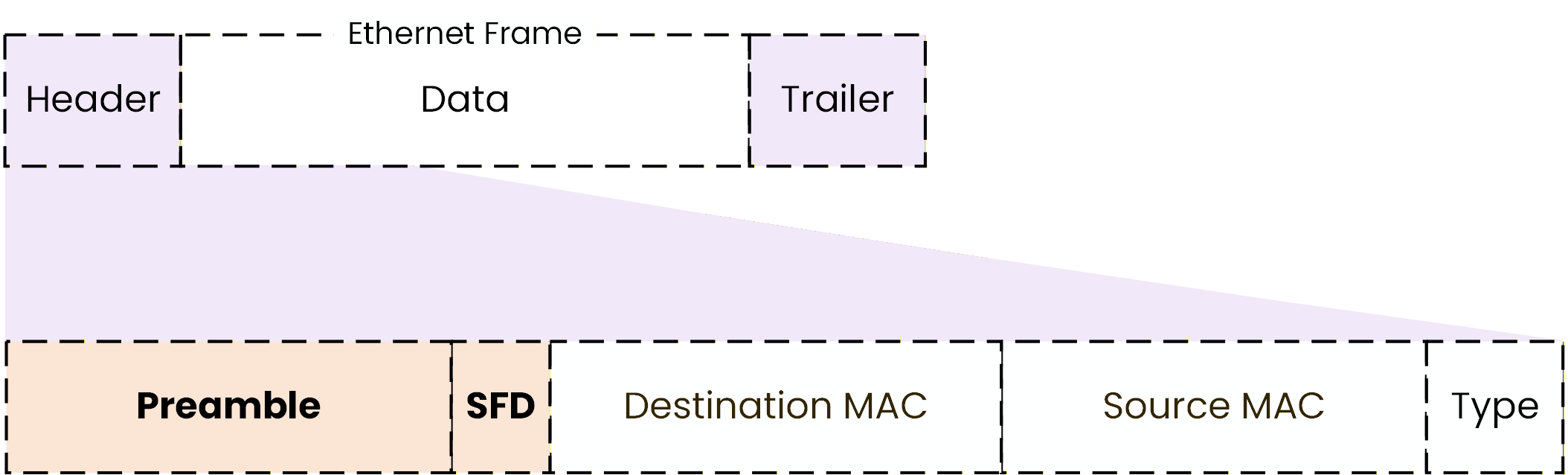
Figure 6 – Ethernet frame preamble and start frame delimiter (SFD)
The preamble allows the sender and receiver to synchronize.
In simple terms, it helps the receiving device get ready to correctly read the incoming data.
The Start Frame Delimiter (SFD) marks the exact start of the Ethernet frame.
It tells the receiver: “The frame begins here.”
It is important to understand that these fields are not used by the switch to make decisions.
They are only used to ensure that the frame can be read correctly.Answer the question below
What do the preamble and SFD help the receiving device do?
Source and Destination MAC Addresses
Inside the Ethernet frame header, there are two essential fields that are used by the switch:
Destination MAC Address
Source MAC Address
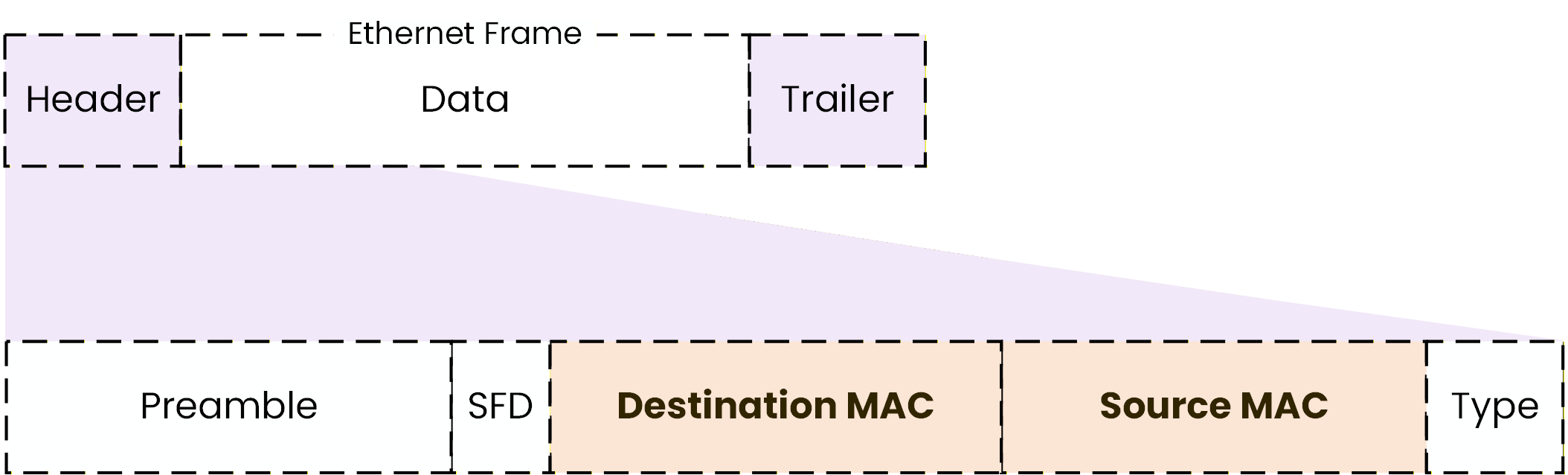
Figure 7 – Ethernet frame header showing source and destination MAC addresses
These two addresses are the core of how switching works inside a LAN.
