Private IPv4 addressing were introduced as a solution to a major issue: the exhaustion of public IPv4 addresses.
Back in 1981, the IPv4 Public Address space was designed with about 4.3 billion unique addresses. At that time, the creators of the Internet did not anticipate how massive adoption would become.Over the years, public IPv4 addresses managed by IANA and the Regional Internet Registries (RIRs) allocated worldwide. As more networks and devices were deployed, the number of available public addresses kept shrinking.
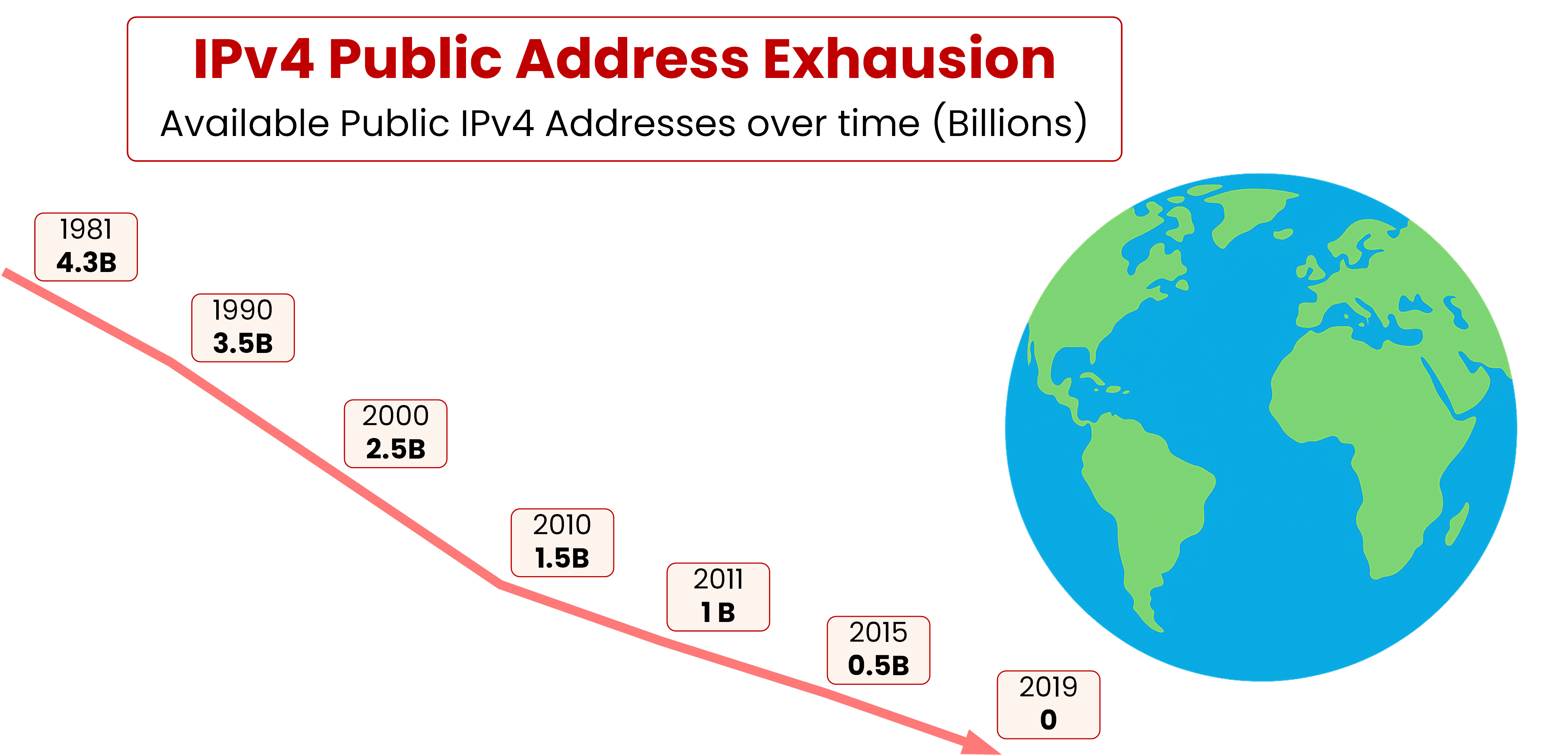
Figure 1 – IPv4 Public Address Exhaustion Curve
By the early 1990s, engineers realized that the public IPv4 space would not be sufficient.
To slow down this depletion, several measures were introduced:
1993 – CIDR (Classless Inter-Domain Routing): allowed more flexible allocation of addresses.
1996 – RFC 1918 (Private IPv4 Addresses): reserved specific ranges for internal networks to avoid wasting public addresses.
Despite these measures, the IPv4 public pool eventually ran out and was officially exhausted in 2019.
