Have you ever wondered what BPDU Guard is and how it protects your network?
Let’s make it simple and let's start with an example.In the diagram above, we see a typical STP topology with three switches: SW1, SW2, and SW3.
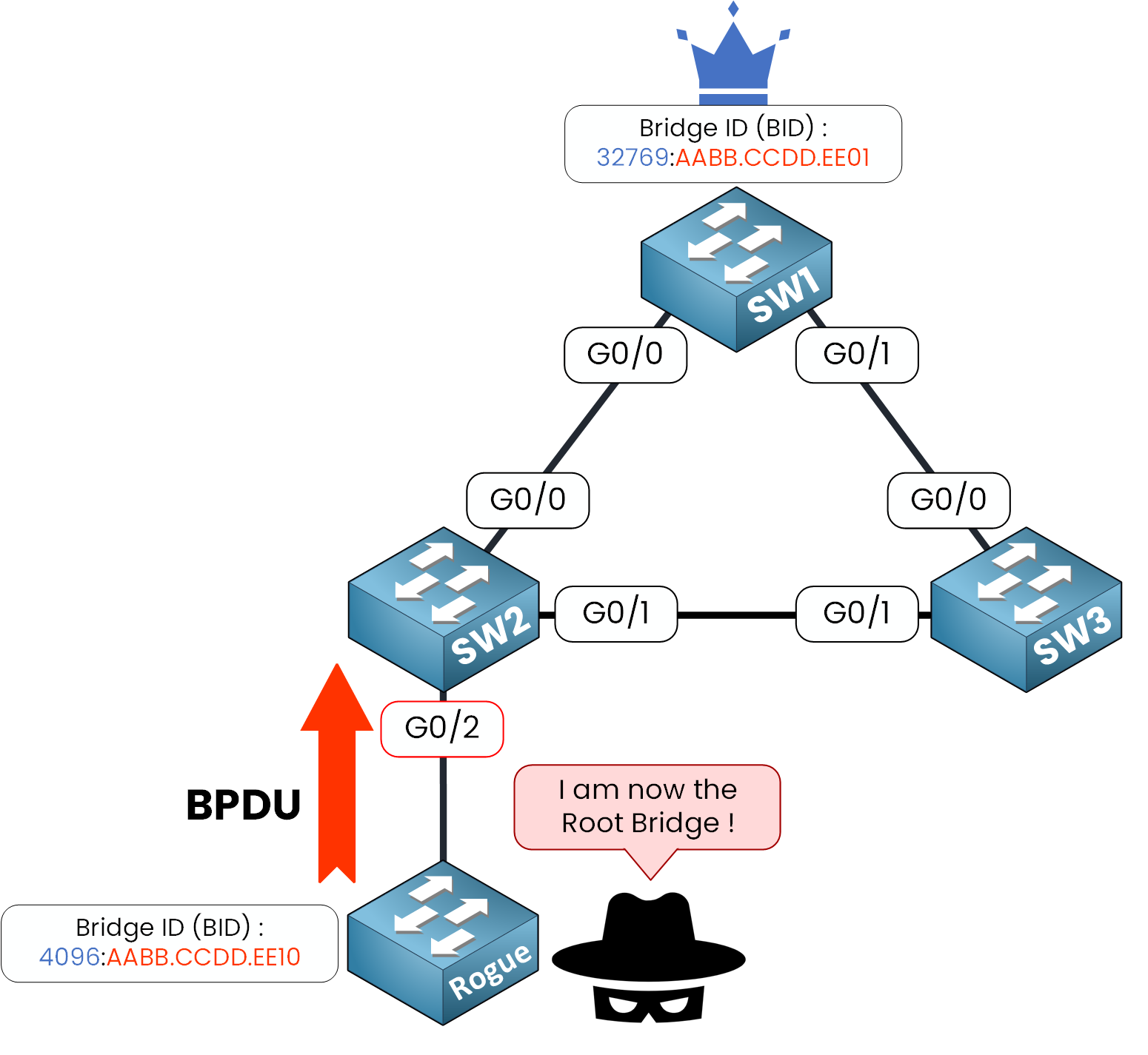
Figure 1 – Rogue switch sends BPDUs to claim Root Bridge role
SW1 is the Root Bridge, with Bridge ID
32769:AABB.CCDD.EE01SW2 has a port (G0/2) configured with PortFast, normally meant for end devices.