The Destination MAC address identifies which device should receive the Ethernet frame.
The Source MAC address identifies which device sent the Ethernet frame.Answer the question below
Which MAC address identifies which device should receive the Ethernet frame?
The Type Field
The Ethernet frame header also includes a field called the Type field.
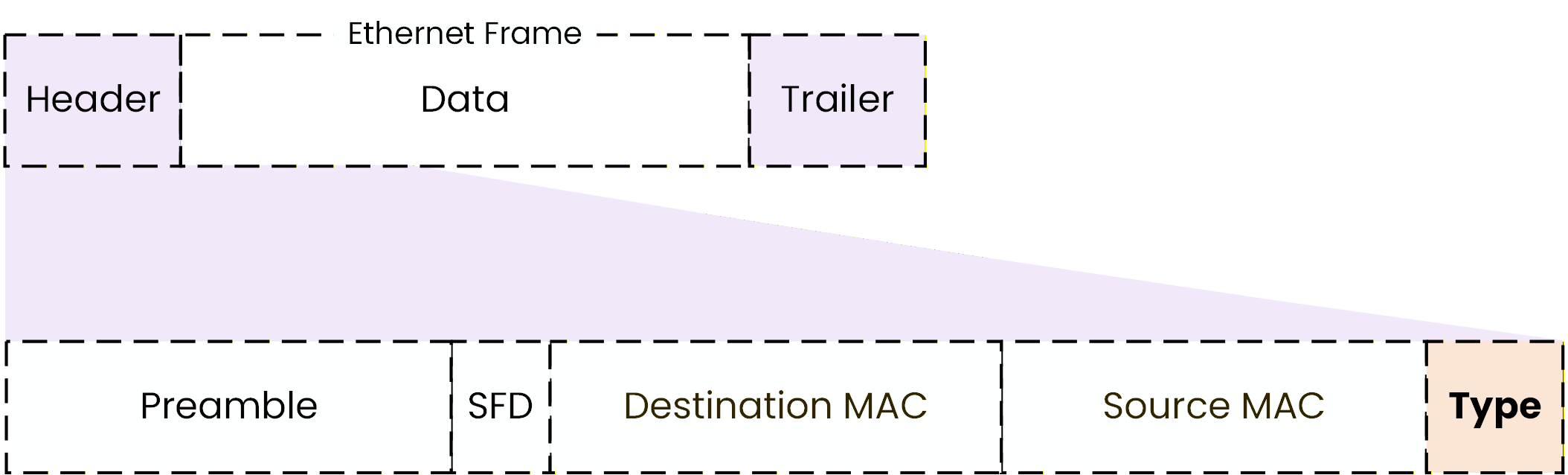
Figure 8 – Ethernet frame header showing the Type field
The Type field simply tells what kind of data is inside the Ethernet frame.
When a device receives an Ethernet frame, it looks at the Type field to know what to do next.
For example:
if the Type field indicates IP, the device processes the data as IP traffic
if the Type field indicates ARP, the device processes the data as an ARP message
Without the Type field, the device would not know how to interpret the data inside the frame.
So, the role of the Type field is very simple:
It tells the device what protocol is being carried inside the Ethernet frame.
The Ethernet Frame Trailer
The last part of the Ethernet frame is called the trailer.
