An IPv6 static route is a manually configured route that tells the router how to reach an IPv6 remote network. Unlike dynamic routing protocols, static routes don’t adjust automatically; they are fixed and must be maintained by the network administrator.
Just like in IPv4, the router needs a route to know where to forward packets. If no dynamic routing protocol is configured, a static route is required to communicate with remote networks.
Answer the question below
What type of route must be configured when no dynamic routing protocol is used?
To learn the concept of IPv6 static route, let's focus on an example together.
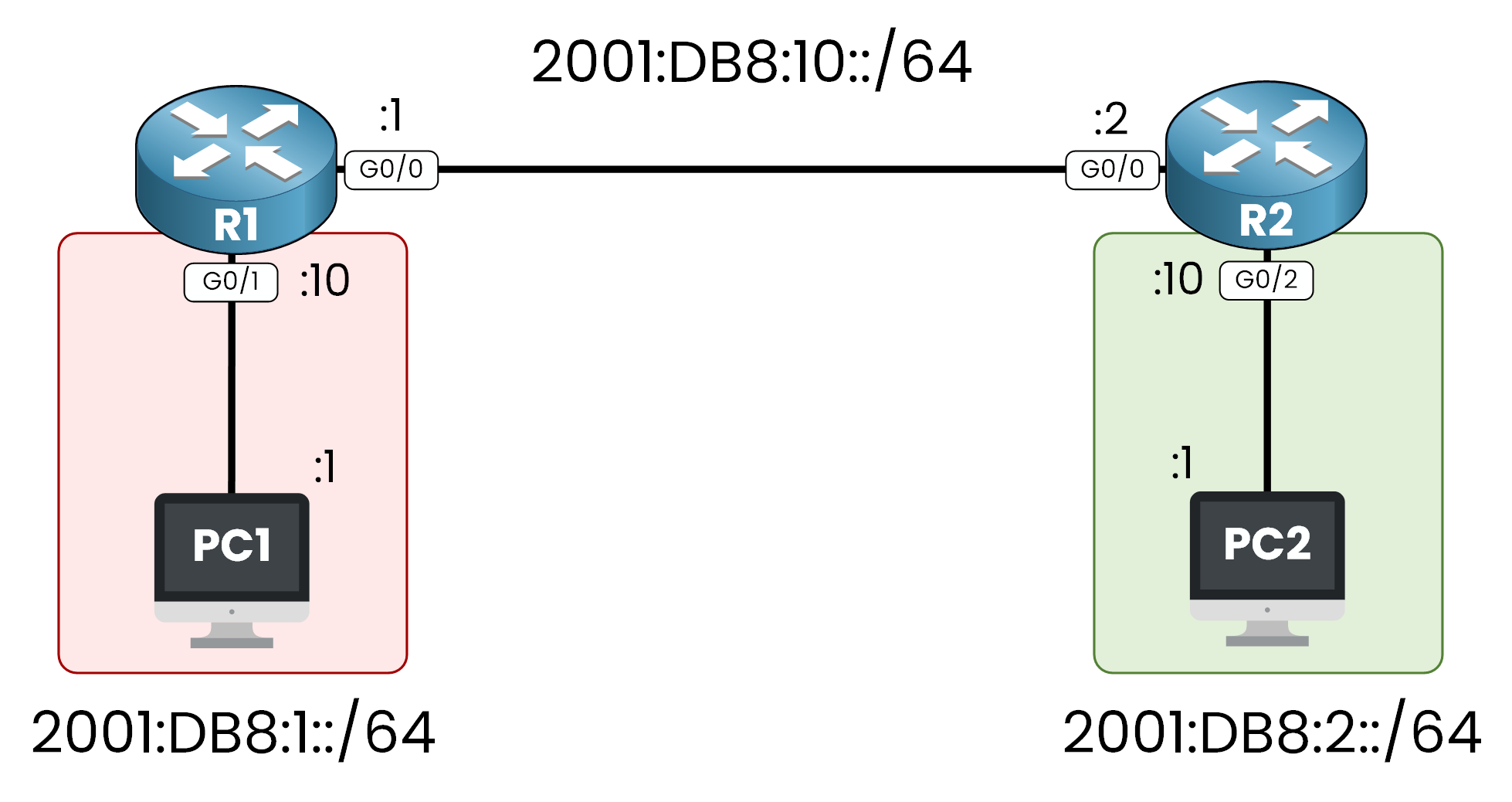
Figure 1 – Initial IPv6 Topology
PC1 is in the
2001:DB8:1::/64network.PC2 is in the
2001:DB8:2::/64network.R1 and R2 are connected via
2001:DB8:10::/64.