But here's the problem:
A rogue switch gets connected to that access port!
Instead of staying quiet, it sends BPDUs with a lower Bridge Priority:4096:AABB.CCDD.EE10better than the current Root Bridge.Since BPDU Guard is not enabled, SW2 accepts the BPDU and forward the BPDU into the STP topology.
Without BPDU Guard
The Rogue Switch win the Root Bridge Election because it advertises a better priority
4096against SW1 priority32769, it’s now selected as the new Root Bridge.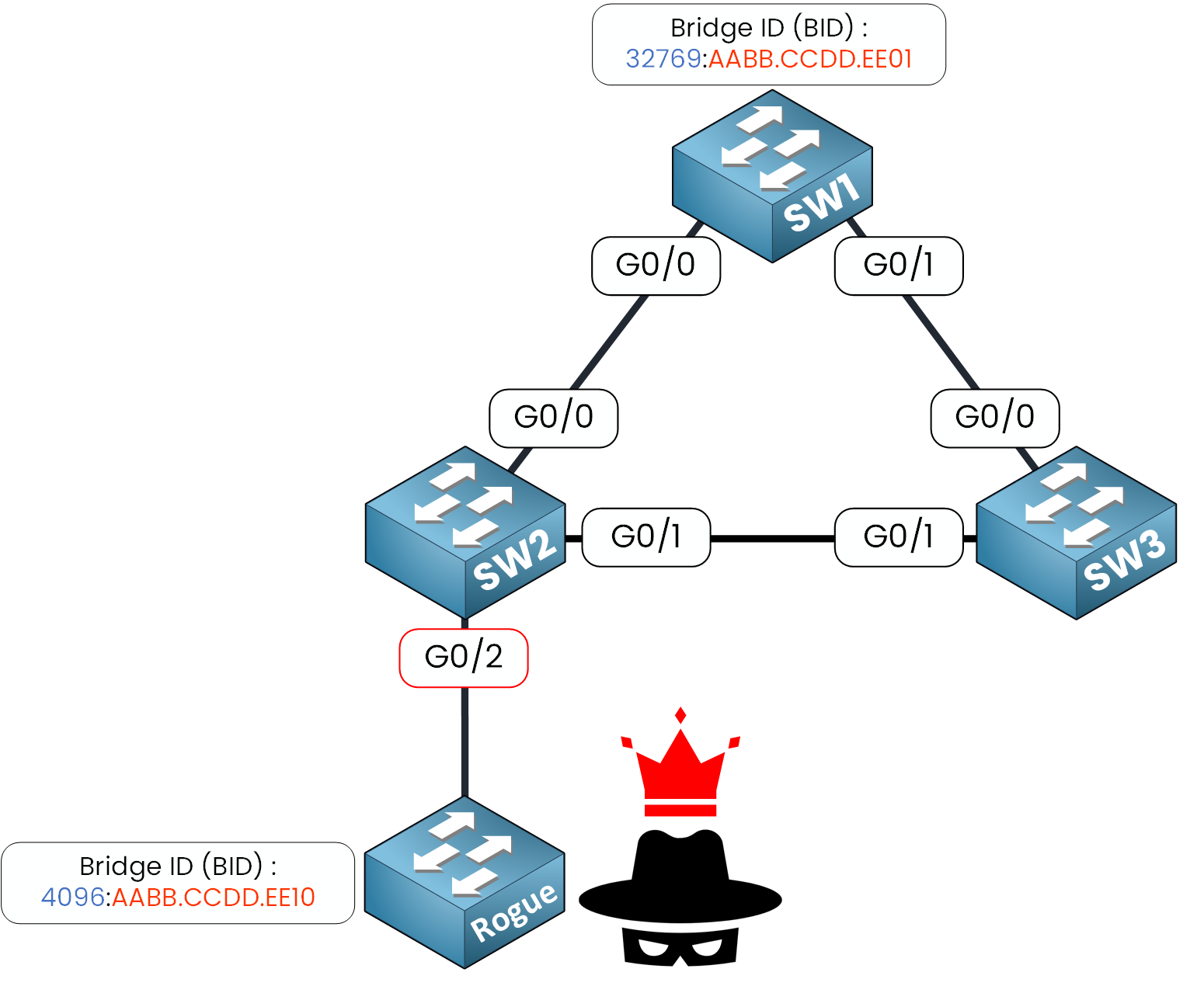
Figure 2 – Rogue switch becomes Root Bridge by sending superior BPDUs
Your entire Spanning Tree topology is now compromised and all of this started from a single access port not properly secured... This is exactly what BPDU Guard feature is designed to prevent.
