Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol (RSTP), defined in IEEE 802.1w, is an enhanced version of the original Spanning Tree Protocol (STP).
Its goal is simple:
reduce convergence time.While STP can take up to 50 seconds to recover from a topology change, RSTP reduces this to a few hundred milliseconds.
Before enabling RSTP, let’s check which Spanning Tree mode the switch is currently running.RSTP on Cisco Switches
On Cisco switches, RSTP is implemented as Rapid-PVST+.
This means:
The protocol is based on IEEE 802.1w (RSTP)
It runs one spanning tree instance per VLAN
Each VLAN has its own independent Rapid Spanning Tree
So instead of having a single spanning tree for the whole switch, Cisco runs:
VLAN 1 → RSTP instance VLAN 10 → RSTP instance VLAN 20 → RSTP instance ...Each VLAN converges independently and rapidly.
Enabling Rapid-PVST
Let’s enable RSTP on the switch.
SW2# conf t Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z. SW2(config)# spanning-tree mode rapid-pvst SW2(config)# endVerifying the Mode
SW2# show spanning-tree summary Switch is in rapid-pvst mode Root bridge for: VLAN0001 Extended system ID is enabled Portfast Default is disabled Portfast Edge BPDU Guard Default is disabled Portfast Edge BPDU Filter Default is disabled Loopguard Default is disabled PVST Simulation Default is enabled but inactive in rapid-pvst mode Bridge Assurance is enabled EtherChannel misconfig guard is enabled Configured Pathcost method used is short UplinkFast is disabled BackboneFast is disabled Name Blocking Listening Learning Forwarding STP Active ---------------------- -------- --------- -------- ---------- ---------- VLAN0001 8 0 0 0 8 ---------------------- -------- --------- -------- ---------- ---------- 1 vlan 8 0 0 0 8The switch is now running in rapid-pvst mode, which confirms that RSTP is enabled.
On Cisco switches, RSTP is implemented as Rapid-PVST+, which means:
It runs one spanning tree instance per VLAN
Each VLAN has its own independent Rapid Spanning Tree
Faster convergence applies independently to each VLAN
In our current topology:
Only VLAN 1 exists
The output shows VLAN0001
This confirms that Rapid-PVST+ is active for VLAN 1.
If additional VLANs were created (for example VLAN 10 or VLAN 20), each VLAN would automatically run its own Rapid Spanning Tree instance.
Answer the question below
What is the main advantage of RSTP over STP?
RSTP simplifies the port states used in STP by merging some of them:
STP vs. RSTP Port States
Listening is not a port state included in RSTP, it goes right from discarding to learning.
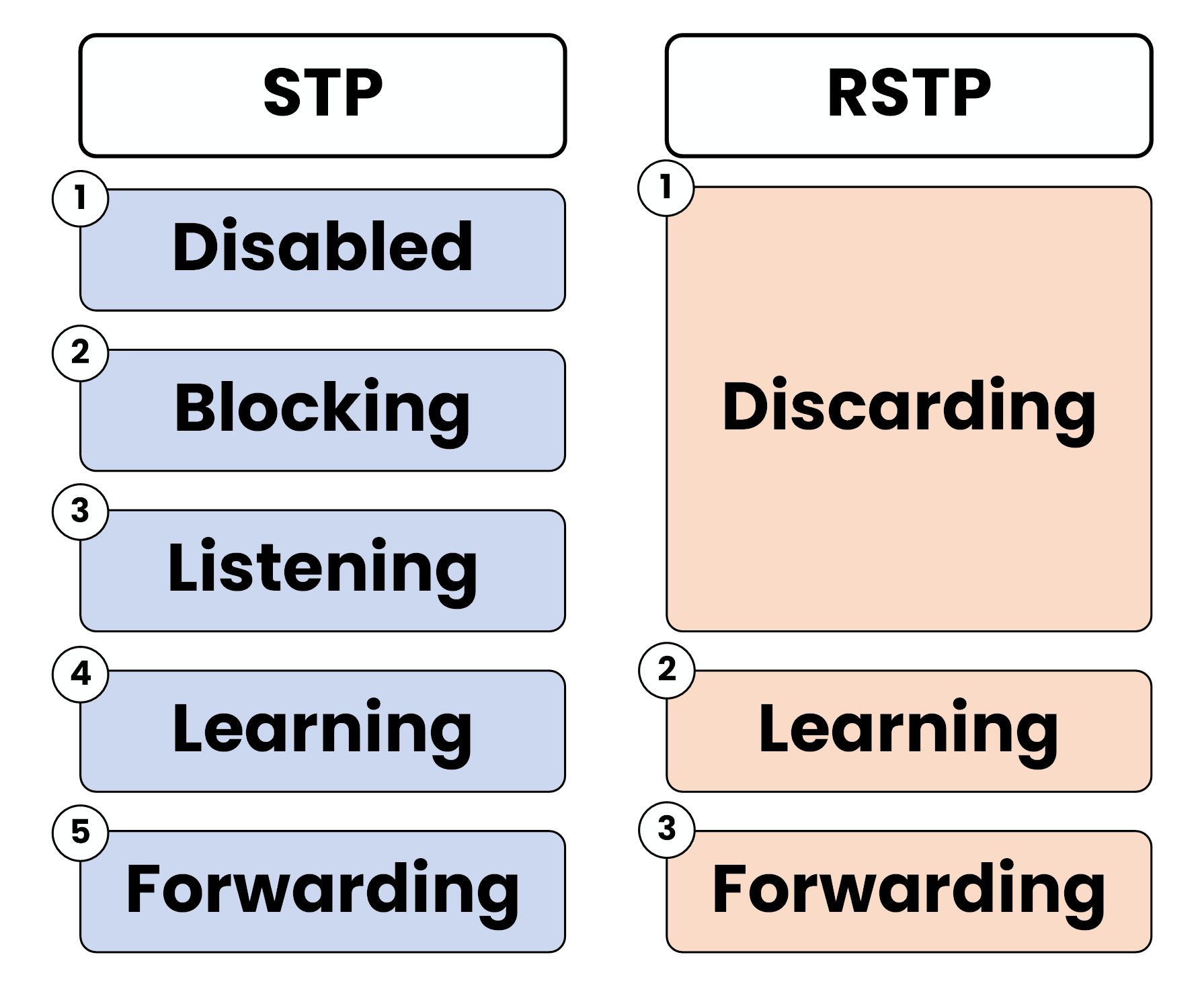
Figure 1 – Comparison of STP and RSTP Port States
Answer the question below
Which RSTP state replaces Blocking, Listening, and Disabled?
