In this lesson, we will walk through how the Spanning Tree Protocol works. You will learn how it detects loops, elects the root bridge and activates only the necessary links to ensure a stable network.
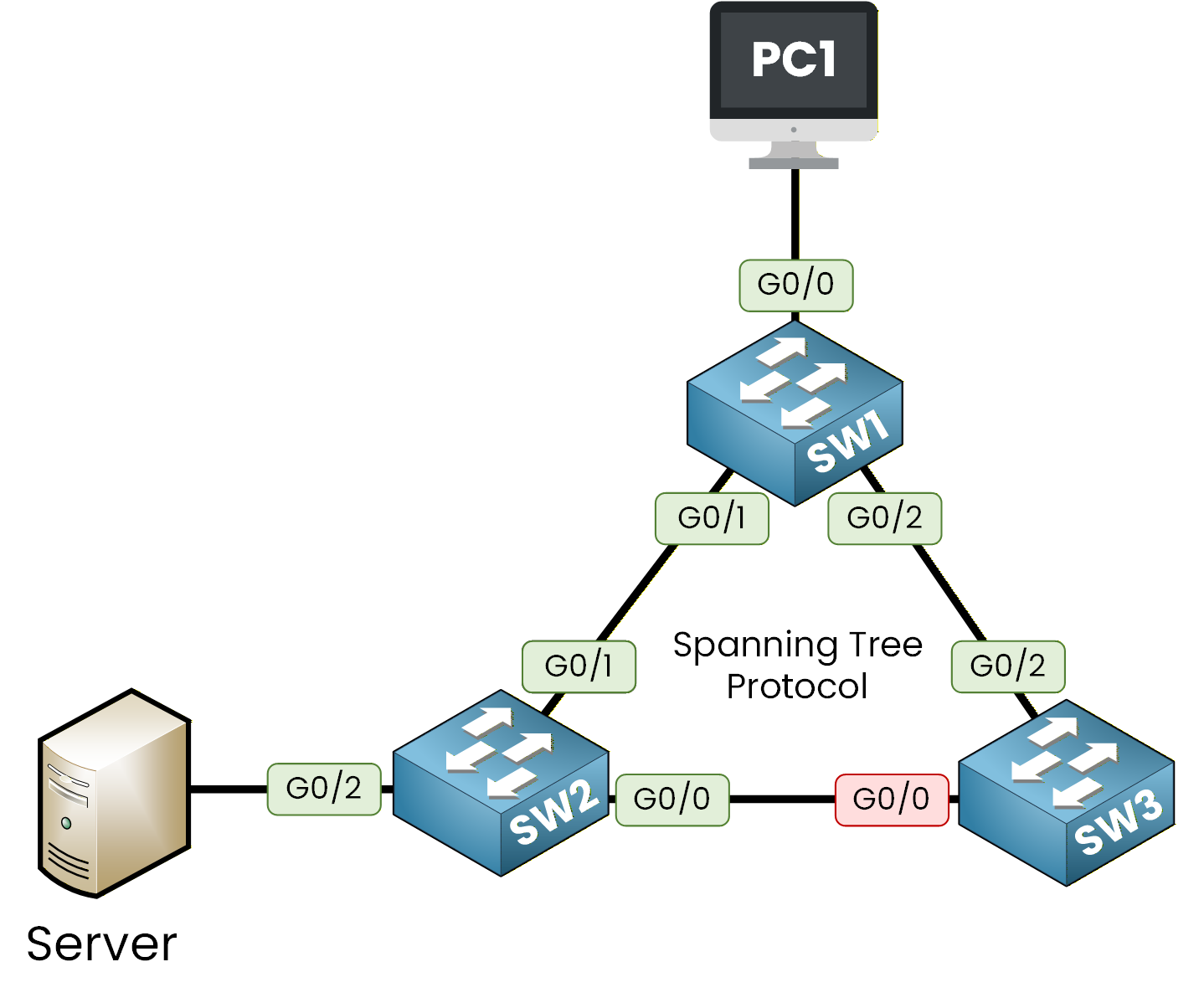
Figure 1 - Spanning Tree Protocol Topology
In this network topology with three switches, STP blocks one redundant link to prevent loops. If the active link fails, the previously blocked link becomes active, ensuring uninterrupted communication.
