Power over Ethernet (PoE) is a networking technology that allows a single Ethernet cable to carry both data and electrical power.

Figure 1 – Power over Ethernet supplying a VoIP phone
It is mainly used to power VoIP phones, IP cameras, wireless access points, and IoT devices, all through the same cable that provides their network connection.
Benefits of PoE in Networking
Cost efficiency – no need to install electrical outlets next to each device.
Simplified cabling – one cable for both power and data.
Flexible placement – devices can be installed in areas without nearby power sources.
Centralized management – administrators can reboot or control power directly from the switch.
Answer the question below
IEEE 802.3af (PoE)
Introduced in 2003, this standard provides up to 15.4 watts of DC power per port from the Power Sourcing Equipment (PSE), with about 12.95 watts available at the Powered Device (PD) after cable loss. It is suitable for low-power equipment such as basic VoIP phones or small wireless access points.
IEEE 802.3at (PoE+)
Introduced in 2009, PoE+ increased the available power to 30 watts per port, with 25.5 watts reaching the PD. This improvement supports devices that require more energy, such as IP cameras with pan, tilt, and zoom (PTZ) functions.
IEEE 802.3bt (UPoE and UPoE+)
The most recent standard extends power delivery by using all four wire pairs of the Ethernet cable. In Type 3 (UPoE), it can supply up to 60 watts per port, which is suitable for video conferencing systems or larger wireless access points. In Type 4 (UPoE+), it delivers up to 100 watts per port, making it possible to power advanced devices such as interactive displays and high-consumption IoT systems.
Standard
Year Introduced
Power at PSE (per port)
Power at PD (usable)
Typical Devices
IEEE 802.3af (PoE)
2003
15.4W
12.95W
Basic VoIP phones, small wireless APs
IEEE 802.3at (PoE+)
2009
30W
25.5W
PTZ cameras, more demanding APs
IEEE 802.3bt Type 3 (UPoE)
2018
60W
~51W
Video conferencing systems, large APs
IEEE 802.3bt Type 4 (UPoE+)
2018
100W
~71–90W
Interactive displays, advanced IoT devices
Table 1 – Comparison of PoE Standards
Answer the question below
Which PoE standard delivers up to 30 watts at the port?
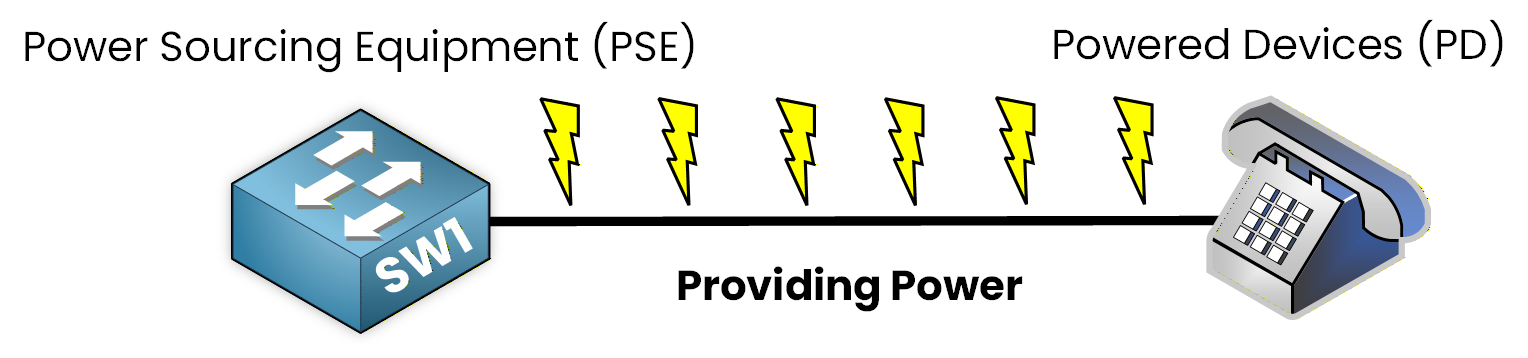
Figure 2 – Components of Power over Ethernet (PoE)
40 % Complete: you’re making great progress
Unlock the rest of this lesson
If you’d like to continue your CCNA journey, simply create your free account.
Access all CCNA lessons
Practice with hands-on labs
Train with Practice exams and Quizzes
Progress tracking in your dashboard
Made by network engineers - CCNP certified
learners globally
Power Over Ethernet (PoE)
Power over Ethernet (PoE) lets one cable carry both power and data. In this lesson, you’ll see how it powers phones, cameras, and access points without extra adapters.