PC1 want to sends traffic to PC2. R1 receives the packet but doesn’t know how to reach the destination network, because
2001:DB8:2::/64network is not in his IPv6 Routing Table.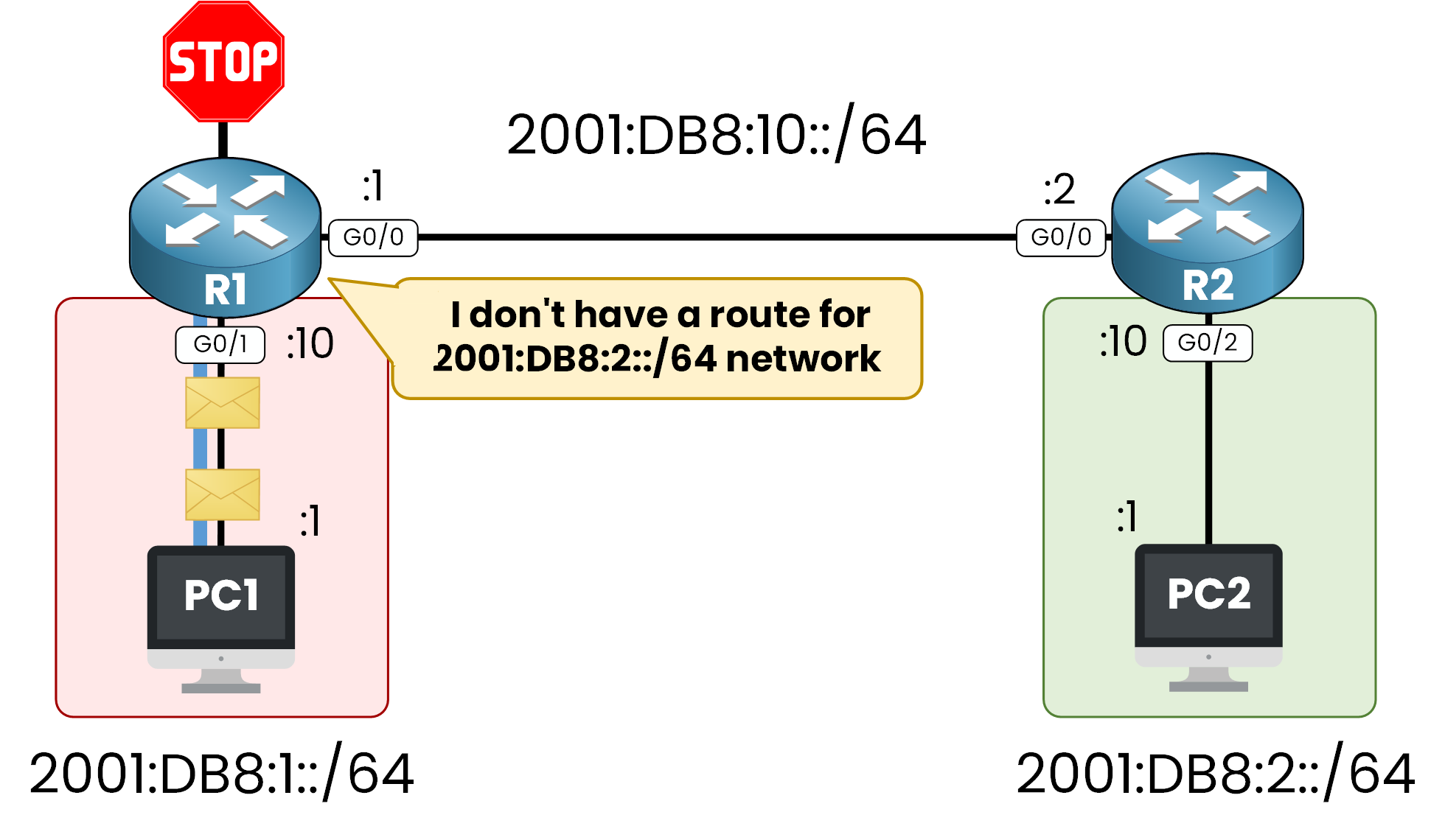
Figure 2 – Missing Static Route on R1
Without any static or dynamic route configured, R1 drops the packets and the communication between PC1 and PC2 fails.
