In a Local Area Network (LAN), each device is identified by a MAC address.
Each Device Has Its Own MAC Address
Here, you can see three PCs connected to the same network.
Each of them has a different MAC address.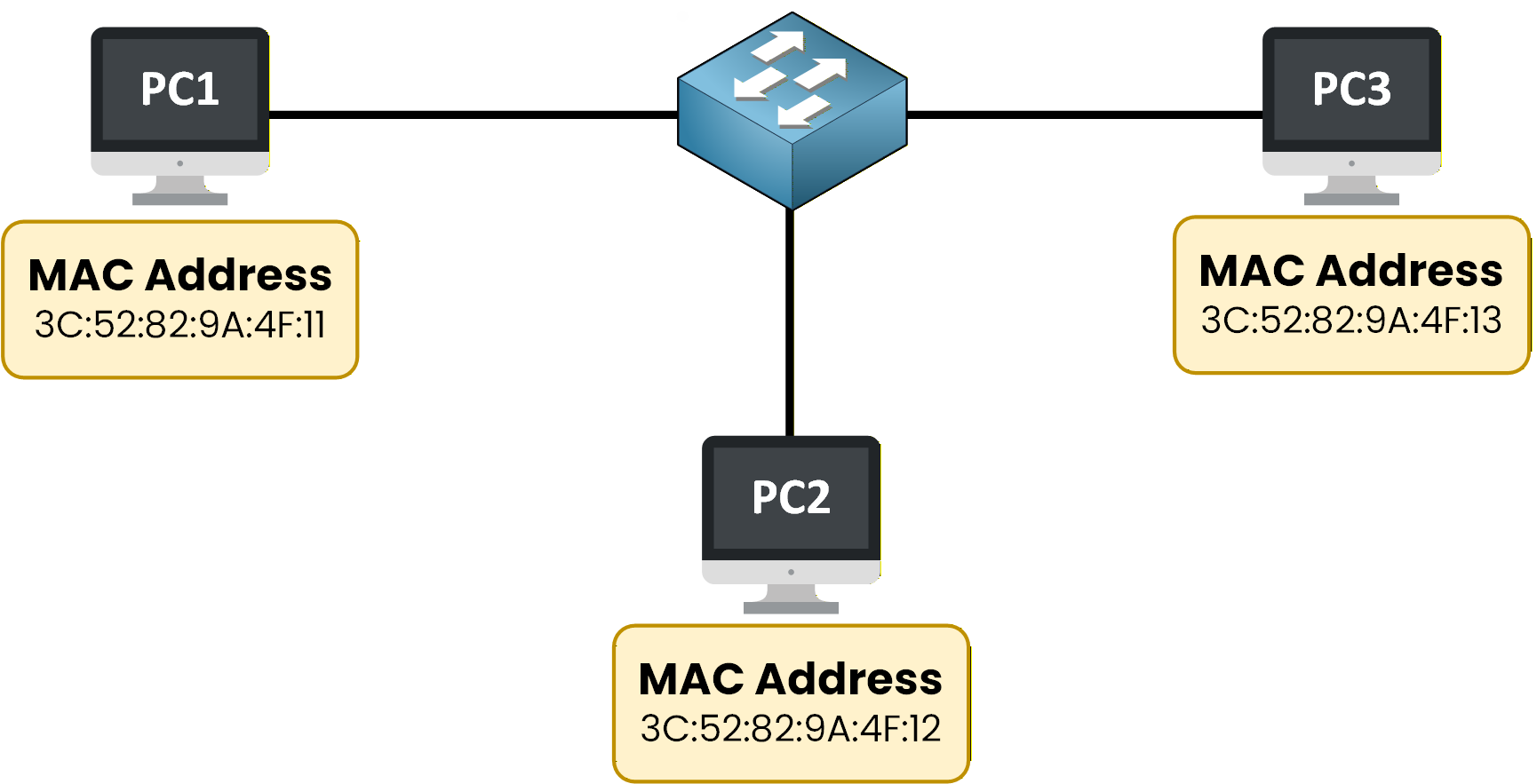
Figure 1 – Devices in a LAN identified by their MAC addresses
To confirm this, we can check the switch’s MAC address table:
SW1# show mac address-table Mac Address Table ------------------------------------------- Vlan Mac Address Type Ports ---- ----------- -------- ----- 1 3c52.829a.4f11 dynamic Fa0/1 1 3c52.829a.4f12 dynamic Fa0/2 1 3c52.829a.4f13 dynamic Fa0/3This output shows that:
Each device has a unique MAC address
The switch has learned these addresses automatically
Each MAC address is associated with a specific switch port
For example:
PC1 is connected to Fa0/1
PC2 is connected to Fa0/2
PC3 is connected to Fa0/3
On each computer, there is at least one network interface, and each network interface has a unique MAC address.