Solution: Enabling BPDU Guard
To prevent this situation, BPDU Guard must be applied to the PortFast-enabled port.
BPDU Guard discard any incoming BPDU and placed the port into an err-disable state (down/down).This ensures that access ports typically connected to end-user devices like PCs or printers can’t participate in STP.
With BPDU Guard
Let's review our example with BPDU Guard enabled on the interface connected to the rogue switch.
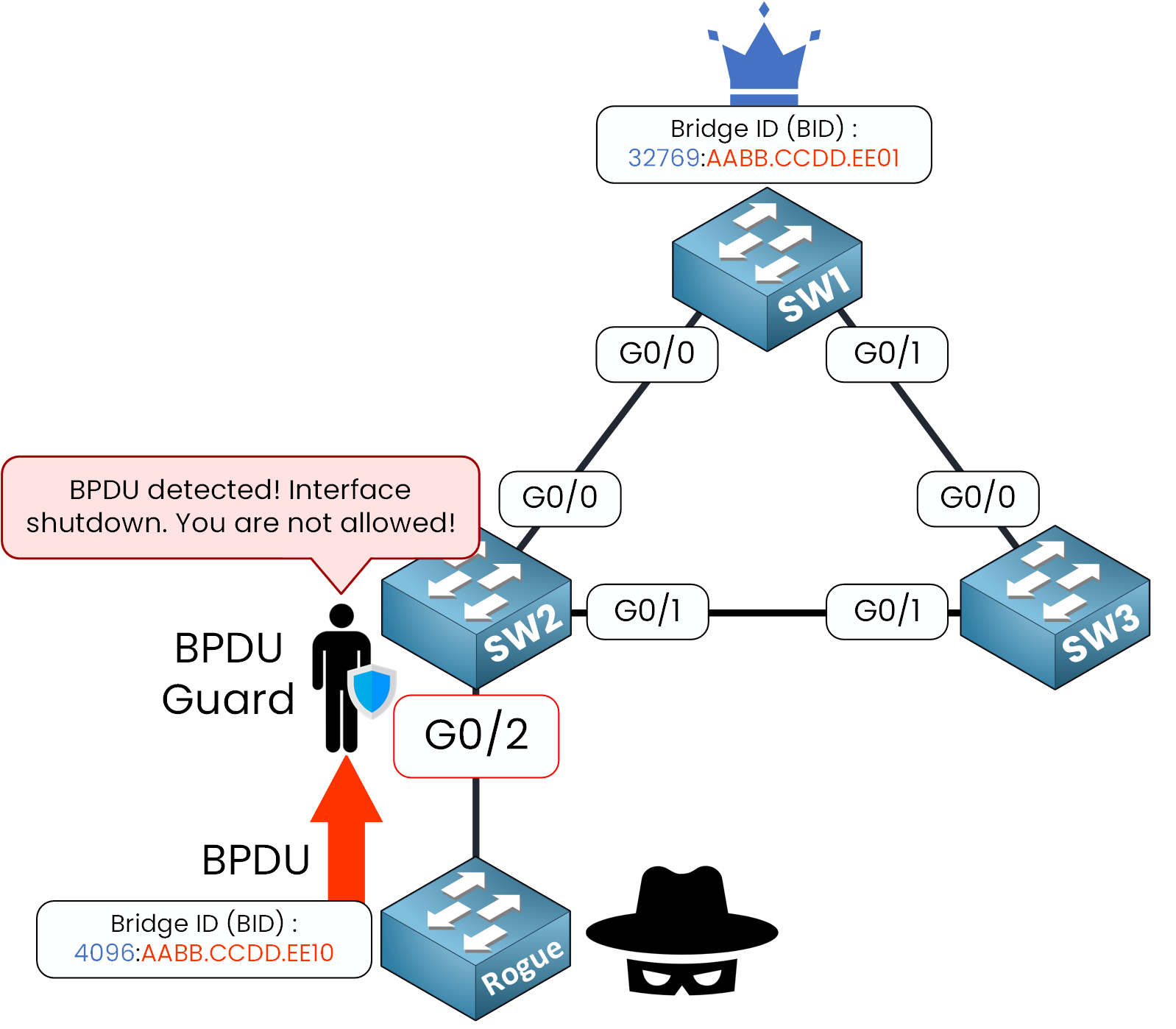
Figure 3 – BPDU Guard blocks the rogue switch by shutting down the interface
The BPDU Guard feature detects the incoming BPDU on the interface and immediately disables the port to protect the network.
*Dec 8 12:58:28.065: %SPANTREE-2-BLOCK_BPDUGUARD: Received BPDU on port Gi0/2 with BPDU Guard enabled. Disabling port. *Dec 8 12:58:28.066: %PM-4-ERR_DISABLE: bpduguard error detected on Gi0/2, putting Gi0/2 in err-disable state *Dec 8 12:58:29.073: %LINEPROTO-5-UPDOWN: Line protocol on Interface GigabitEthernet0/2, changed state to down *Dec 8 12:58:30.109: %LINK-3-UPDOWN: Interface GigabitEthernet0/2, changed state to downAs you can see above, BPDU was received on interface G0/2 with BPDU Guard enabled, this event trigger the shutdown of the interface.
Answer the question below
What does the rogue switch try to become by sending superior BPDUs?
Before diving into the configuration, let's clarify an important point: BPDU Guard and PortFast are separate features.
While they are often used together, they can be configured independently based on your network requirements.If you want end-user devices (like PCs or printers) to access the network instantly and be protected from rogue switches, you should activate both PortFast and BPDU Guard on the same port.
In this example, we will configure :
PortFast to skip the usual STP State delay.
BPDU Guard to shut down the port if an unexpected BPDU is received.