Answer the question below
What does R1 do with packets when the destination network is not in its IPv6 routing table?
To fix the issue, as a network administrator we can configure a IPv6 static route on R1, pointing to R2’s
IPv6 address 2001:db8:1::2.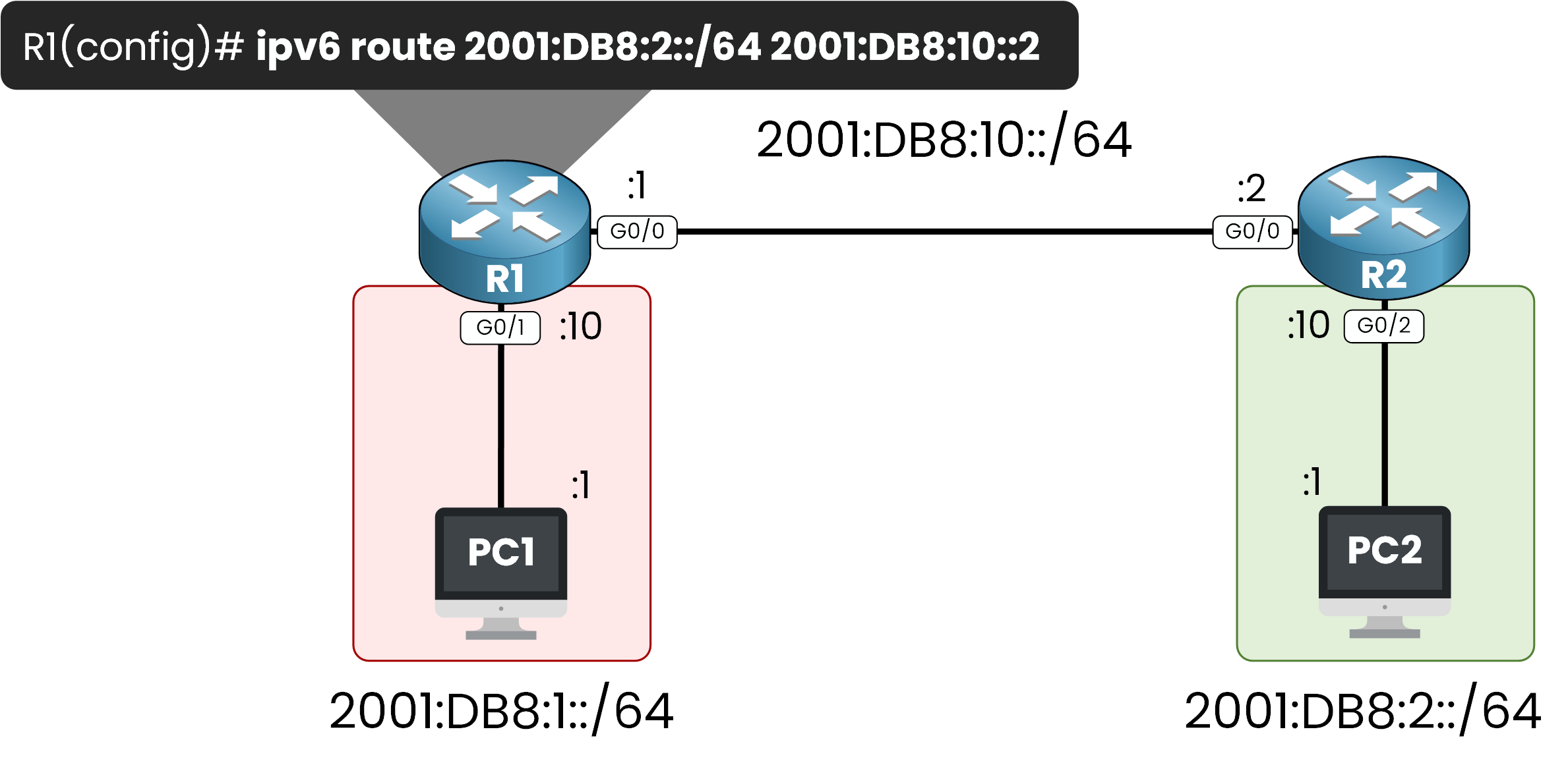
Figure 3 – Adding an IPv6 Static Route on R1
At this point, R1 is now able to forward traffic destinated to 2001:db8:2::/64 to his next hop 2001:db8:10::2.