You may be curious about MAC addresses. Their format may seem unusual.
There is a reason behind this design.Let’s continue so you can learn more.
Answer the question below
What address is used to uniquely identify a device in a local network?
Let’s take the MAC address of PC1 as an example.
MAC Address Example
As you can see, a MAC address is made up of numbers and letters.

Figure 2 – MAC address Example
We can also confirm this directly from the computer itself.
On Windows, the MAC address can be displayed using:C:\> ipconfig /all Windows IP Configuration Ethernet adapter Ethernet: Description . . . . . . . . . . : Intel(R) Ethernet Connection Physical Address. . . . . . . . : 3C-52-82-9A-4F-11 DHCP Enabled. . . . . . . . . . : Yes IPv4 Address. . . . . . . . . . : 192.168.1.10 Subnet Mask . . . . . . . . . . : 255.255.255.0 Default Gateway . . . . . . . . : 192.168.1.1You may notice that Windows uses hyphens (-) instead of colons (:), but it represents the exact same address.
Understanding the Structure
This format may look unusual at first, but it follows a precise structure designed to ensure uniqueness.
To understand why it is written this way, let’s take a closer look at how a MAC address is built.MAC Address Structure
A MAC address is divided into two well-defined parts.
Organizationally Unique Identifier (OUI)
Network Interface Controller (NIC)
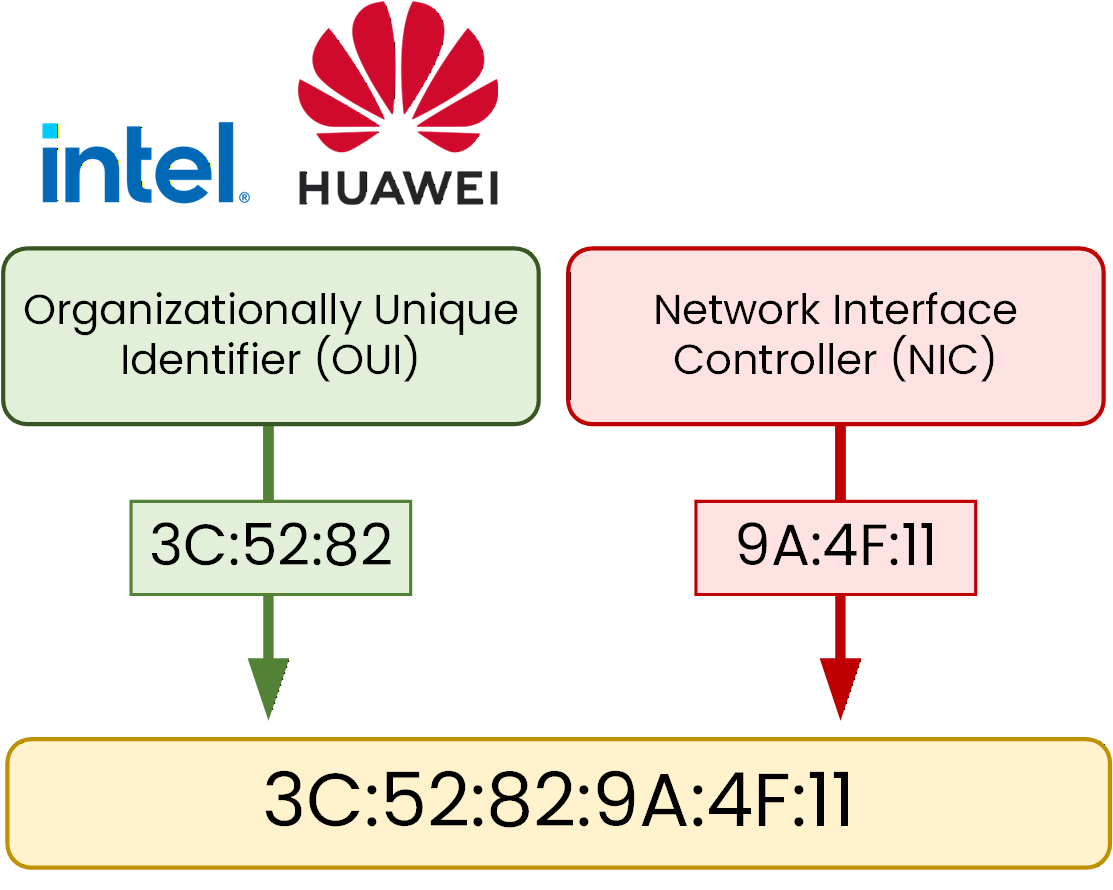
Figure 3 – MAC address structure with OUI and NIC
Organizationally Unique Identifier (OUI)
