RADIUS stands for Remote Authentication Dial-In User Service. It is a AAA protocol (Authentication, Authorization, and Accounting) developed by the Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF). RADIUS is widely used to manage secure access to network devices across different platforms and vendors.
Purpose of RADIUS
The main purpose of RADIUS is to verify the identity of users trying to log in. Instead of managing user accounts on each device, RADIUS centralizes access control, which simplifies administration across the network.
Client-Server Model
RADIUS works on a client-server architecture:
RADIUS Client → the device (such as a router or switch) where the user logs in. It forwards credentials to the server.
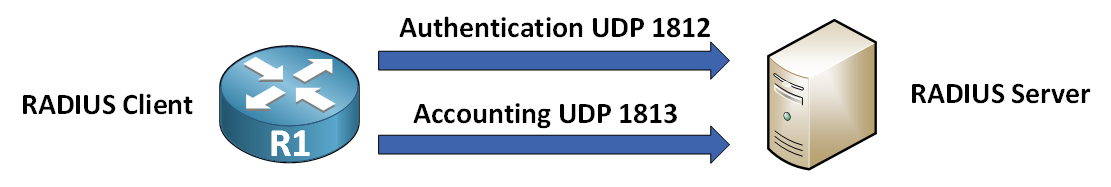
Figure 1 – RADIUS client-server model
RADIUS Server → the system that verifies those credentials and decides whether to accept or reject the connection.
RADIUS communicates using UDP as its transport protocol, with:
Authentication → Port 1812
Accounting → Port 1813
Older systems may still rely on legacy ports 1645/1646, but modern implementations use 1812/1813.
⚠️ One important limitation: RADIUS only encrypts passwords during transmission. Other data, such as usernames or session details, are sent in plain text. For highly secure networks, TACACS+ is often preferred because it encrypts all communication.
Answer the question below
Which transport protocol does RADIUS use for communication?
Now that we understand the basics, let’s see how RADIUS handles authentication and authorization.
Combined Authentication and Authorization
With RADIUS, these two steps happen at the same time. When a user attempts to log in, the RADIUS server verifies their credentials and immediately sends back the access permissions.
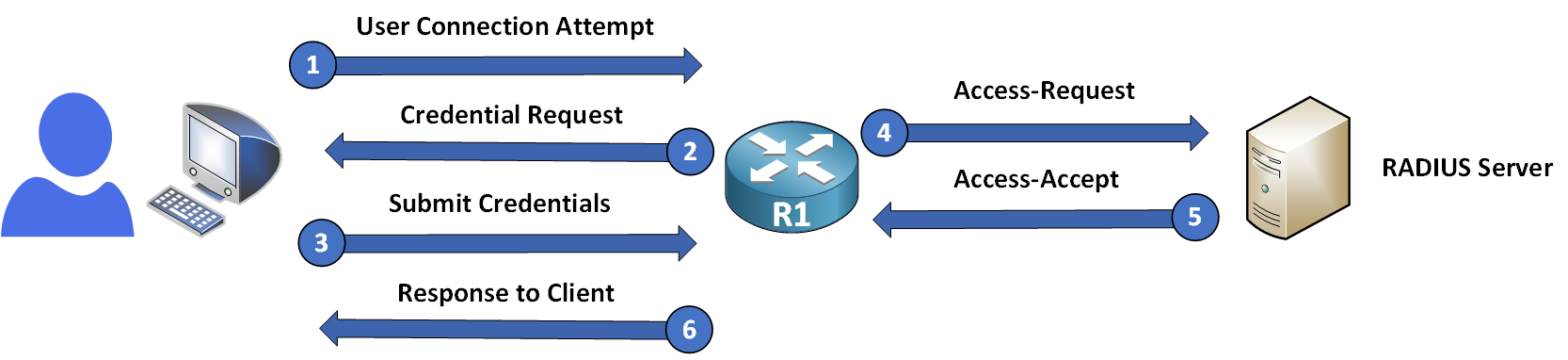
Figure 2 – RADIUS authentication and authorization workflow
Authentication Workflow
The typical workflow is as follows:
Access-Request → The RADIUS client forwards the credentials to the server.
Access-Accept / Access-Reject → The server approves or denies access depending on the credentials.
Access-Challenge → In some cases, the server may require extra verification (such as a one-time password).
Answer the question below
When a user’s credentials are correct, what message does the RADIUS server return?
RADIUS also plays a role in authorization and accounting, but with some limitations.
Authorization
The server grants access permissions at the moment of authentication. However, RADIUS does not allow fine-grained control over individual commands, only user-level permissions are supported.
Accounting
RADIUS keeps track of user sessions through accounting logs. It can record:
When users log in and log out
How long they remain connected
How much data they use
But unlike TACACS+, it does not log specific commands, making it less useful for detailed auditing.
40 % Complete: you’re making great progress
Unlock the rest of this lesson
If you’d like to continue your CCNA journey, simply create your free account.
Access all CCNA lessons
Practice with hands-on labs
Train with Practice exams and Quizzes
Progress tracking in your dashboard
Made by network engineers - CCNP certified
learners globally
RADIUS
Centralized authentication is essential when multiple devices need consistent and secure access control. In this lesson, you’ll see how RADIUS supports AAA services, ensures scalable management, and how it’s configured on Cisco networks.