Answer the question below
What problem did private IPv4 addresses help slow down?
Private IPv4 addresses were formally defined in RFC 1918 (1996) by the IETF (Internet Engineering Task Force).
They are special IPv4 ranges reserved exclusively for internal networks such as homes, enterprises, and campuses.
The introduction of private addressing changed the way internal networks were designed and organized. Instead of consuming valuable public IP space, organizations could freely use private ranges for their internal devices. This helped preserve the limited pool of public IPv4 addresses.
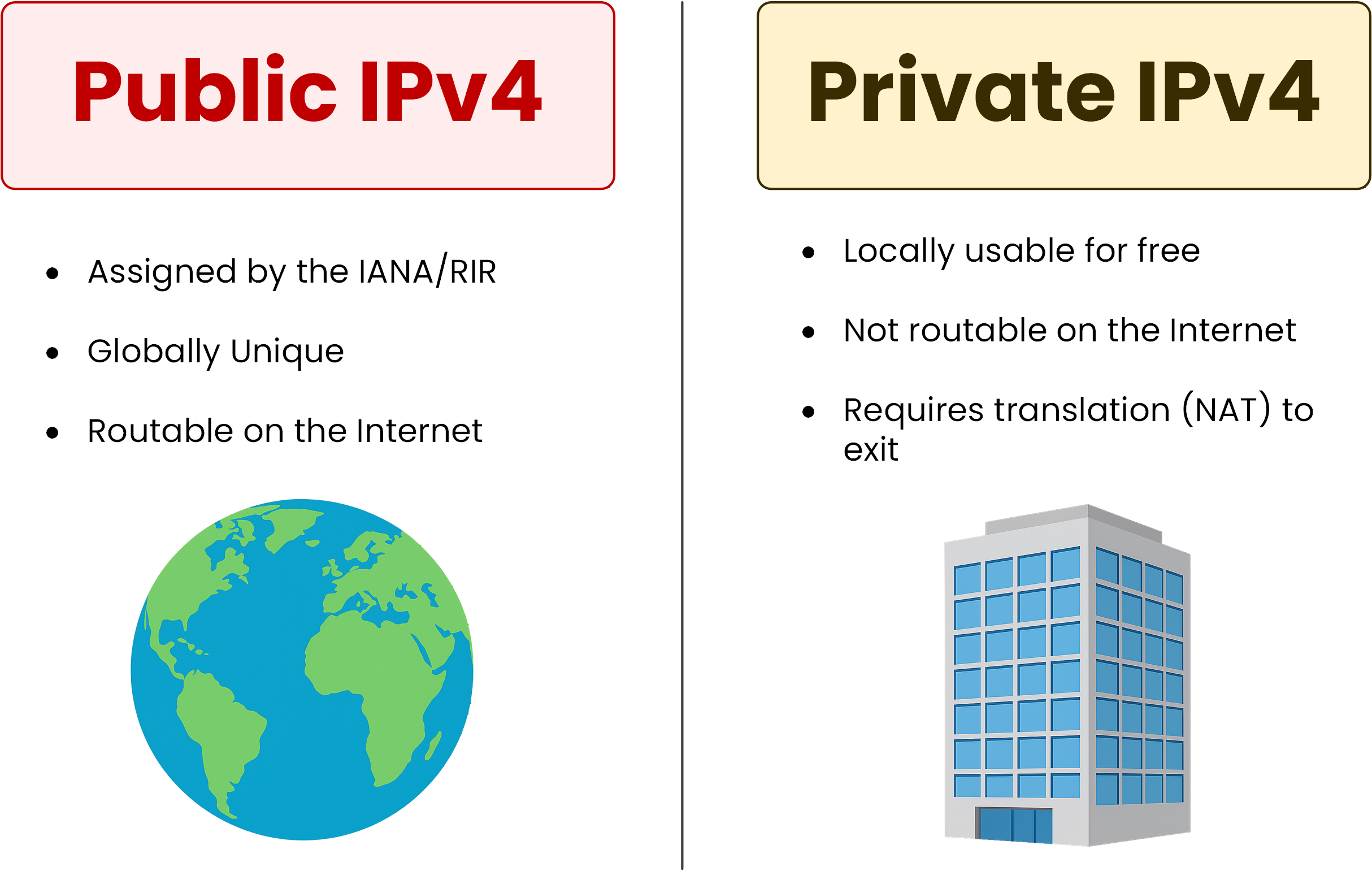
Figure 2 – Comparison between Public IPv4 and Private IPv4 Addresses
Advantages of Private IPv4 Addresses
Cost savings – no need to purchase or request public IPs for internal devices.
Security by isolation – private IPs are not reachable from the Internet.
Flexibility – the same ranges can be reused by different organizations without conflict.