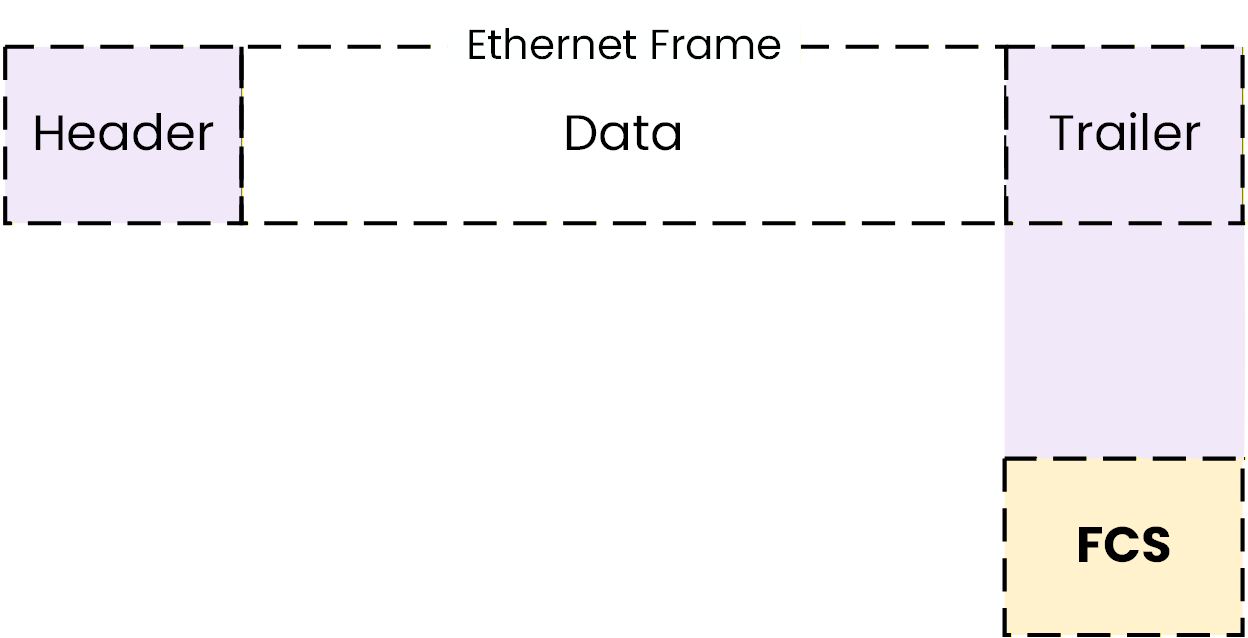
Figure 9 – Ethernet frame trailer showing the Frame Check Sequence (FCS)
The trailer contains the Frame Check Sequence (FCS).
The FCS is used to detect errors during transmission.When a device receives an Ethernet frame, it checks the FCS:
if the frame is correct, it is accepted
if an error is detected, the frame is discarded
Ethernet does not correct errors at Layer 2.
Frames that contain errors are simply dropped.Answer the question below
What does the Frame Check Sequence (FCS) detect?
Now that you understand the structure of an Ethernet frame, let’s see how it is actually used inside a LAN.
Every time a PC sends data, that data is encapsulated inside an Ethernet frame.
This frame contains all the information the switch needs to make a forwarding decision.Generating Traffic Inside the LAN
To make this practical, let’s generate traffic from PC1 to PC3.
From PC1:C:\> ping 192.168.1.13 Pinging 192.168.1.13 with 32 bytes of data: Reply from 192.168.1.13: bytes=32 time<1ms TTL=128 Reply from 192.168.1.13: bytes=32 time<1ms TTL=128 Reply from 192.168.1.13: bytes=32 time<1ms TTL=128 Reply from 192.168.1.13: bytes=32 time<1ms TTL=128Each time PC1 sends an ICMP Echo Request, an Ethernet frame is created.
That Ethernet frame contains:
A Source MAC address (PC1)
A Destination MAC address (PC3)
A Type field (IP)
The actual payload (data)
This frame is then sent to the switch.
How the Switch Processes the Frame
When the switch receives the Ethernet frame, it operates strictly at Layer 2.
It does not analyze the IP address to make its forwarding decision.
