For the CCNA exam, you need to be able to understand and interpret JSON (JavaScript Object Notation).
To begin this lesson, we will answer two questions:Why do we need JSON?
What problem does JSON solve in networking?
Let’s start with a simple example.
Why we need JSON
Imagine you are using a network monitoring application.
This application needs to regularly check the status of interfaces on multiple routers to make sure the network is operating correctly.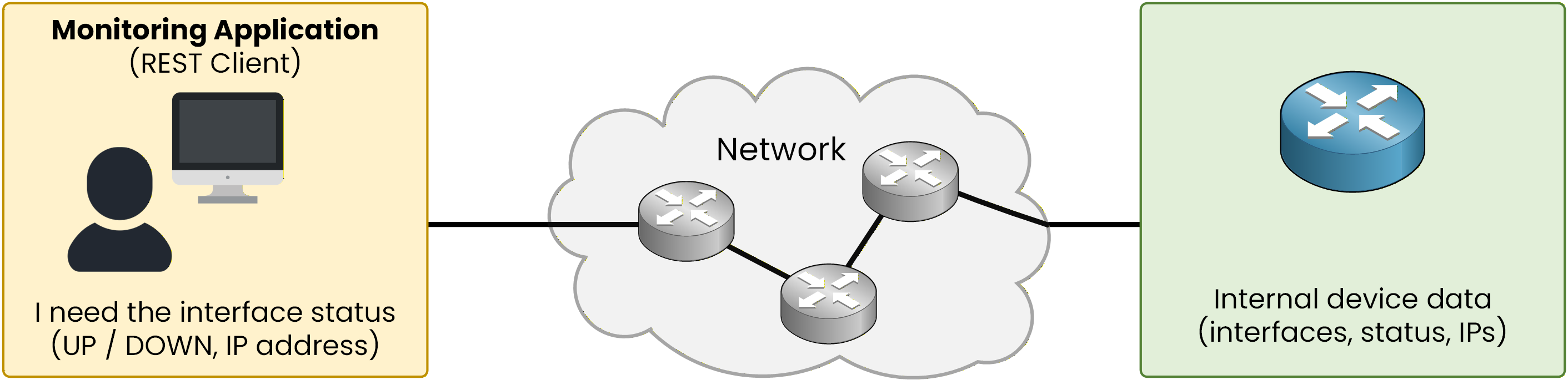
Figure 1 - Network monitoring application requesting interface status information
Modern network devices provide APIs that allow applications to request this information.
At first glance, this seems simple:
the monitoring application sends a GET request
the router replies with the requested information
The Problem Without a Standard Format
Figure 2 illustrates this process.
The monitoring application sends a GET request to the router.
The router accesses its internal variables, such as interface status and IP address.
The router sends the information back without a standardized format, making the response not machine-readable.
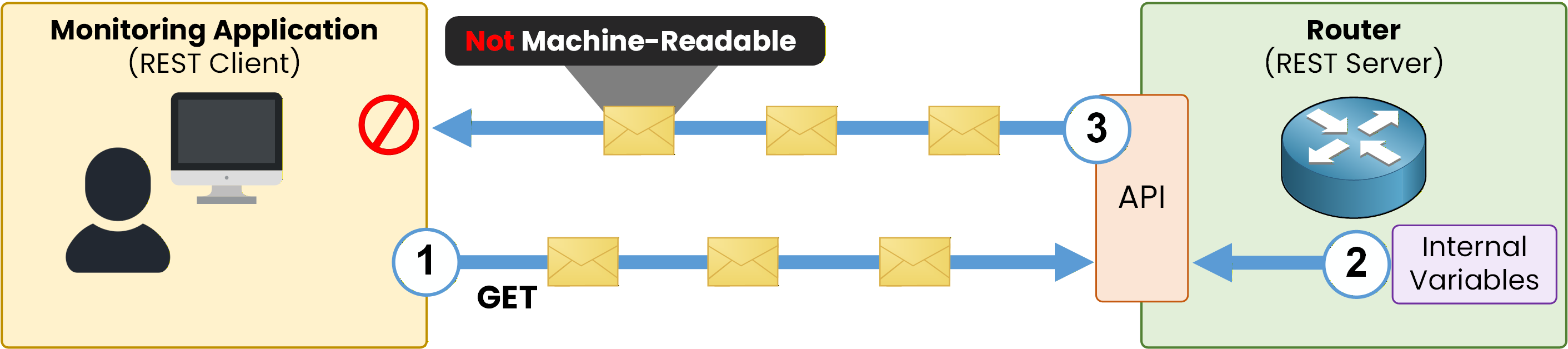
Figure 2 – Interface information exchanged without a standardized format
However, this is where the problem appears.
