Terraform is an automation tool, but not the same kind of tool as Ansible.
To understand Terraform clearly, let’s start with a simple comparison.Terraform vs Ansible: key differences
You already know that Ansible is used to configure existing devices and maintain their configuration over time.
As shown in the figure below, Ansible connects to infrastructure that already exists and pushes configuration changes to it.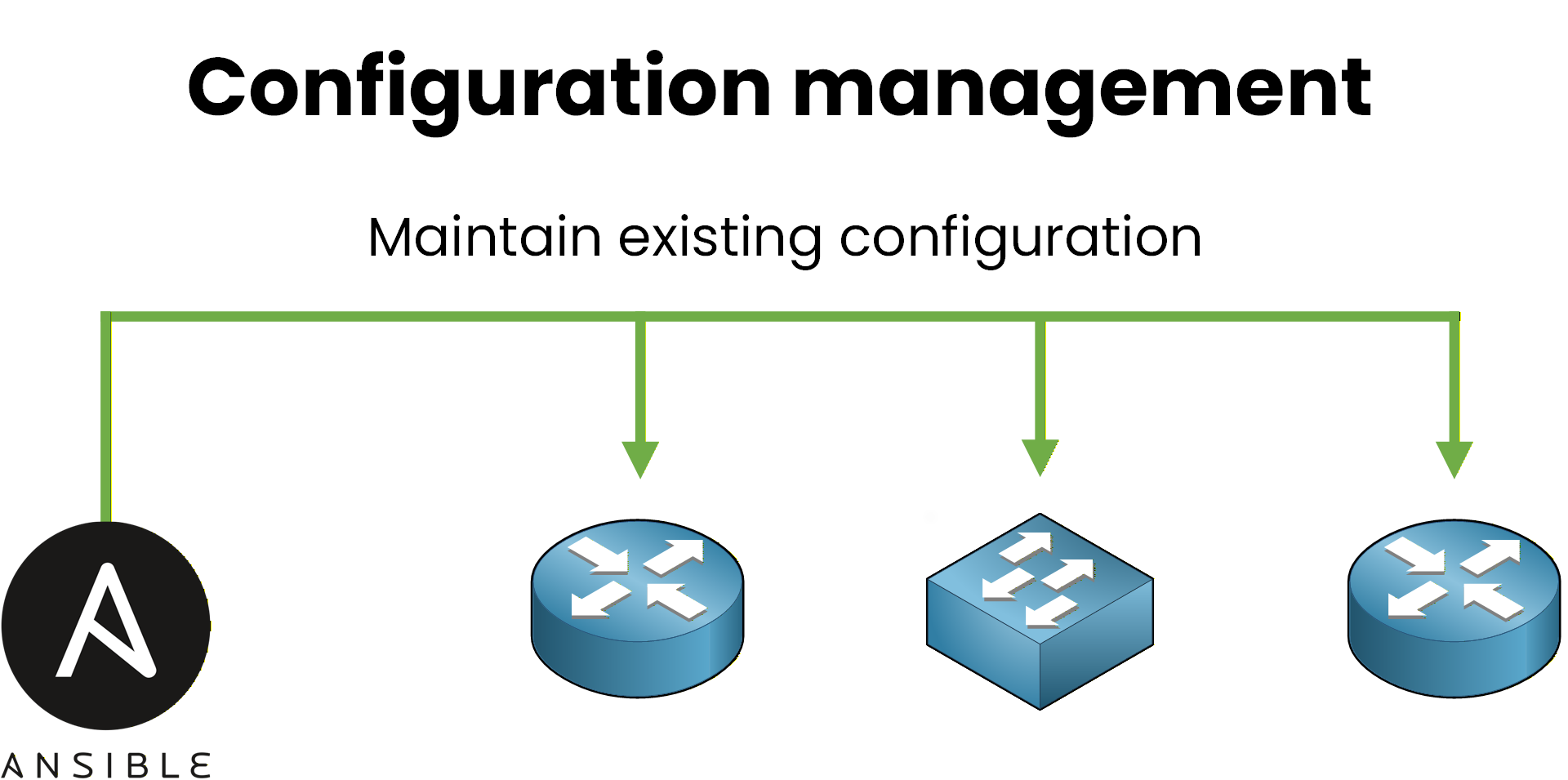
Figure 1 - Configuration management
Here is the key difference you must remember:
Ansible manages the configuration of existing infrastructure
Terraform creates the infrastructure resources
Yes, this can feel surprising at first.
Until now, you have always worked with infrastructure that already exists:
in the CLI, you connect to routers or switches that are already deployed
with Ansible, devices are already reachable on the network
Infrastructure provisioning with Terraform
With Terraform, the logic is different.
As shown in the figure below, Terraform allows you to describe the infrastructure you want before it even exists.
