A Wide Area Network (WAN) is a network that connects multiple Local Area Networks (LANs) over large geographical distances. It allows organizations to communicate, share data, and access resources between sites that are far apart.
So far in this course, we’ve seen how devices communicate inside a Local Area Network (LAN).
But what happens when we need to connect two LANs that are located in different cities or even on different continents?Why Do We Need a WAN?
Many organizations have more than one location. They often operate offices, branches, or data centers in various regions. If we look at Figure 1 below, we can see two buildings separated geographically that still need to communicate with each other.
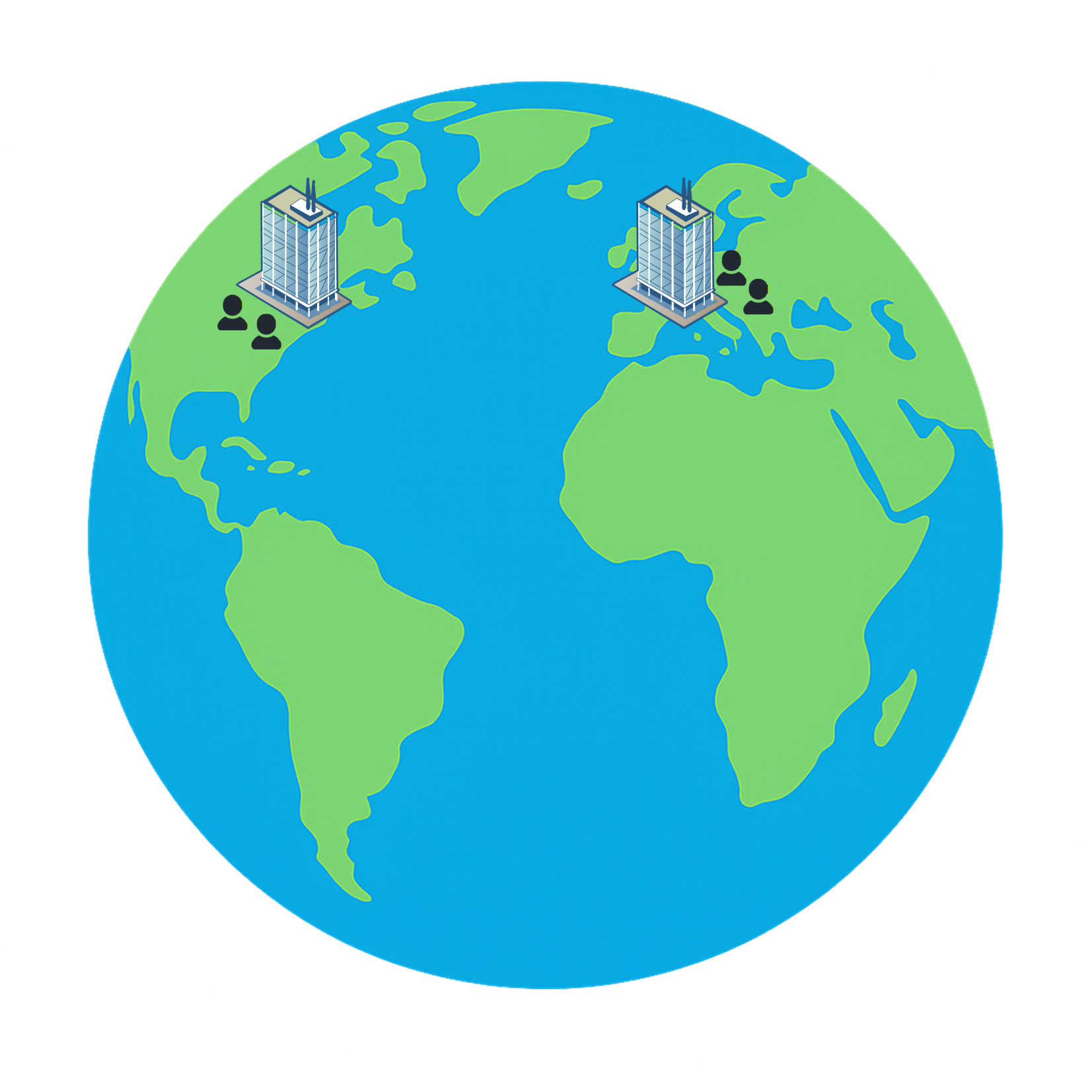
Figure 1 – Two networks located in different parts of the world that need to communicate.
