Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP), introduced in 1988 and declared in RFC 1157, is a protocol used for monitoring and managing devices on a network.
It allows network administrators to collect information about devices, monitor their status, and even control them remotely. SNMP simplifies the management of various devices like routers, switches, and servers.
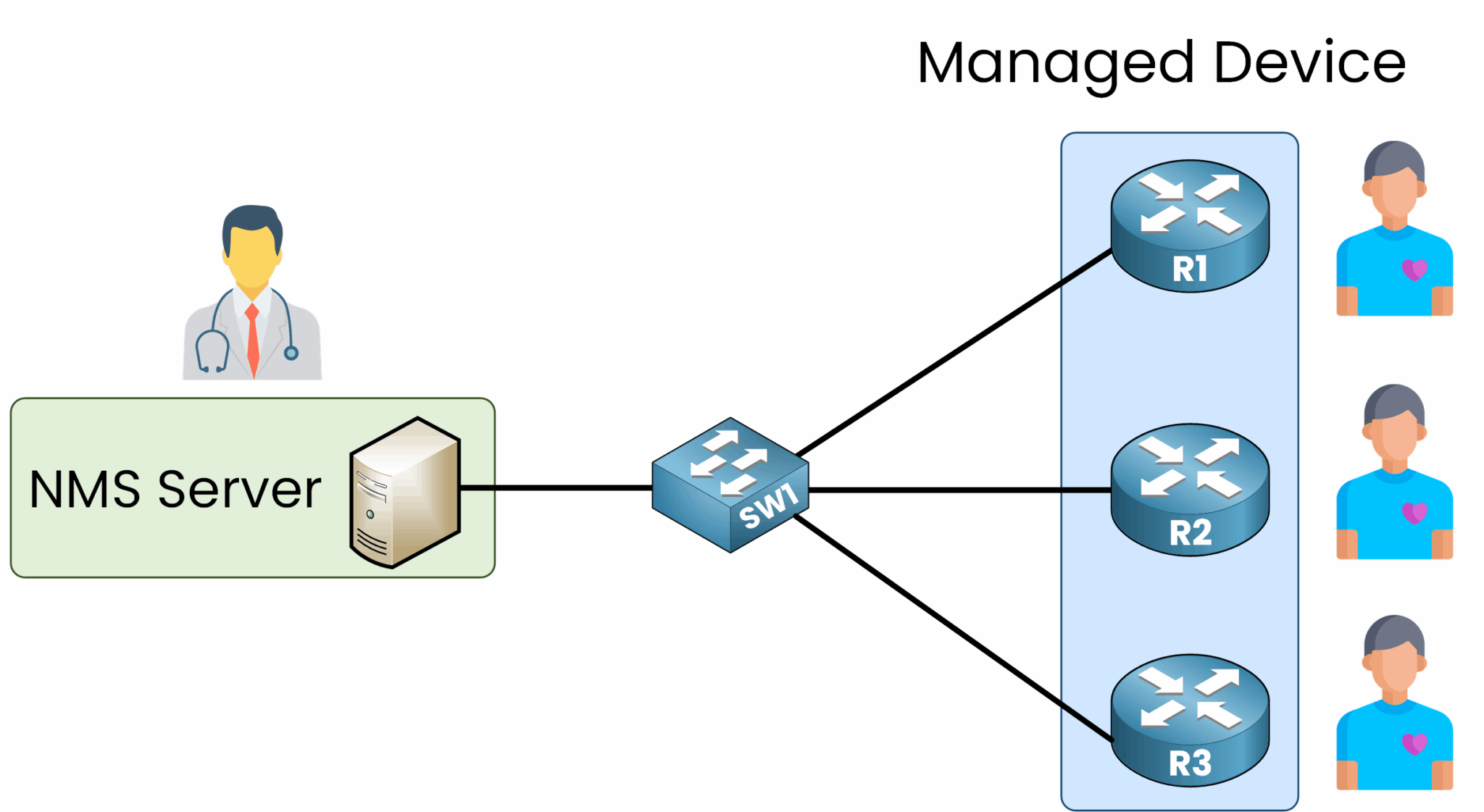
Figure 1 – SNMP Overview: Monitoring Network Devices
Think of the SNMP Server as a doctor monitoring the health of their patients (the network devices).