However, R2 still doesn’t know how to reach the 2001:DB8:1::/64 network.To complete the communication, we must add a return IPv6 static route on R2, pointing to R1.
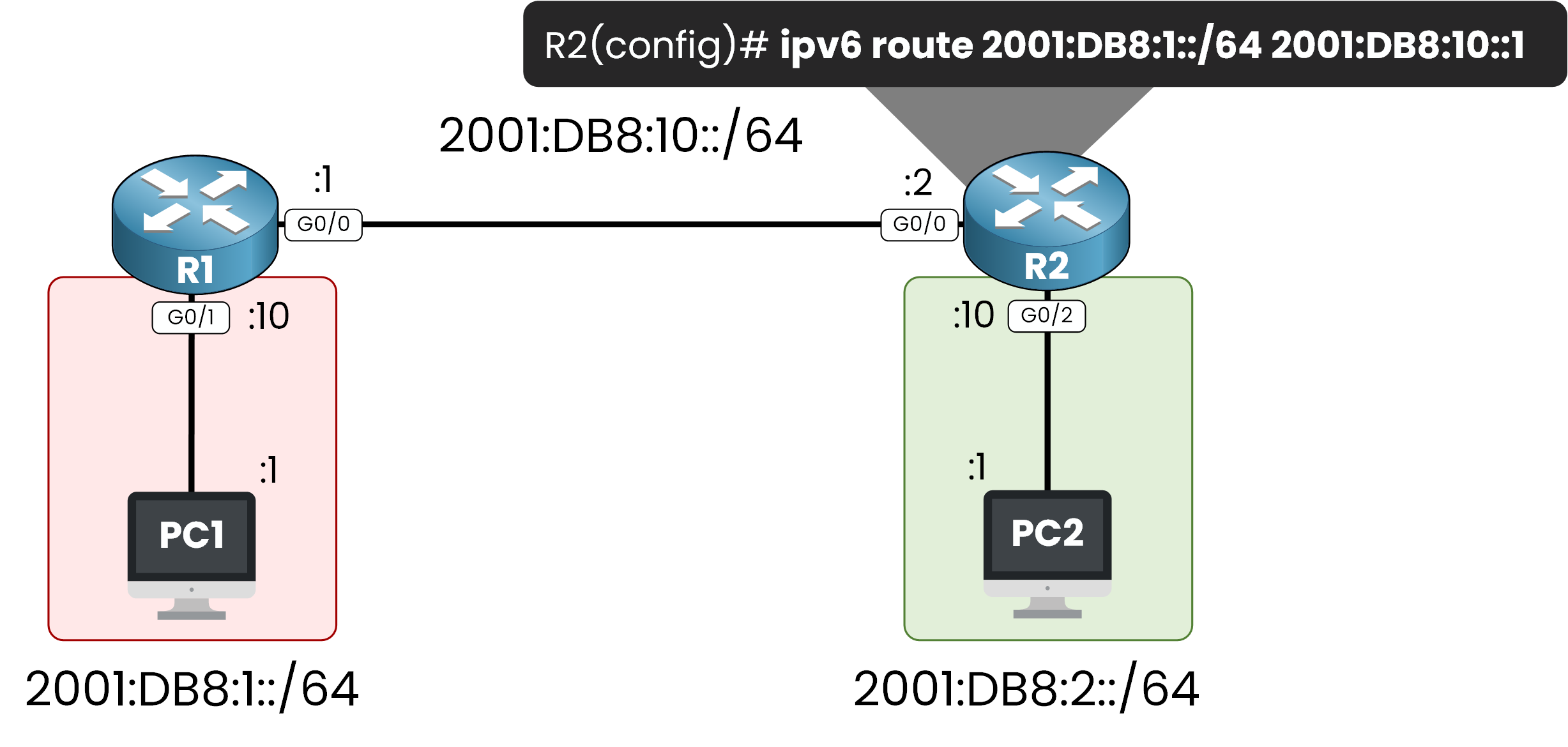
Figure 4 – IPv6 Static Route on R2
With static routes now configured on both routers, communication is possible between PC1 and PC2.
