In Ethernet networks, multiple physical links between devices may appear to provide more bandwidth and enhance reliability.
However, this approach creates a problem.
Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) prevents Layer 2 loops by blocking redundant links.Without EtherChannel
When several parallel links exist between switches, STP disables the extra ones to avoid loops.
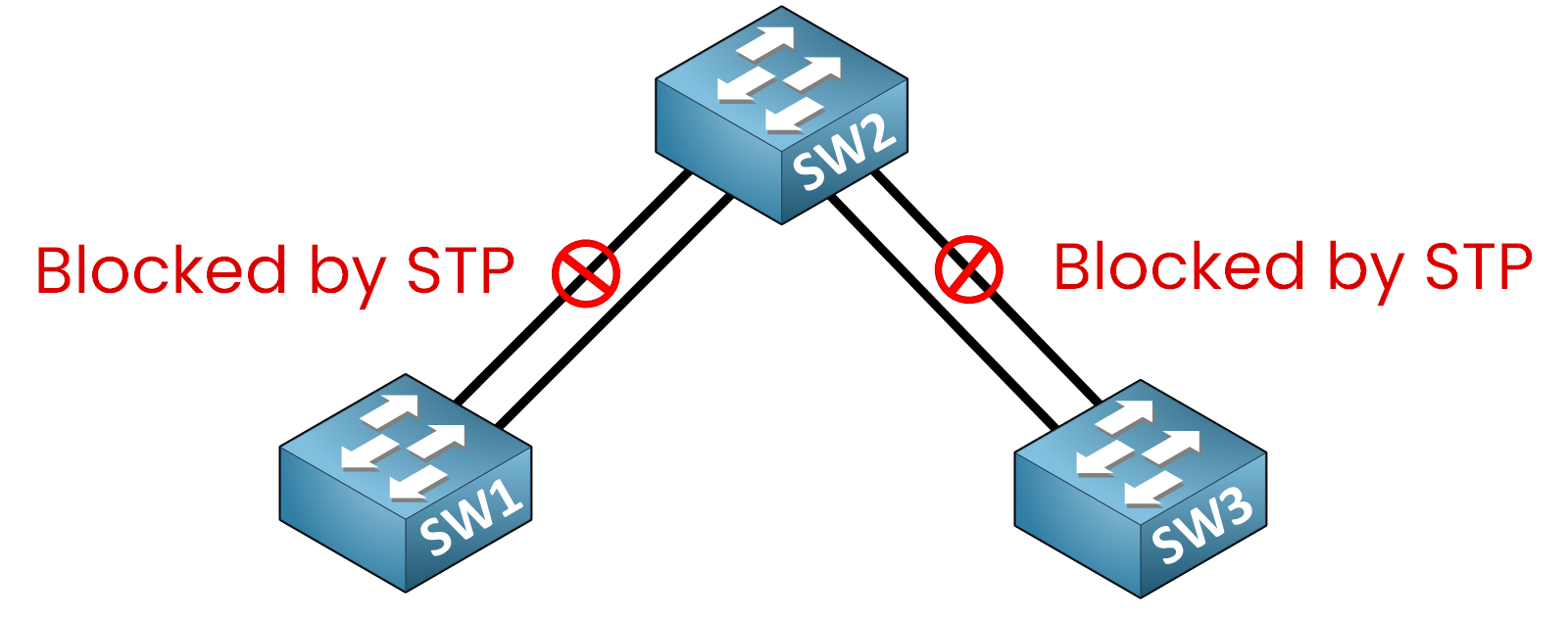
Figure 1 – Many Physical Links Without EtherChannel
🔴 Only one link per redundant pair remains active.
🔴 Extra links stay idle, wasting available bandwidth.
If we look at SW2, we can verify this behavior using the following command:
SW2# show spanning-tree Interface Role Sts Cost Prio.Nbr Type ---------------- ---- --- --------- -------- ---- Gi0/1 Root FWD 4 128.1 P2p Gi0/2 Altn BLK 4 128.2 P2p Gi0/3 Desg FWD 4 128.3 P2p Gi0/4 Altn BLK 4 128.4 P2pIf we examine the output on SW2, we can see that:
The interfaces highlighted in green (Gi0/1 and Gi0/3) are in Forwarding (FWD) state.
The interfaces highlighted in red (Gi0/2 and Gi0/4) are in Blocking (BLK) state.
This means that although four physical links are connected, only two are actively forwarding traffic.
The other links remain unused due to STP.As a result, adding more physical links does not improve bandwidth utilization.