Now, you might wonder : "How does STP determine which paths to block and which to keep active?"
Good question! It starts by identifying and organizing switches using a unique identifier known as the Bridge ID (BID).
Let’s see how this works.
Answer the question below
To manage redundant paths and organize the network, STP assigns a Bridge ID (BID) to each switch. This unique identifier is used to differentiate switches in the spanning tree topology.
What Is a Bridge ID ?
A Bridge ID consists of:
Priority + VLAN ID: A configurable priority value combined with the VLAN ID. The default priority value is 32,768
MAC Address: The unique MAC address of the switch (Example : AABB:CCDD:EE01)
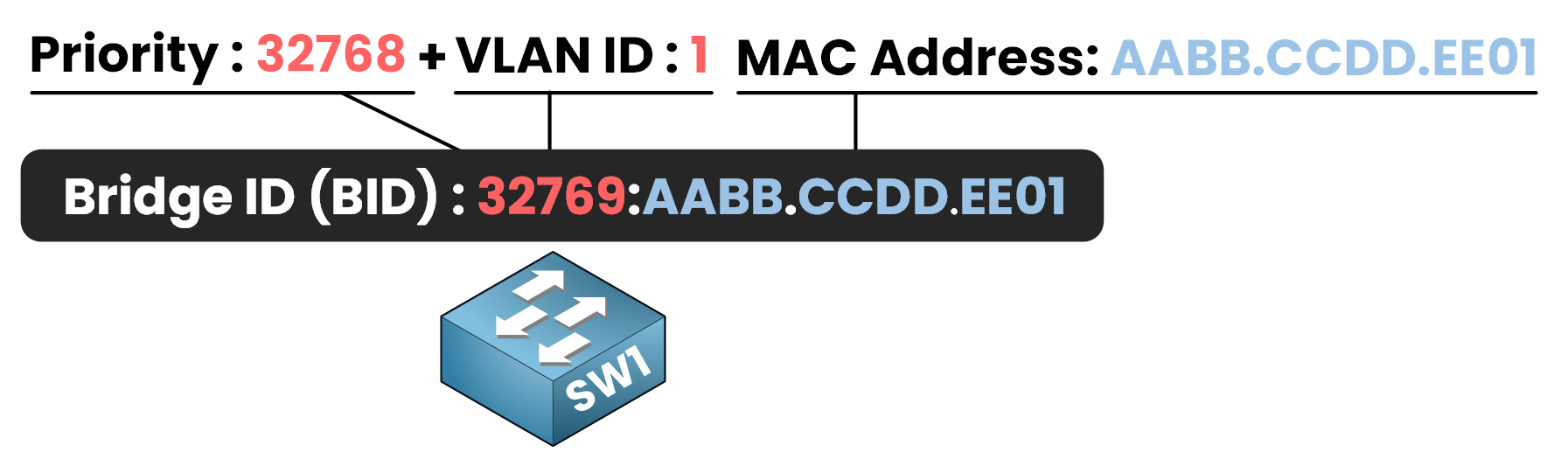
Figure 2 – Bridge ID (BID) Structure
A Switch has the following components for its BID:
Priority + VLAN ID: 32768 + VLAN 1 = 32769.
MAC Address: AABB:CCDD:EE01.
The BID for SW1, 32769.AABB.CCDD.EE01, uniquely identifies it in the network by combining the priority, VLAN, and MAC address.
As you can see in our topology, every switch has a different BID.