Figure 2 - Infrastructure provisioning
In this example, Terraform is used to create virtual machines, but the idea is broader.
Terraform is used to create infrastructure resources.Why Terraform matters for networking
It is important to clarify one thing: Terraform does not create physical routers or switches by itself.
Instead, it is mainly used in cloud and virtualized environments, where infrastructure and networking components can be created programmatically.At this point, you might be thinking:
“Okay, but why are we learning Terraform for the CCNA? What does this have to do with networking?”
The answer is that modern networks are increasingly deployed inside infrastructures that are built automatically, not only configured manually.
As a network engineer, you need to understand the difference between:
building infrastructure with Terraform
configuring and maintaining it with Ansible
For the CCNA, you are not expected to use Terraform to configure routers.
You are expected to understand when Terraform is used in a network workflow, and how it differs from configuration tools like Ansible.In the next section, we will break down how Terraform works step by step.
Answer the question below
Terraform is used to ______ infrastructure.
Terraform works differently from traditional configuration tools, so we will go through its logic step by step.
You do not need to become a Terraform expert for the CCNA.
You only need to understand how Terraform thinks and how the main components work together.Step 1 - Defining the desired state
It starts with the Network / Infrastructure Engineer.
The engineer writes Terraform configuration files.
These files describe the infrastructure Terraform should create.
Figure 3 - Desired state definition
These configuration files are written in HCL (HashiCorp Configuration Language).
For this course, you do not need to know how to write HCL, you only need to understand the idea:The configuration files define what you want
They represent the desired state of the infrastructure
In other words, they are your infrastructure requirements written as code.
Answer the question below
According to Figure 3, which element defines the desired state of the infrastructure in Terraform?
Step 2 - Comparing desired state with the current state
Terraform also uses a file called the state file.
The state file is Terraform’s record of the current infrastructure state, at a given moment.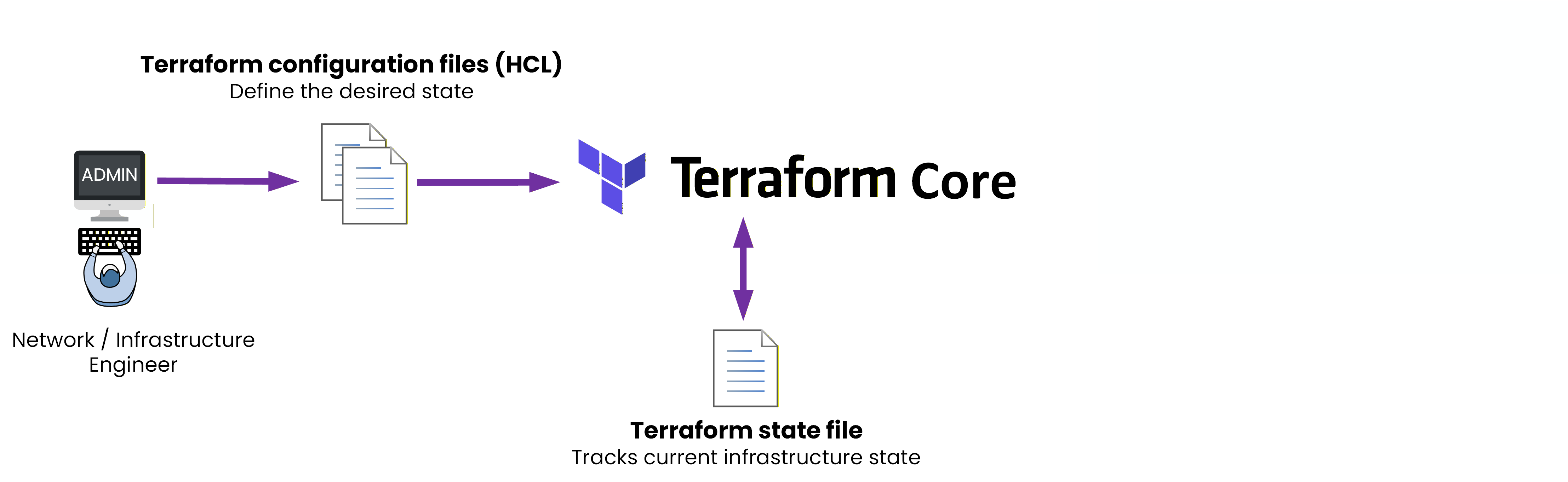
Figure 4 - State comparison logic
40 % Complete: you’re making great progress
Unlock the rest of this lesson
If you’d like to continue your CCNA journey, simply create your free account.
Access all CCNA lessons
Practice with hands-on labs
Train with Practice exams and Quizzes
Progress tracking in your dashboard
Made by network engineers - CCNP certified
learners globally