Let's apply the PortFast Feature first on interface G0/2:
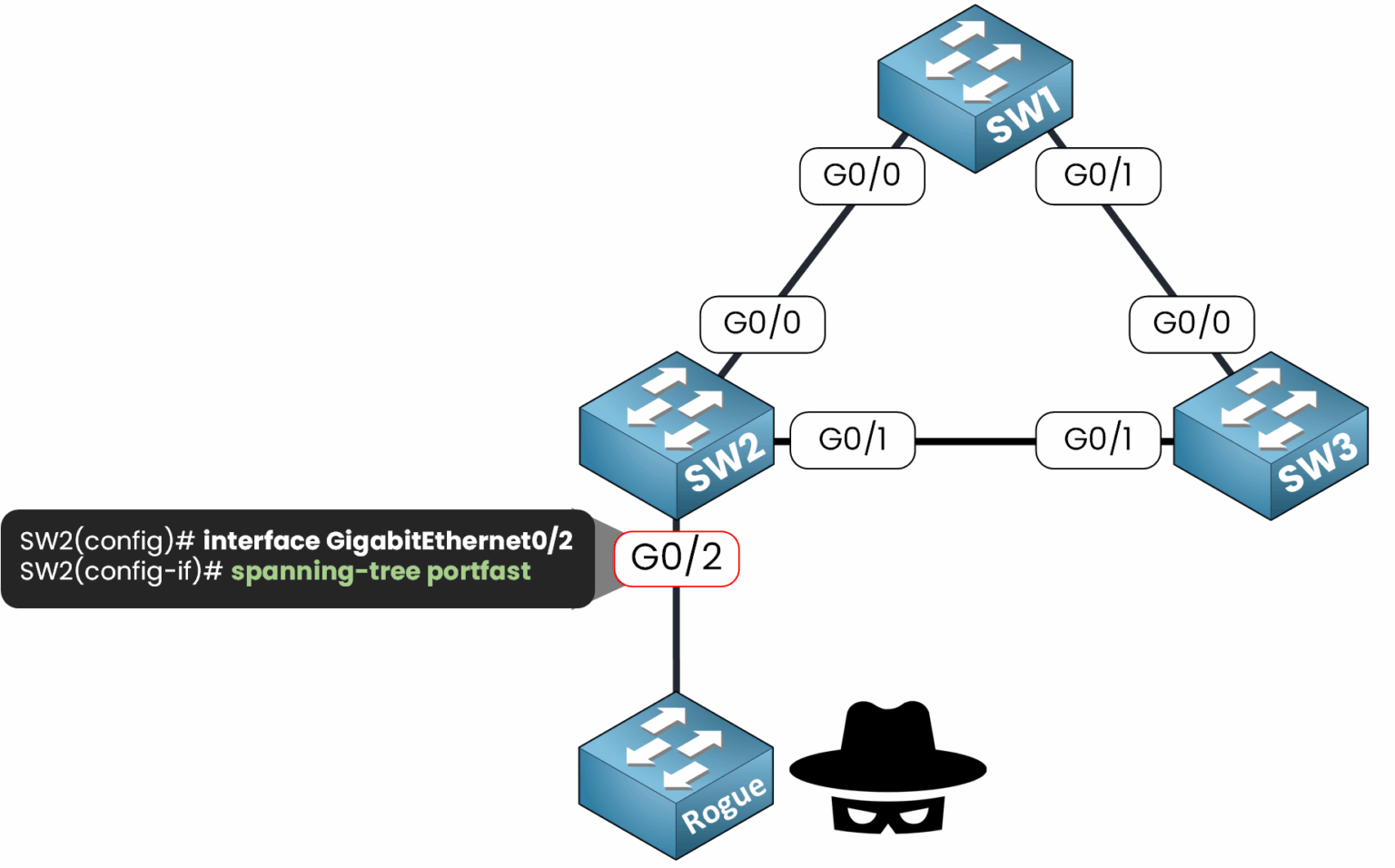
Figure 4 – Configuring PortFast on SW2 interface G0/2 before enabling BPDU Guard
Now we can configure BPDU Guard.
BPDU Guard can be configured in two ways:
On Individual Ports: Applied manually to each specific port.
Globally: Automatically applied to all interface already configured with PortFast.