Instead, it reads the MAC addresses contained in the Ethernet header.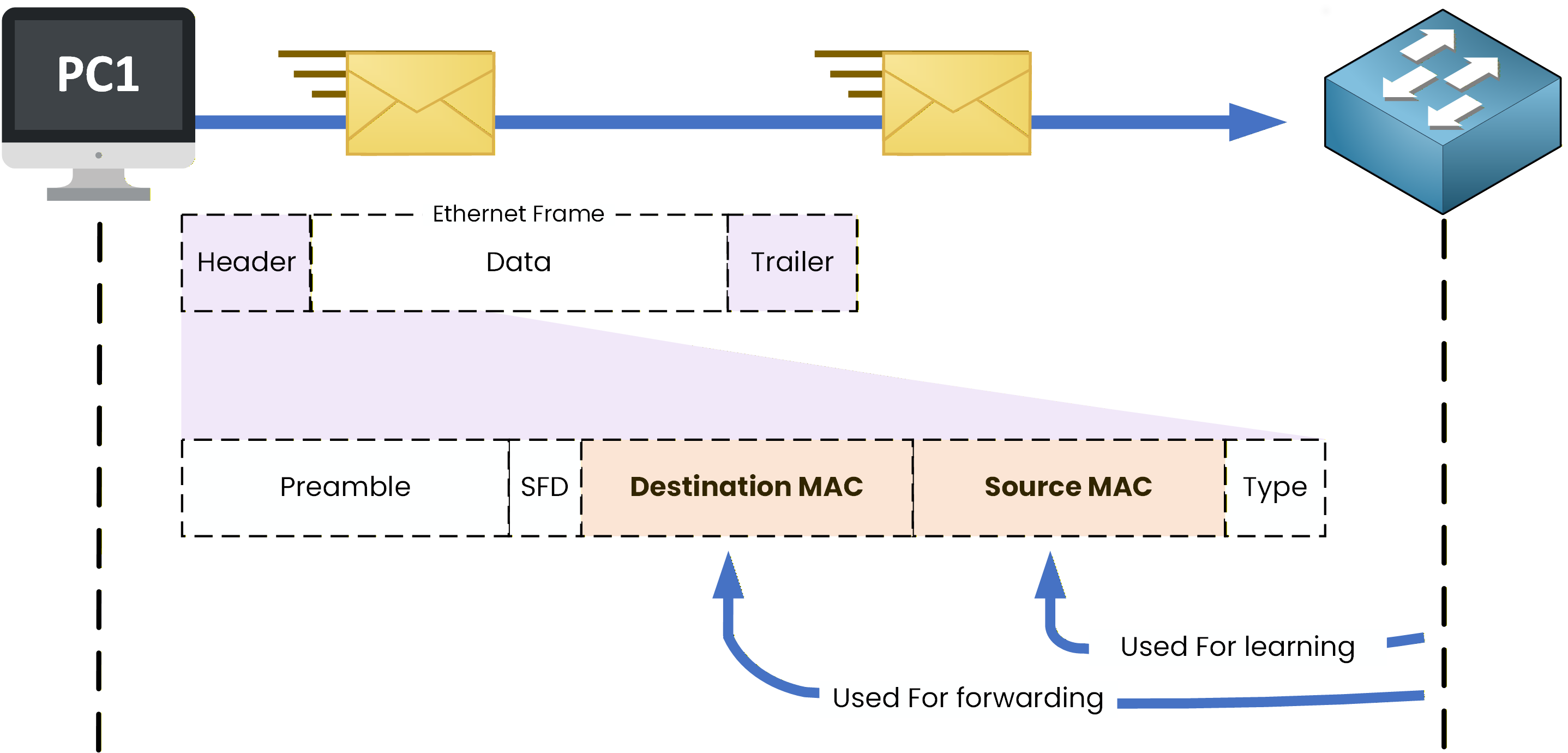
Figure 10 – Switch processing an Ethernet frame using source and destination MAC addresses
The switch performs two essential actions:
1. It checks the Destination MAC address
The Destination MAC address tells the switch which device should receive the frame.
The switch uses this information to forward the frame out of the correct interface.2. It reads the Source MAC address
The Source MAC address allows the switch to identify which device sent the frame and on which port it was received.
This is how the switch begins building knowledge about devices connected to it.What’s Next?
At this point, you understand the overall structure of an Ethernet frame and how it is used inside a LAN.
What really matters now is understanding how the switch dynamically learns these MAC addresses and builds its MAC address table.
That is exactly what we will explore in the next course.Answer the question below
Which MAC address does a switch use to learn where a device is connected?