These sites need to exchange files, access shared servers, and use the same business applications.
That’s where the Wide Area Network (WAN) comes in.
A WAN connects several LANs across long distances. This lets them communicate as if they were one big network.Practical Example
To make this clearer, imagine you are a network administrator in your company’s New York office.

Figure 2 – A single LAN represents a local network within one site.
You need to communicate with another branch located in Paris, as we saw earlier.
You might ask yourself: “How can these two offices communicate with each other?”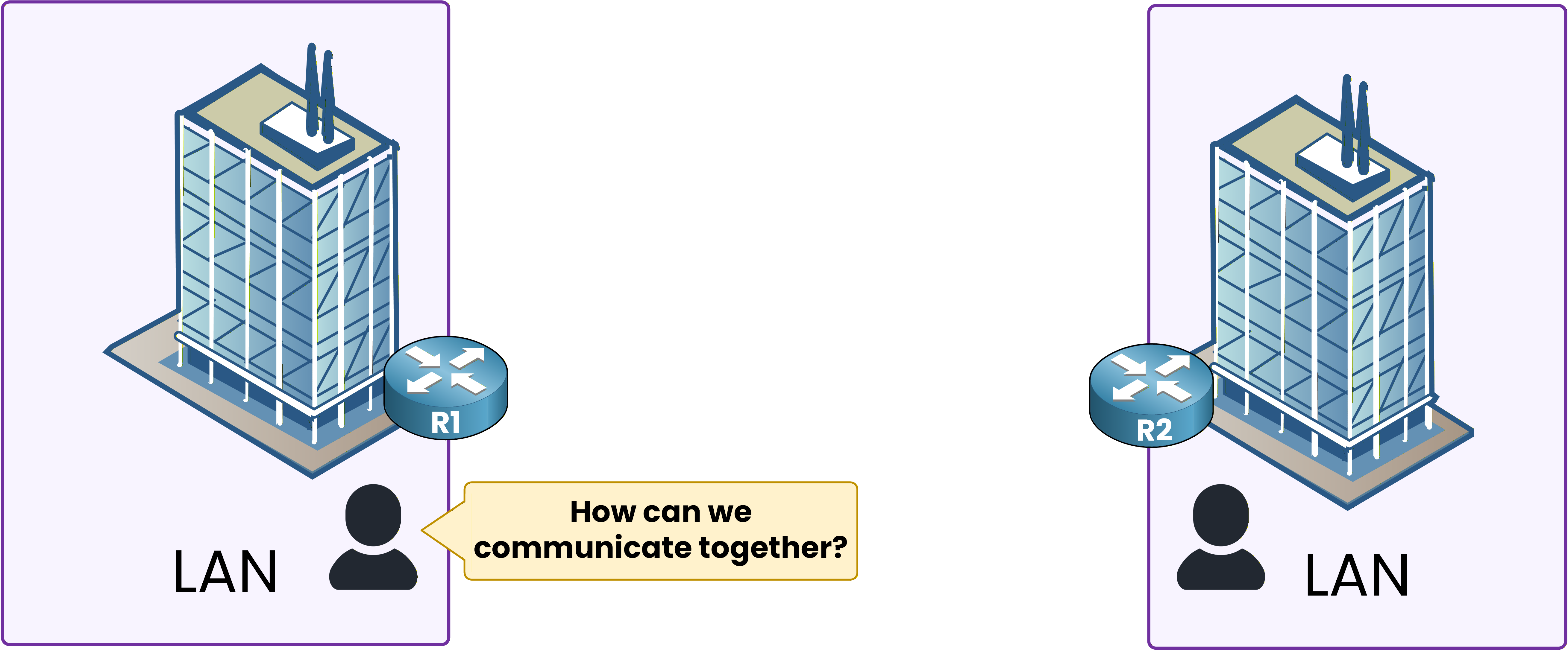
Figure 3 – Two separate LANs that cannot communicate yet.