The router cannot simply send its raw internal variables back to the application in a usable form.Internal device variables:
are designed for the router’s operating system
are not readable by external applications
As a result, the monitoring application cannot interpret the data directly.
Answer the question below
Why can't the monitoring application interpret the data sent by the router?
JSON as the Standard Data Format
We need a standard and structured format to exchange system information.
This format must be:
readable by machines
vendor-independent
easy to parse
JSON is used to represent internal device variables in a standard format that can be exchanged over the network.
This is called a data format.Let’s return to our example.
The monitoring application sends an API request to the router.
The router checks its internal variables to retrieve the requested information.
These internal variables are then converted into JSON format by the API.
The information is sent to the monitoring application encoded in JSON.
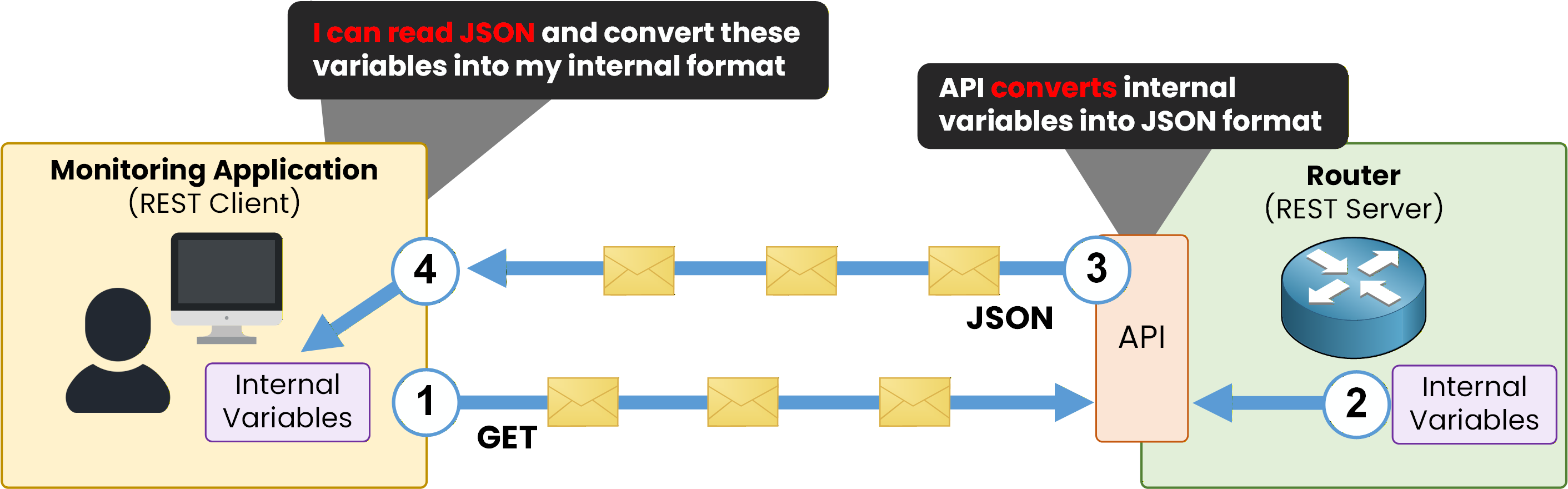
Figure 3 – Interface variables exchanged using JSON format
When the monitoring application receives the JSON message:
it reads the structured data
it extracts the values
it converts them into its own internal representation
In this way, different devices and applications are able to exchange data using the same standard format.