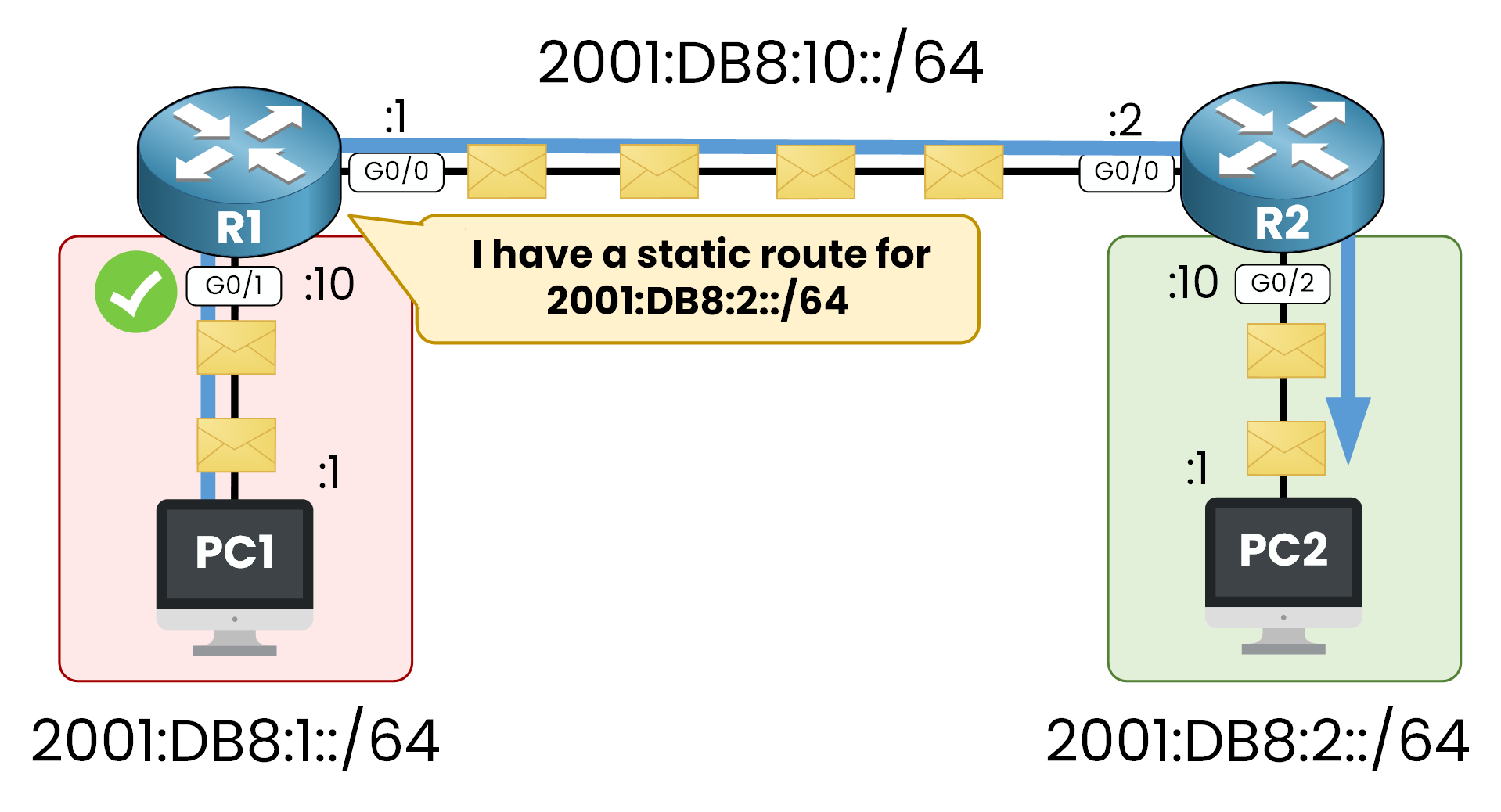
Figure 5 – IPv6 Static Route on R1 Working
Traffic from PC1 reaches PC2 by using R1 and R2.