With EtherChannel
EtherChannel solves this limitation by bundling multiple physical links into a single logical channel.
From the perspective of STP, routing protocols, and the switch itself, this bundle appears as one single interface.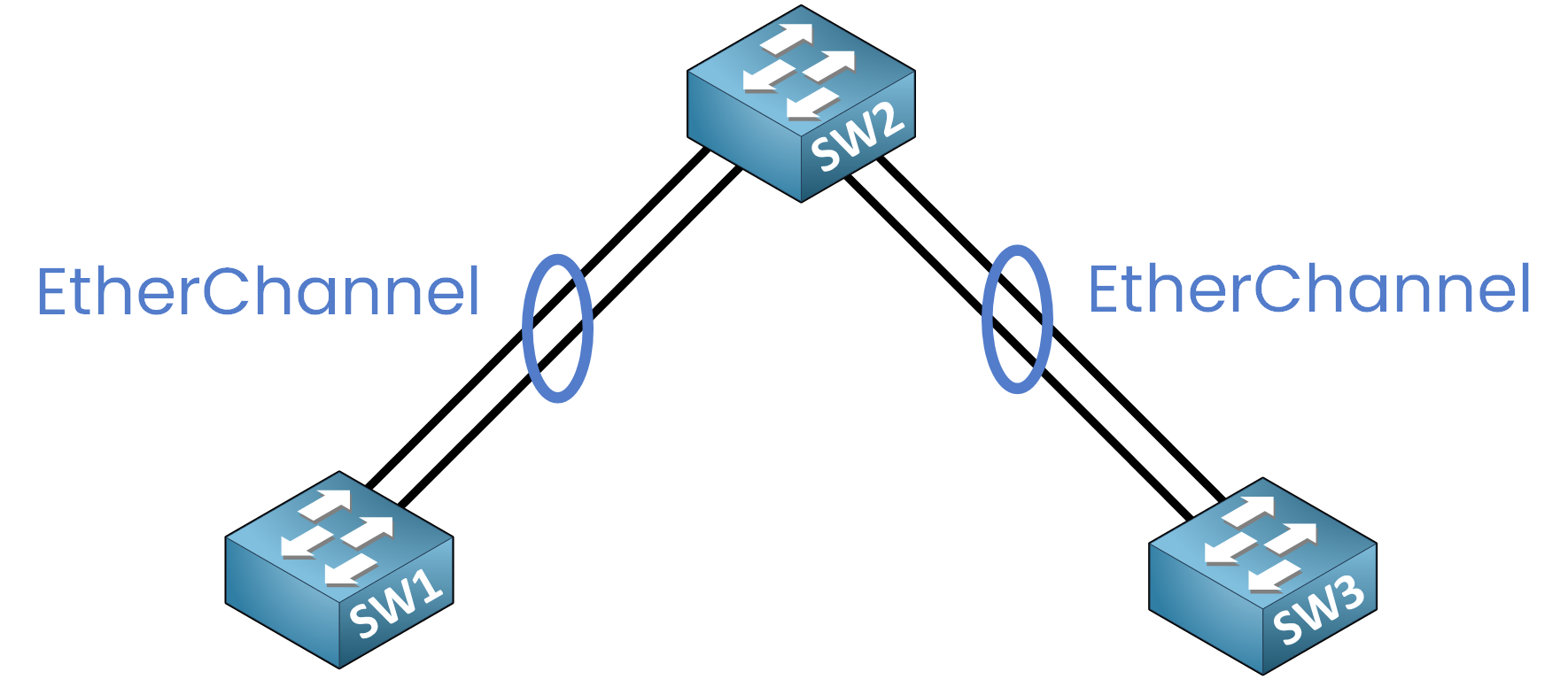
Figure 2 – EtherChannel Logical Bundling
✅ All links are active together, providing aggregated bandwidth.
✅ If one link fails, the remaining links continue forwarding traffic.
✅ STP does not block individual member links because it sees only one logical interface.
If we now look again at SW2, we observe a different result:
40 % Complete: you’re making great progress
Unlock the rest of this lesson
If you’d like to continue your CCNA journey, simply create your free account.
Access all CCNA lessons
Practice with hands-on labs
Train with Practice exams and Quizzes
Progress tracking in your dashboard
Made by network engineers - CCNP certified
learners globally
EtherChannel
EtherChannel lets you combine several physical links into one logical channel for more bandwidth and redundancy. In this lesson, you’ll learn why STP blocks extra links by default and how EtherChannel overcomes this limitation.