While STP defines two primary port roles root and designated ports.
RSTP introduces two additional roles:
Alternate Port: Provides an alternative path to the root bridge.
Example: A redundant connection between switches remains ready for use if the primary link fails.
Backup Port: Acts as a backup for a shared medium like a hub.
Note: This role is less common today due to the rarity of hubs in modern networks.
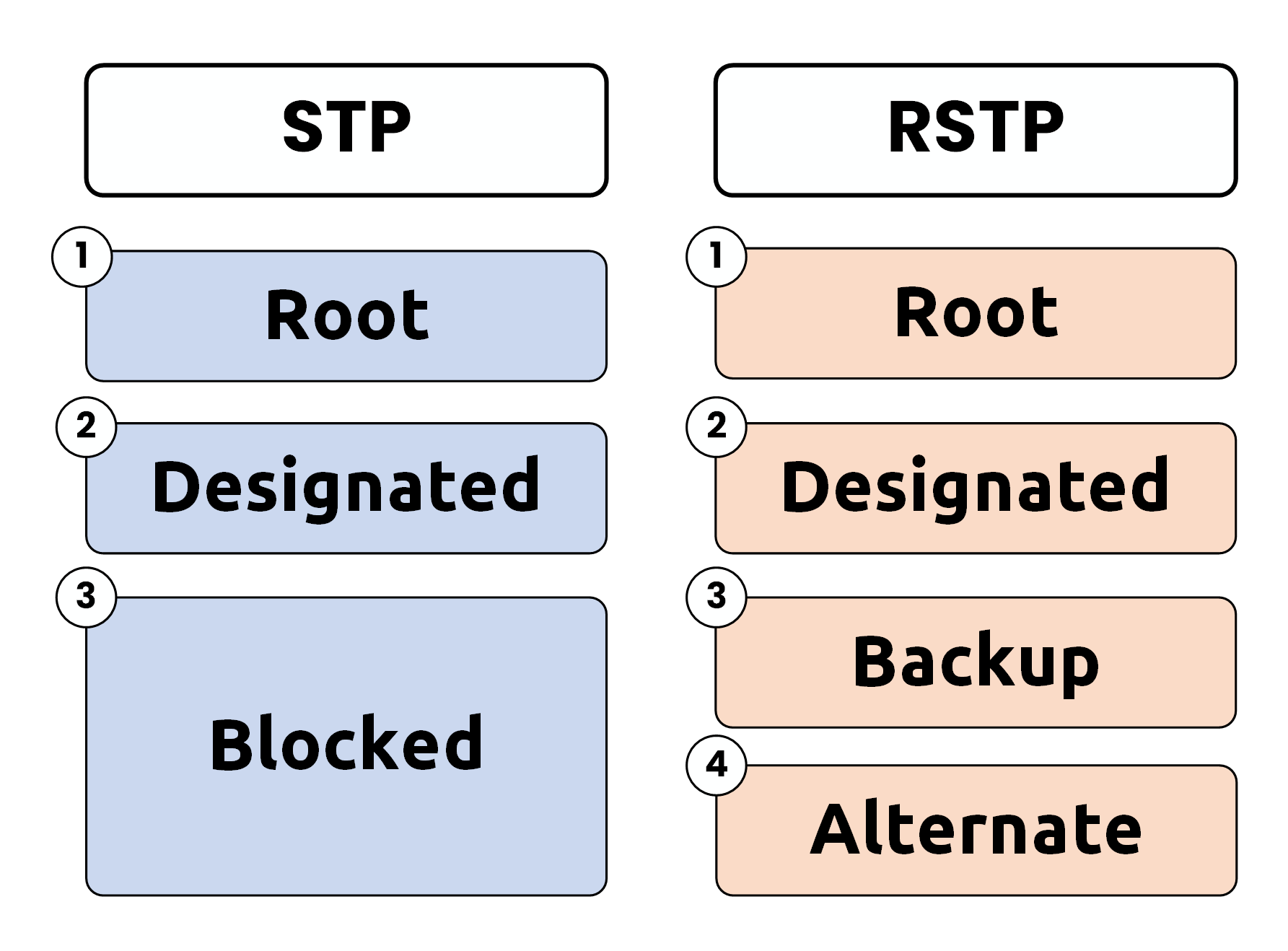
Figure 2 – Comparison of STP and RSTP Port Roles
40 % Complete: you’re making great progress
Unlock the rest of this lesson
If you’d like to continue your CCNA journey, simply create your free account.
Access all CCNA lessons
Practice with hands-on labs
Train with Practice exams and Quizzes
Progress tracking in your dashboard
Made by network engineers - CCNP certified
learners globally
Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol (RSTP)
Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol (RSTP) is an evolution of STP that dramatically reduces convergence time, making networks more resilient to failures. In this lesson, you’ll see how RSTP improves port states and roles to deliver faster recovery and stability.