And you’re right to wonder, because by default, LANs are isolated. They can’t exchange data unless a connection is established between them.
This is exactly where the Wide Area Network (WAN) comes into play. A WAN links multiple LANs over long distances. This setup lets remote sites communicate as if they're on the same network.

Figure 4 – LANs connected through a WAN.
A WAN lets companies share data across offices. They can work together in real time and access shared resources. This is possible regardless of each site's location.
Now that you’ve seen how WANs connect multiple LANs, let’s see what makes this possible behind the scenes.
How WANs Interconnect Networks
WANs are large networks that span wide geographical areas and are operated by service providers.
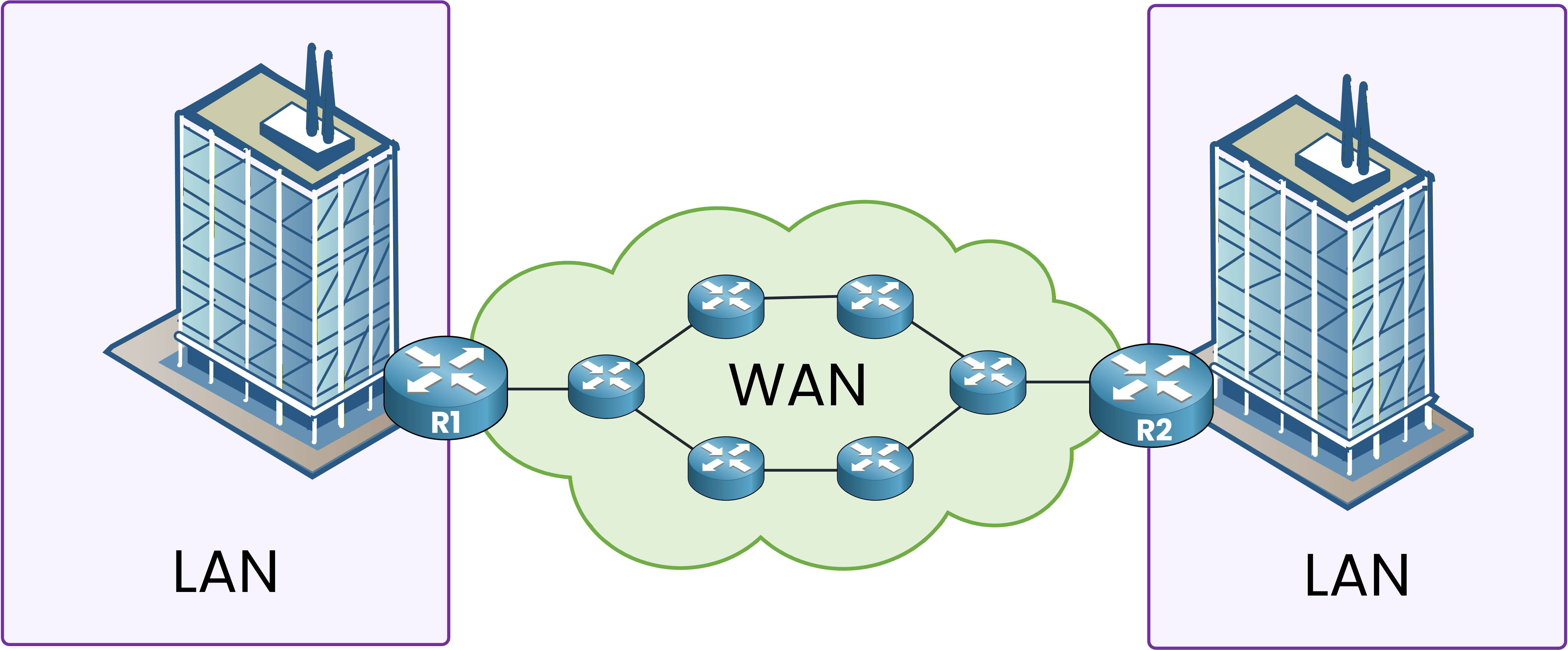
Figure 5 – The WAN infrastructure interconnects two LANs through provider routers.
The WAN infrastructure includes devices such as routers, switches, and transmission links. These components enable secure communication between different LANs. The service provider’s network bridges the gap between remote locations.