Verifying the Bridge ID from the CLI
We can confirm this directly from the switch using the following command:
SW1# show spanning-tree vlan 1 VLAN0001 Spanning tree enabled protocol ieee Root ID Priority 32769 Address aabb.ccdd.ee01 This bridge is the root Bridge ID Priority 32769 (priority 32768 sys-id-ext 1) Address aabb.ccdd.ee01This output confirms:
The priority value is 32768
The VLAN ID (sys-id-ext) is 1
The resulting value is 32769
The MAC address is aabb.ccdd.ee01
The full Bridge ID is therefore 32769.aabb.ccdd.ee01
You would see similar outputs on SW2 and SW3, but with different MAC addresses:
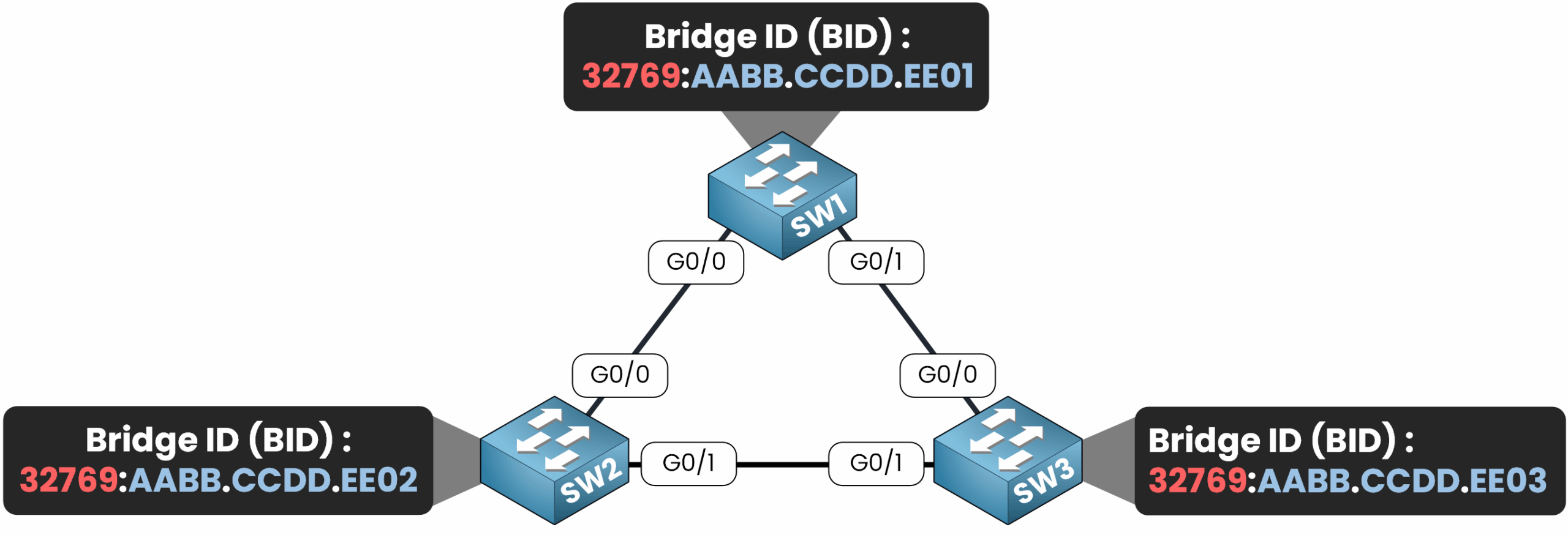
Figure 3 – Bridge IDs in a Spanning Tree Topology
Now that we’ve learned how to identify devices in our Spanning Tree topology using unique identifiers, let’s explore how these devices communicate and exchange information to build and maintain the STP topology.
Answer the question below
What is the default STP priority value?
Bridge Protocol Data Units (BPDUs) are messages exchanged between switches in a Spanning Tree topology. They allow switches to communicate their Bridge ID (BID) and share essential information about the network.
40 % Complete: you’re making great progress
Unlock the rest of this lesson
If you’d like to continue your CCNA journey, simply create your free account.
Access all CCNA lessons
Practice with hands-on labs
Train with Practice exams and Quizzes
Progress tracking in your dashboard
Made by network engineers - CCNP certified
learners globally
How Spanning Tree Protocol Works
The Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) works by preventing loops in redundant Layer 2 topologies through the election of a root bridge and selective port blocking. In this lesson, you will learn how BPDUs control this process to keep the network stable and resilient.