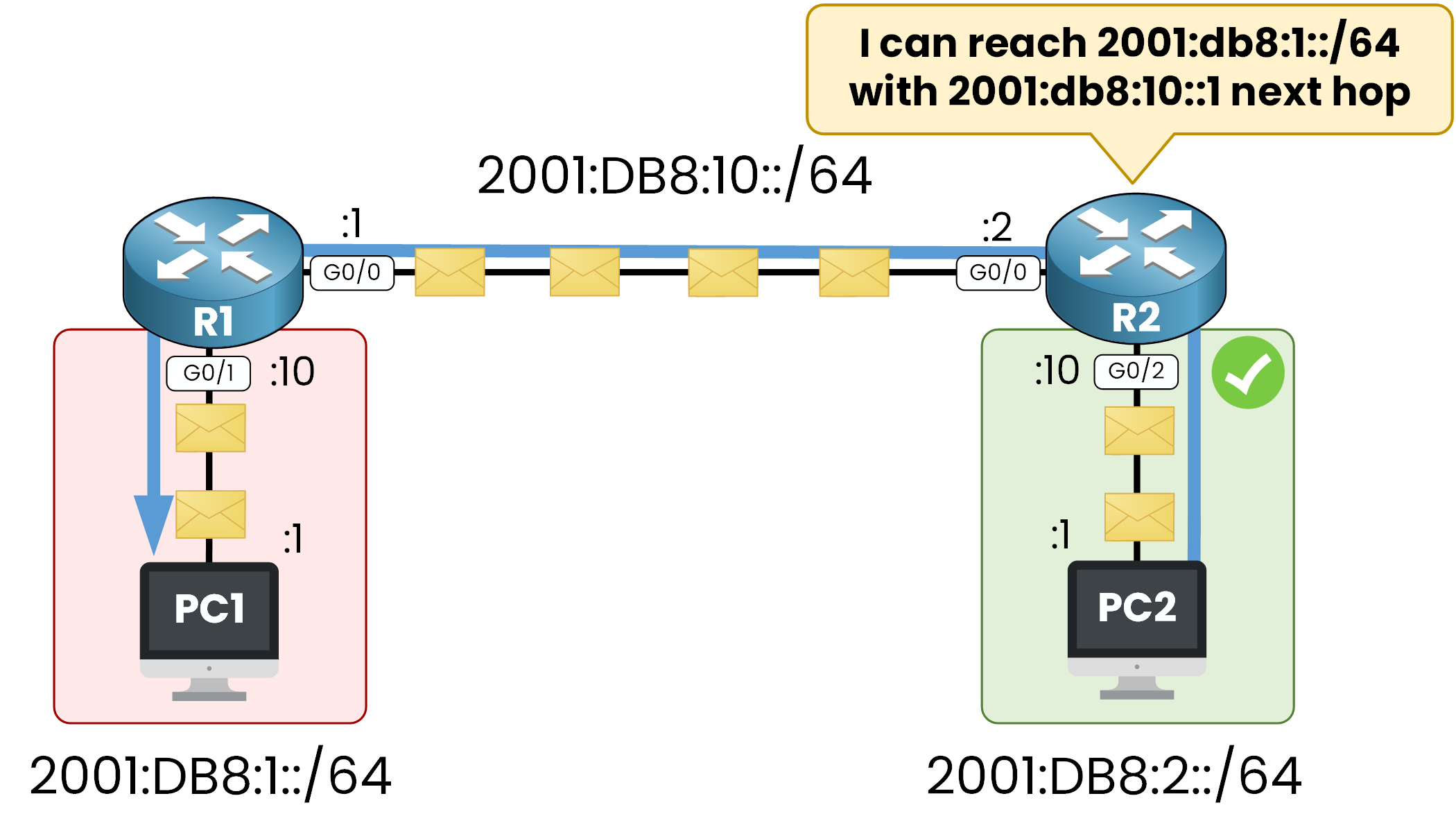
Figure 6 – IPv6 Static Route on R2 for Return Path
Reply packets from PC2 are returned to PC1 using the static route on R2 pointing to R1.
Answer the question below
Which next-hop IPv6 address must R1 use to reach the 2001:DB8:2::/64 network?
Enough theory let's move into the Cisco IOS Cli to show you every step to configure a IPv6 Static Route.