As shown in Figure 3, the OUI represents the manufacturer of the network interface.
This part is important because:
It is assigned by the IEEE
Each manufacturer receives one or more specific address blocks
It allows you to identify which company produced the interface
In this example, the OUI 3C:52:82 belongs to Huawei.
When you see an OUI, you can often determine the manufacturer of a device just by looking at the first part of its MAC address.
Answer the question below
What does the OUI identify?
Network interface Controller (NIC)
The NIC is the second part of the MAC address.
This part is assigned by the manufacturer itself.
It identifies a specific network interface
It differentiates interfaces produced by the same manufacturer
Putting Both Parts Together
By combining both parts, you obtain the full MAC address:
OUI + NIC = MAC address 3C:52:82:9A:4F:11Each part contains 24 bits, for a total of 48 bits.
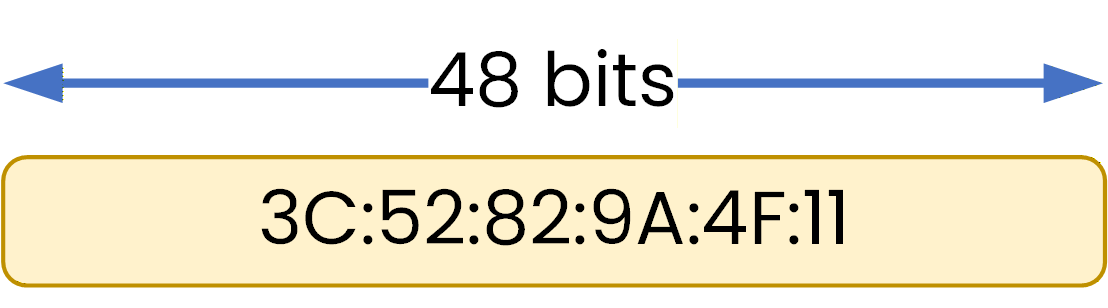
Figure 4 - MAC address with 48 bits
At this stage, you do not need to understand how bits are represented internally.
What matters is that this 48-bit structure allows each network interface to be uniquely identified.Answer the question below
How many bits are in a MAC address?
If I talk about MAC addresses in this course, it is not by chance.
This concept is important, and you will see that it is a foundation for what comes nextMAC Addresses and Switching
In the next course, I want to show you that switches use MAC addresses to make decisions inside a local network.