Enabling BPDU Guard on Individual Ports
1. Enter interface configuration mode:
SW2# conf t Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z. SW2(config)# int g0/22. Enable BPDU Guard on the interface:
SW2(config-if)# spanning-tree bpduguard enable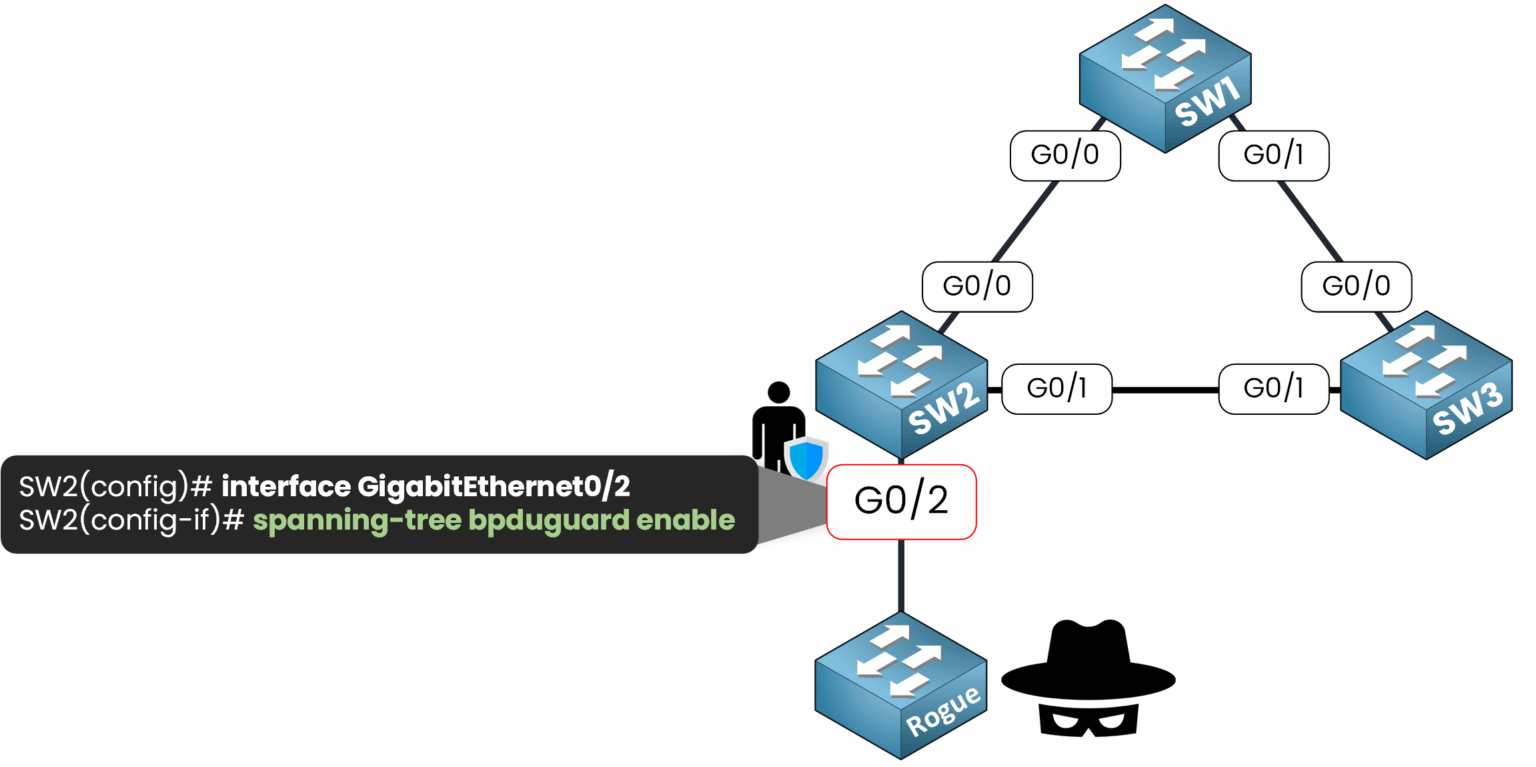
Figure 5 – Enabling BPDU Guard on interface G0/2
40 % Complete: you’re making great progress
Unlock the rest of this lesson
If you’d like to continue your CCNA journey, simply create your free account.
Access all CCNA lessons
Practice with hands-on labs
Train with Practice exams and Quizzes
Progress tracking in your dashboard
Made by network engineers - CCNP certified
learners globally
BPDU Guard
BPDU Guard is a security feature in Spanning Tree Protocol that shuts down a port if unexpected BPDUs are received. Learning how to configure and recover it will protect your network from rogue switches and unwanted topology changes.