Answer the question below
Which RFC defines private IPv4 addresses?
The RFC 1918 standard defines three reserved ranges for private use:
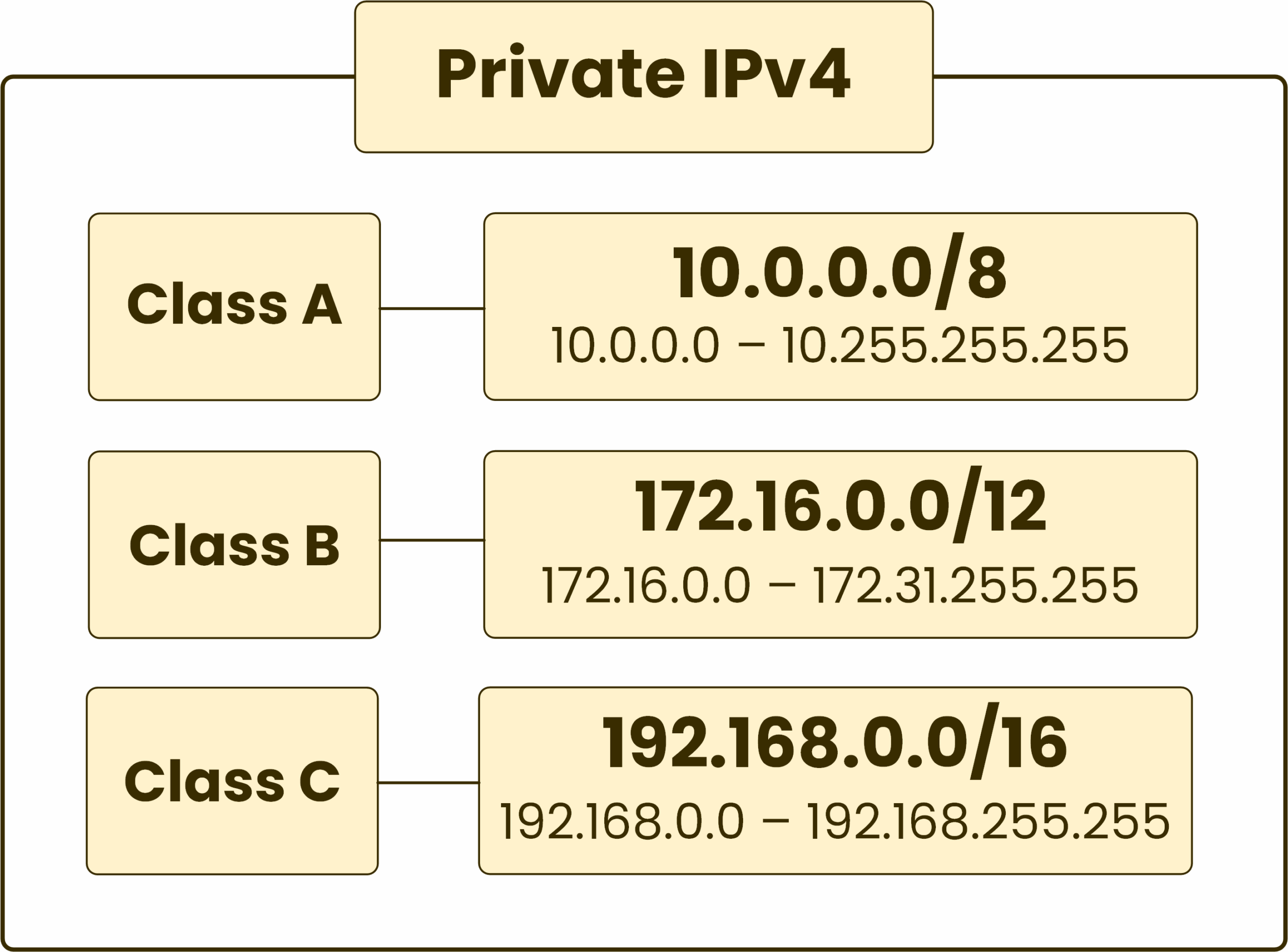
Figure 3 – RFC 1918 Reserved for Private IPv4 Addressing
40 % Complete: you’re making great progress
Unlock the rest of this lesson
If you’d like to continue your CCNA journey, simply create your free account.
Access all CCNA lessons
Practice with hands-on labs
Train with Practice exams and Quizzes
Progress tracking in your dashboard
Made by network engineers - CCNP certified
learners globally
Private IPv4 Addressing (RFC1918)
Private IPv4 addresses are special ranges defined in RFC 1918 to allow internal networks to function without consuming limited public IPv4 space. In this lesson, you’ll see why they were introduced, how they are used in real networks, and why NAT is required for Internet access.