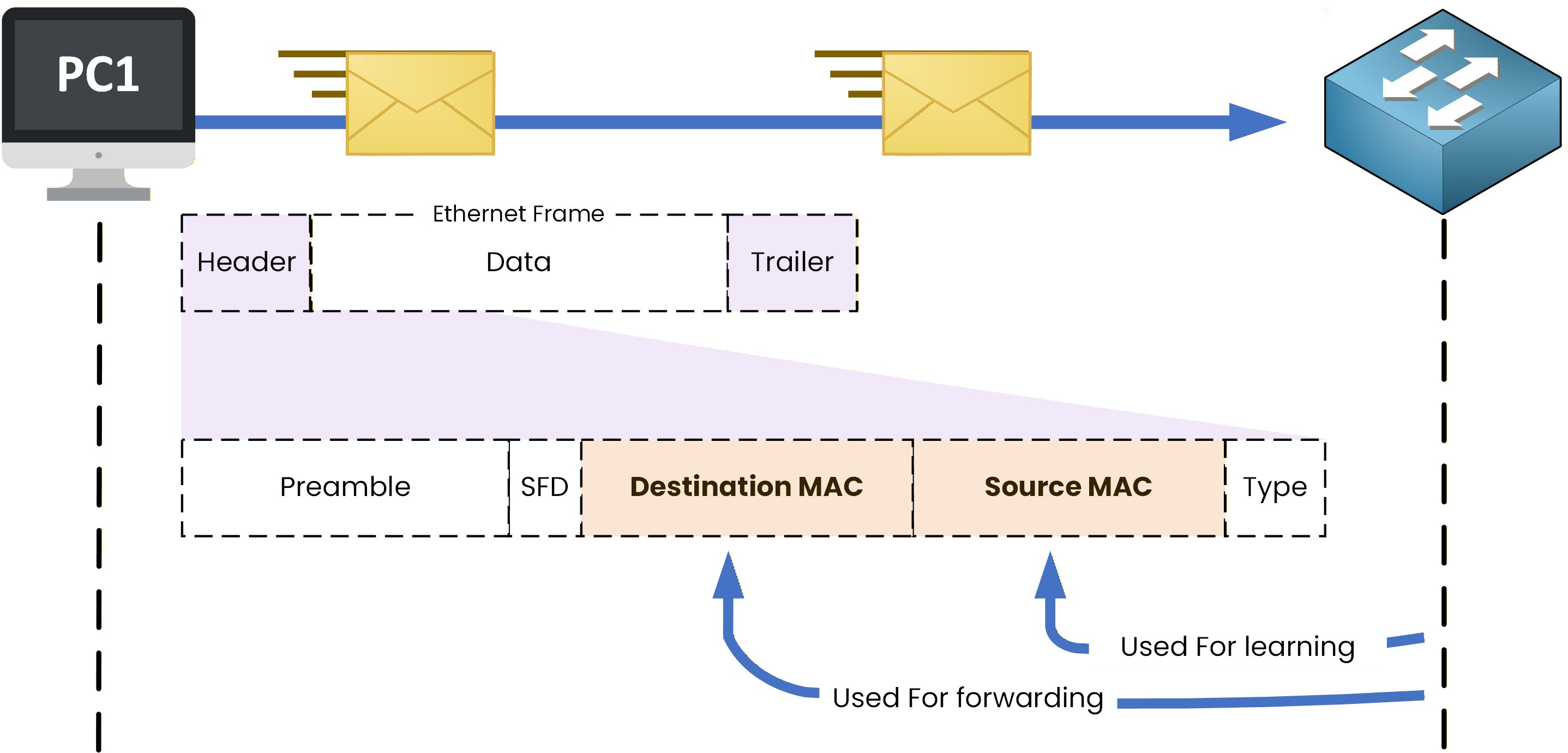
Figure 5 – Switch processing an Ethernet frame using source and destination MAC addresses
Here, you can see PC1 sending data to another device in the LAN.
To reach its destination, the data must pass through a switch.The switch is able to learn and use MAC addresses found in what is called the Ethernet frame header.
Is this starting to feel more complex?
That’s normal.For now, let’s validate this course.
We will explore this process step by step in the next one.Answer the question below
What device uses MAC addresses to forward traffic in a LAN?