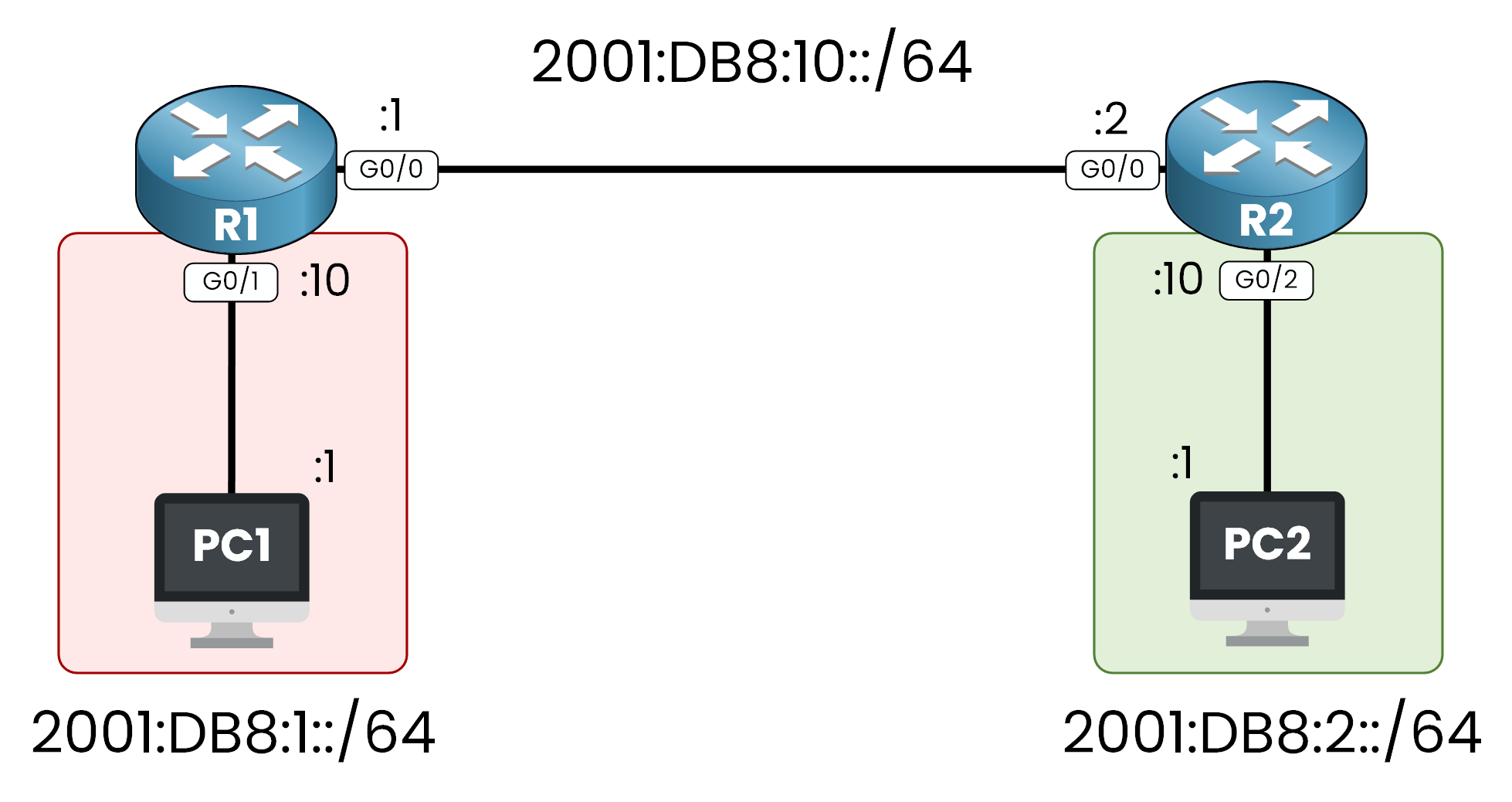
Figure 7 – Lab Topology IPv6 Static Route
Step 1 – Enable IPv6 Routing
First, you need to know that Cisco routers do not have IPv6 routing enabled by default.
We must activate this feature on both routers R1 and R2 using the commandipv6 unicast-routing40 % Complete: you’re making great progress
Unlock the rest of this lesson
If you’d like to continue your CCNA journey, simply create your free account.
Access all CCNA lessons
Practice with hands-on labs
Train with Practice exams and Quizzes
Progress tracking in your dashboard
Made by network engineers - CCNP certified
learners globally
IPv6 Static Route
An IPv6 static route defines how reach a remote IPv6 network when no dynamic routing protocol is used. This lesson shows step-by-step how to configure it for reliable communication.