A trust boundary is the point in a network where traffic markings, such as DSCP (Layer 3) or Priority Code Point (PCP) / Class of Service (CoS) (Layer 2) are trusted.
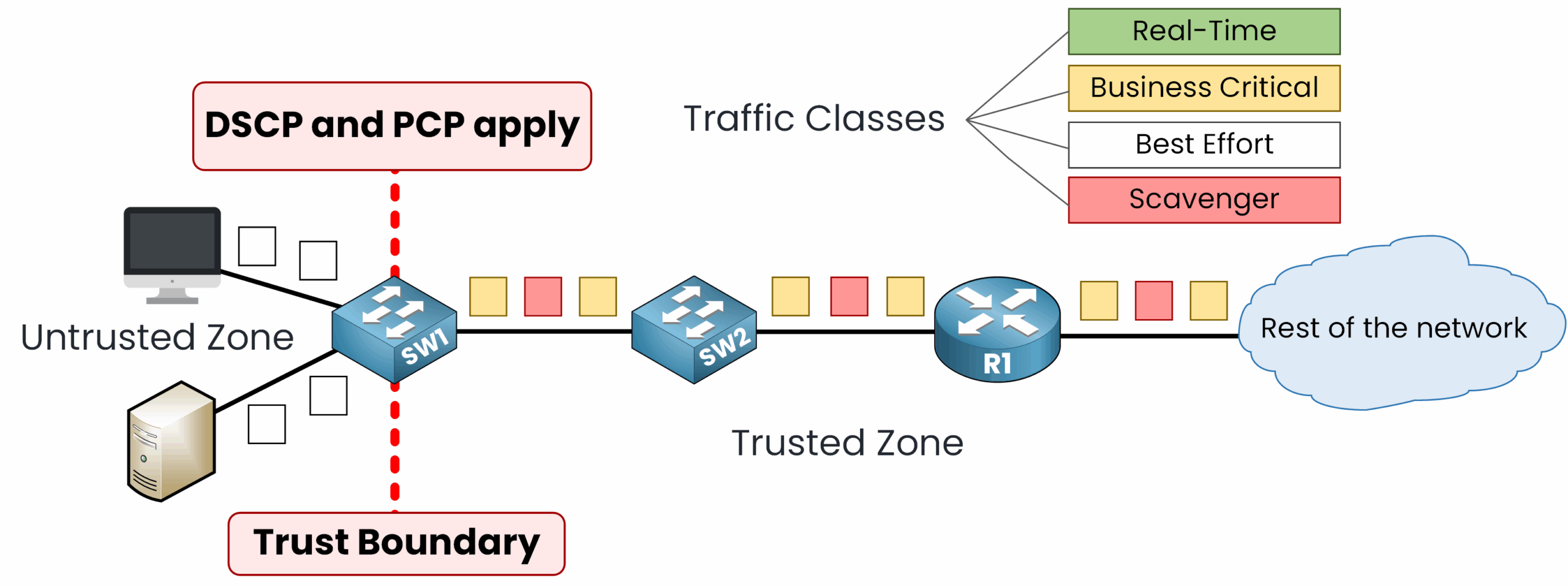
Figure 1 – The trust boundary is where DSCP and PCP markings are trusted
Beyond this point, the network devices rely on these markings to prioritize traffic based on Quality of Service (QoS) policy.
Why Trust Boundaries Are Needed
But here’s something to think about: What happens if a device outside your control marks its own traffic as high priority to gain an unfair advantage?
Traffic markings applied by devices outside the trust boundary are considered untrusted and will be re-marked to align with the network's policies. This ensures that only traffic from trusted devices influences network performance.
The trust boundary is established on devices controlled by IT, such as access layer switches or IP phones.
Answer the question below
When a PC sends traffic to an access switch, where is the first point where markings become trusted?
The trust boundary is typically placed on network devices where traffic markings can be verified and adjusted if needed. These devices must be fully controlled and managed by IT staff. Common locations for trust boundaries include:
Access Layer Switches: These devices receive traffic from end-user devices and re-mark it to align with network QoS policies.
Trust Boundary at the Access Switch
Imagine you’re managing a network where devices like PCs are directly connected to access switches. Would you trust the traffic markings coming from these PCs? Probably not, right? That’s where the access switch steps in as the trust boundary.
Here’s how it looks:
40 % Complete: you’re making great progress
Unlock the rest of this lesson
If you’d like to continue your CCNA journey, simply create your free account.
Access all CCNA lessons
Practice with hands-on labs
Train with Practice exams and Quizzes
Progress tracking in your dashboard
Made by network engineers - CCNP certified
learners globally
Trust Boundaries
In networking, a trust boundary defines the point where traffic markings like DSCP or CoS are verified and accepted as reliable. In this lesson, you’ll learn how trust boundaries prevent misuse of QoS markings and where they should be placed in real Cisco networks.