Now that you know what a WAN is, let’s see who provides these connections and how they operate behind the scenes.
Answer the question below
What does a WAN connect across long distances?
The role of Internet Service Providers (ISPs) is crucial in interconnecting networks around the world. Without them, organizations would only be able to communicate within their local sites.
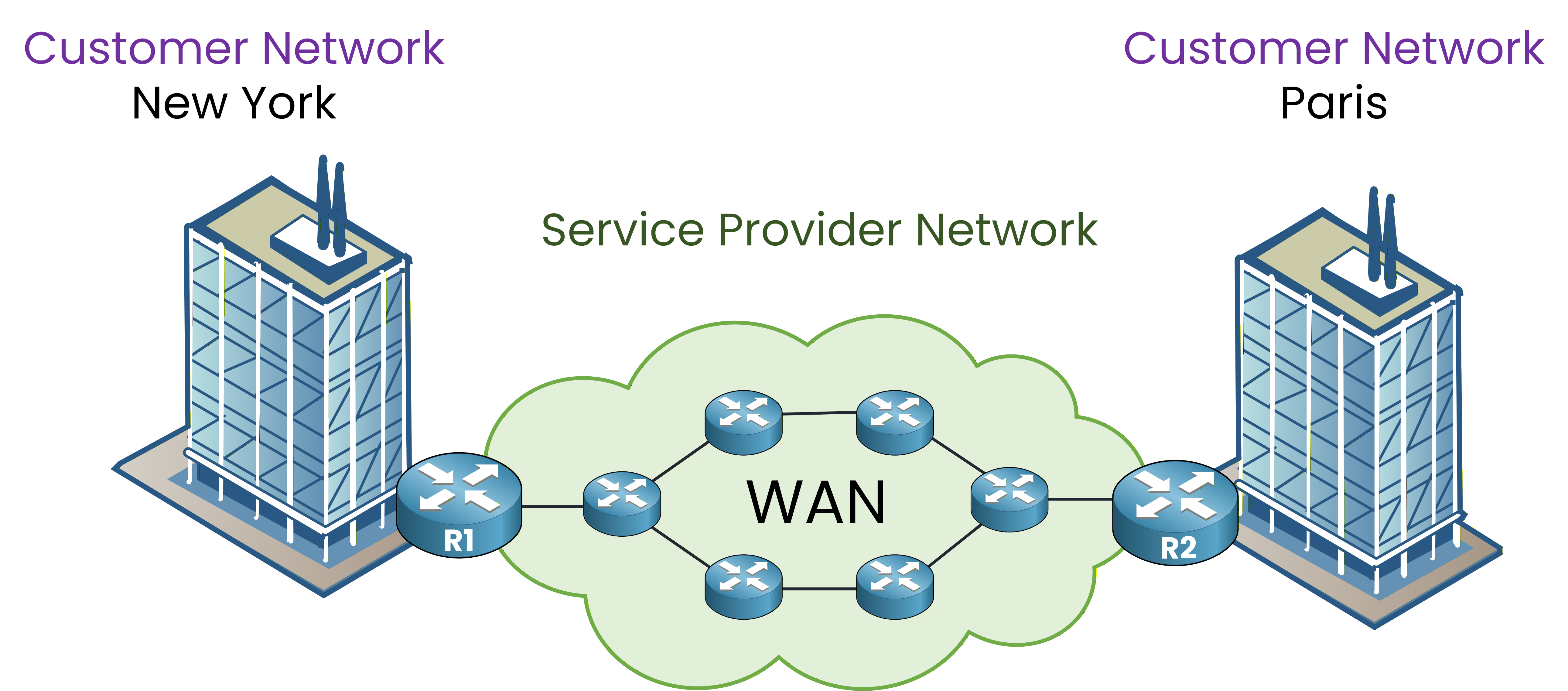
Figure 6 – The service provider network connects customer LANs across distant locations.
40 % Complete: you’re making great progress
Unlock the rest of this lesson
If you’d like to continue your CCNA journey, simply create your free account.
Access all CCNA lessons
Practice with hands-on labs
Train with Practice exams and Quizzes
Progress tracking in your dashboard
Made by network engineers - CCNP certified
learners globally