Answer the question below
What data format is used for exchanging information?
Now that we understand why JSON is used in networking, we need to learn what a JSON message represents.
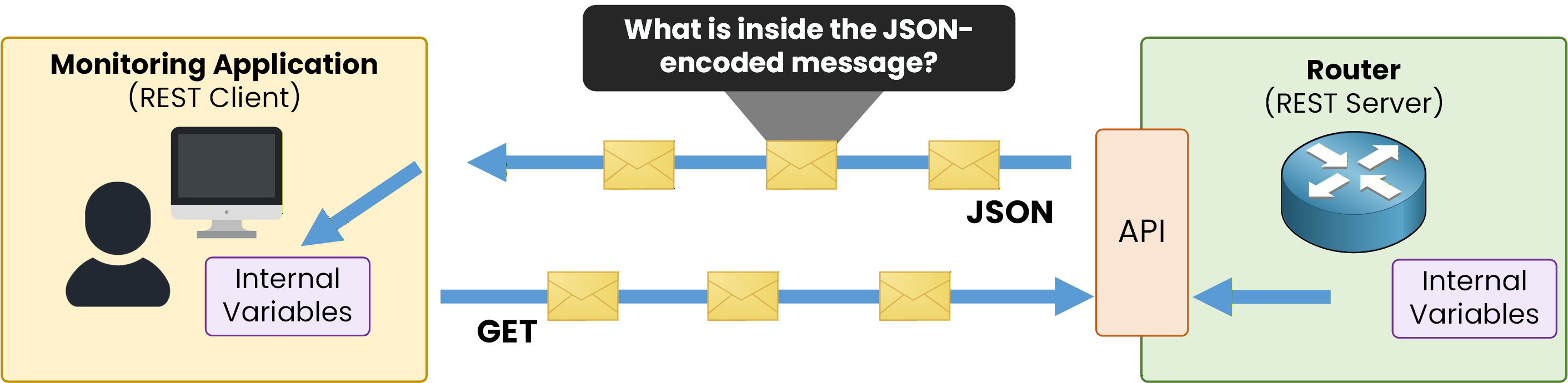
Figure 4 - JSON data exchange
To do this, we will start with something you already know well: the Cisco CLI.
Checking Interface Information with the CLI
When we check the status of an interface on a router, we use a CLI command such as:
R1# show ip interface g0/1 GigabitEthernet0/1 is up, line protocol is up (connected) Internet address is 10.10.12.2/24 Broadcast address is 255.255.255.255This output is:
human-readable
easy for a network engineer to understand
The Same Interface Information in JSON
JSON represents the exact same information, but in a machine-readable format.
Important to understand:
nothing new is added
nothing is removed
only the format changes
{ "interface": "GigabitEthernet0/1", "status": "up", "protocol": "up", "connection_state": "connected", "ip_address": "10.10.12.2", "prefix": 24, "broadcast_address": "255.255.255.255" }JSON organizes the information in a structured way so applications can easily read and interpret it.
JSON does not replace the CLI.
The CLI is designed for humans, while JSON is designed for machines."At first, JSON may look unfamiliar".
This is only because we have not yet learned how to read it.The next section focuses on understanding the structure of JSON, step by step.
Answer the question below
What is the main difference between CLI output and JSON?
To understand JSON, we need to move step by step.
In JSON, the root element can be:
an object
or an array
We will start with the most common one: the JSON object.
40 % Complete: you’re making great progress
Unlock the rest of this lesson
If you’d like to continue your CCNA journey, simply create your free account.
Access all CCNA lessons
Practice with hands-on labs
Train with Practice exams and Quizzes
Progress tracking in your dashboard
Made by network engineers - CCNP certified
learners globally