Purpose and Importance of SNMP in Networking
SNMP plays a vital role in ensuring the health and performance of a network. Its main benefits include:
Centralized Monitoring: Administrators can oversee the health of all devices from a single management station.
Example: An administrator can monitor the CPU usage of routers across the network from one tool.
Real-Time Alerts: SNMP sends immediate alerts (Traps) to notify administrators of critical events like a failed interface or high CPU usage.
Example: If a switch port goes down, the SNMP Manager receives an alert in real time, enabling quick action.
Remote Configuration: Administrators can modify device configurations without physical access.
Example: An administrator can change a router’s hostname remotely through the SNMP Manager.
Answer the question below
Which protocol is used for monitoring and managing devices on a network?
The NMS (Network Management Station) acts as the central system that communicates with network devices to monitor and manage them. It sends requests for data (such as CPU usage, memory, or traffic) and can issue commands to adjust configurations.
Each device runs an SNMP Agent that responds to these requests and can also generate alerts (Traps or Informs) to notify the Manager of critical events, such as an interface failure or high CPU usage.
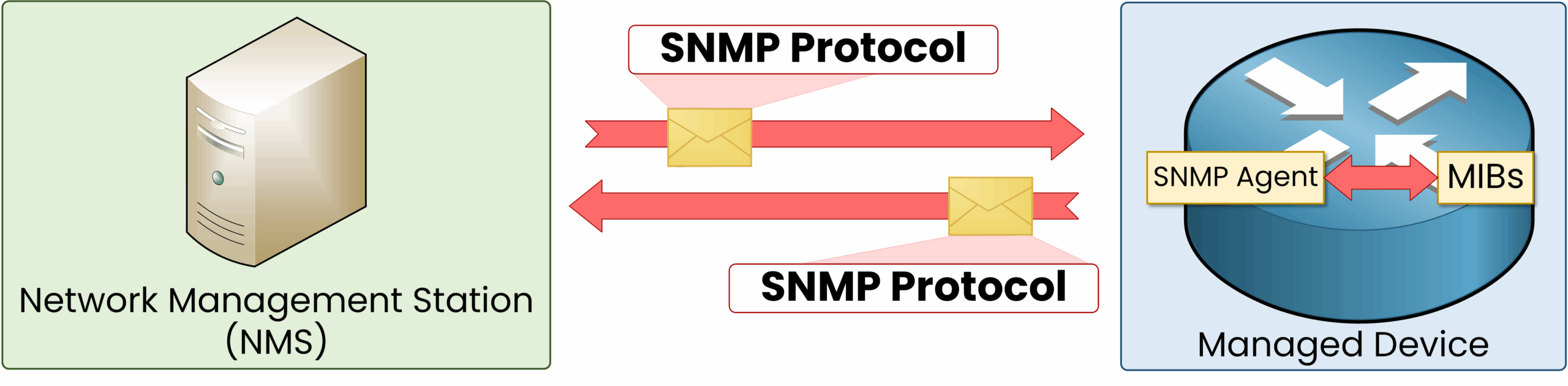
Figure 2 – SNMP Architecture and Protocol Flow
As you can see above, the NMS can communicate with this router by using the SNMP protocol.
To make this exchange possible, device information must be structured and accessible. This is where the Management Information Base (MIB) comes into play.
Management Information Base (MIB)
The MIB is a hierarchical database that organizes device information accessible via SNMP. It serves as a reference for retrieving or updating network metrics and configurations.
Structure:
Organized in a tree-like hierarchy
Standardized branches store general data such as system uptime
Vendor-specific branches (e.g., Cisco-specific metrics) provide manufacturer-specific information
Example MIB Tree
MIB-2 (1.3.6.1.2.1) ├── system (1) // General device information │ ├── sysDescr (1.3.6.1.2.1.1.1) // Device description │ ├── sysUpTime (1.3.6.1.2.1.1.3) // Device uptime ├── interfaces (2) // Network interfaces │ ├── ifNumber (1.3.6.1.2.1.2.1) // Number of interfaces │ └── ifTable (1.3.6.1.2.1.2.2) └── enterprises (4.1) └── Cisco (9) // Vendor-specific dataThe MIB enables consistent device management by defining where each type of data (CPU usage, memory status, interface count, etc.) is stored. This standardization ensures compatibility across devices from different vendors.
Object Identifiers (OIDs)
OIDs are unique numerical addresses used to identify data points in the MIB. You can think of an OID as the precise address that points to a specific piece of information.
Format: Dot-separated sequence (e.g.,
1.3.6.1.2.1.1.3for system uptime). Each level in the sequence represents a branch in the MIB tree.
Role in SNMP: The Manager sends requests that reference OIDs. The Agent retrieves the corresponding value from the MIB and sends it back.
Example: Retrieving Uptime with an OID
A network administrator wants to check the uptime of a router.
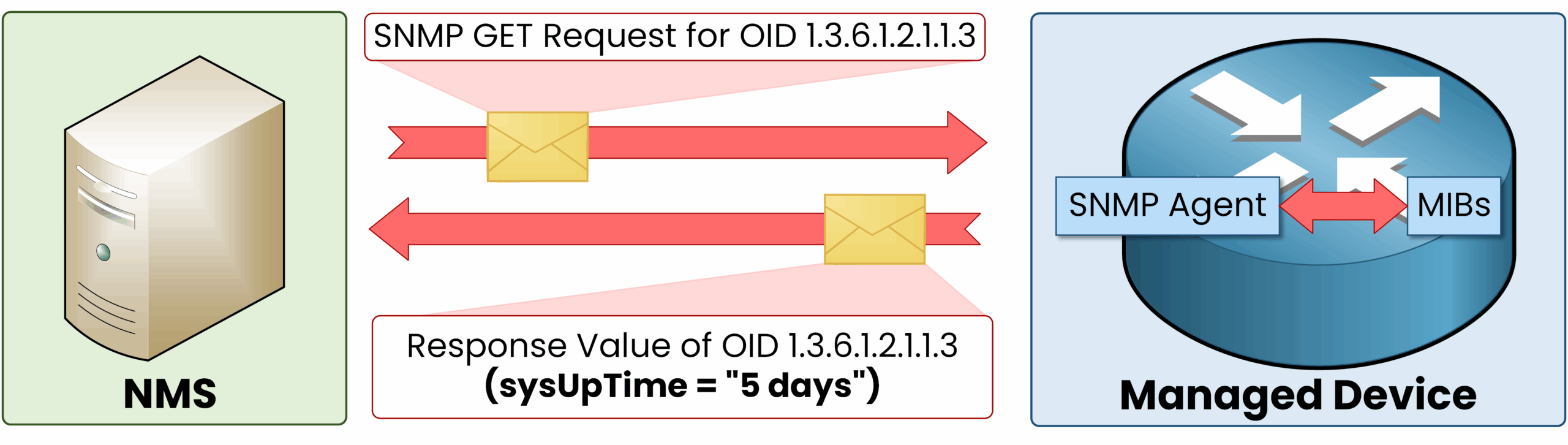
Figure 3 – Example: Retrieving Uptime Using an SNMP OID
The SNMP Manager sends a Get Request for OID 1.3.6.1.2.1.1.3.
The SNMP Agent on the router looks up the corresponding value in its MIB.
The Agent replies with the uptime, which the Manager displays for analysis.
This ensures precise and efficient monitoring across network devices.
Answer the question below
What database stores device information for SNMP?
SNMP allows the Manager to interact with network devices through their Agents. SNMPv1 relies on four essential message types. Other types exist, but they will be introduced when we cover SNMPv2 and SNMPv3.
SNMP Message Types
Get – Retrieves specific information from an SNMP Agent.
GetNext – Retrieves the next item in a list, useful for tables.
Set – Modifies a configuration parameter remotely.
Trap – Sends an alert when a critical event occurs.
SNMP Get Request
The Get Request is the most common operation. It is initiated by the SNMP Manager to retrieve specific data from an Agent, such as device status, CPU load, memory usage, or interface statistics.
40 % Complete: you’re making great progress
Unlock the rest of this lesson
If you’d like to continue your CCNA journey, simply create your free account.
Access all CCNA lessons
Practice with hands-on labs
Train with Practice exams and Quizzes
Progress tracking in your dashboard
Made by network engineers - CCNP certified
learners globally
Introduction to SNMP
Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) is widely used in real networks to monitor device health, receive alerts, and apply remote changes. In this lesson, you will learn step-by-step how SNMP works in practice and why it remains central to network management.