FTP (File Transfer Protocol) and TFTP (Trivial File Transfer Protocol) are two protocols used by network devices to transfer files across the network. You’ll often need them when working with routers and switches. They’re useful for tasks like configuration backups, IOS upgrades, and restoring systems after maintenance.
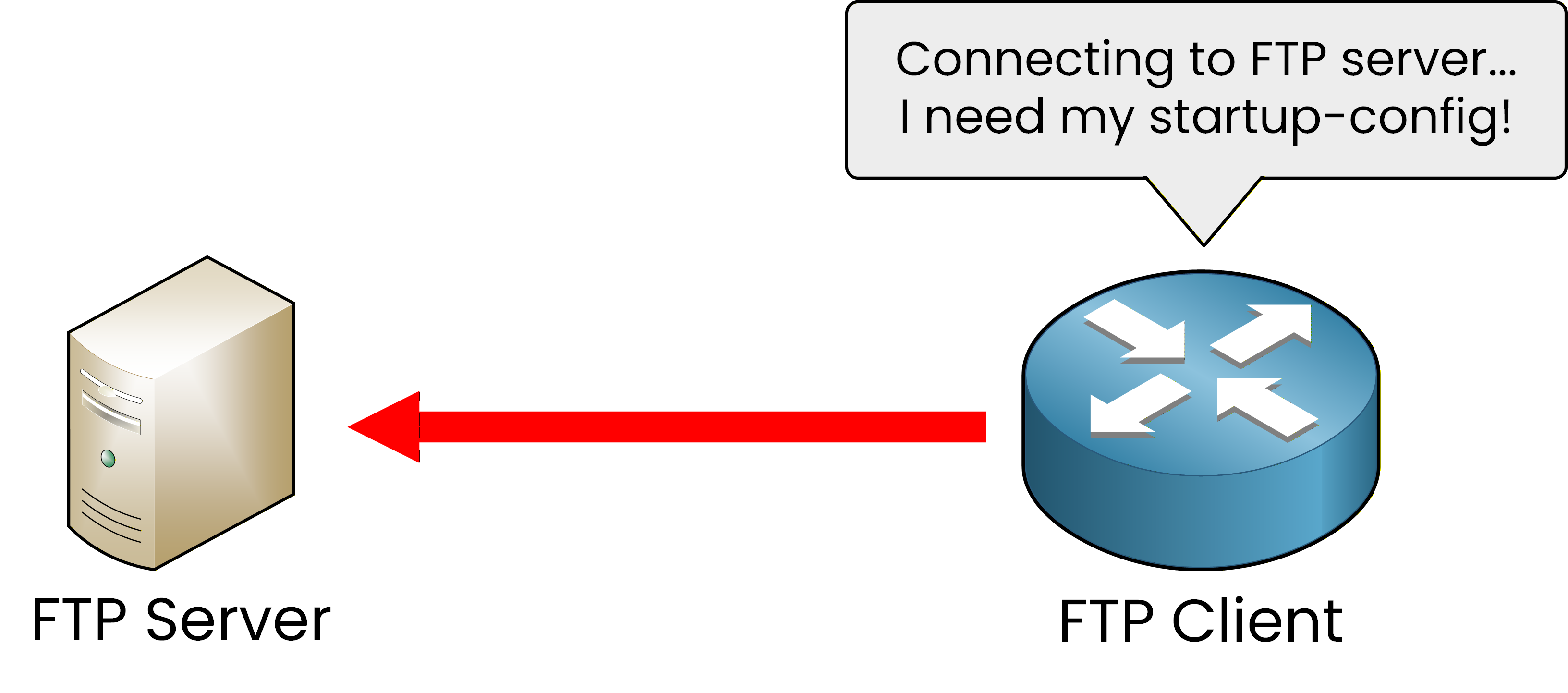
Figure 1 – The FTP client connects to the server to request its startup-config
In a typical scenario, the client connects to the FTP server and requests a specific file, such as the startup configuration. This type of communication allows network devices to retrieve or store configuration files as part of regular maintenance tasks.
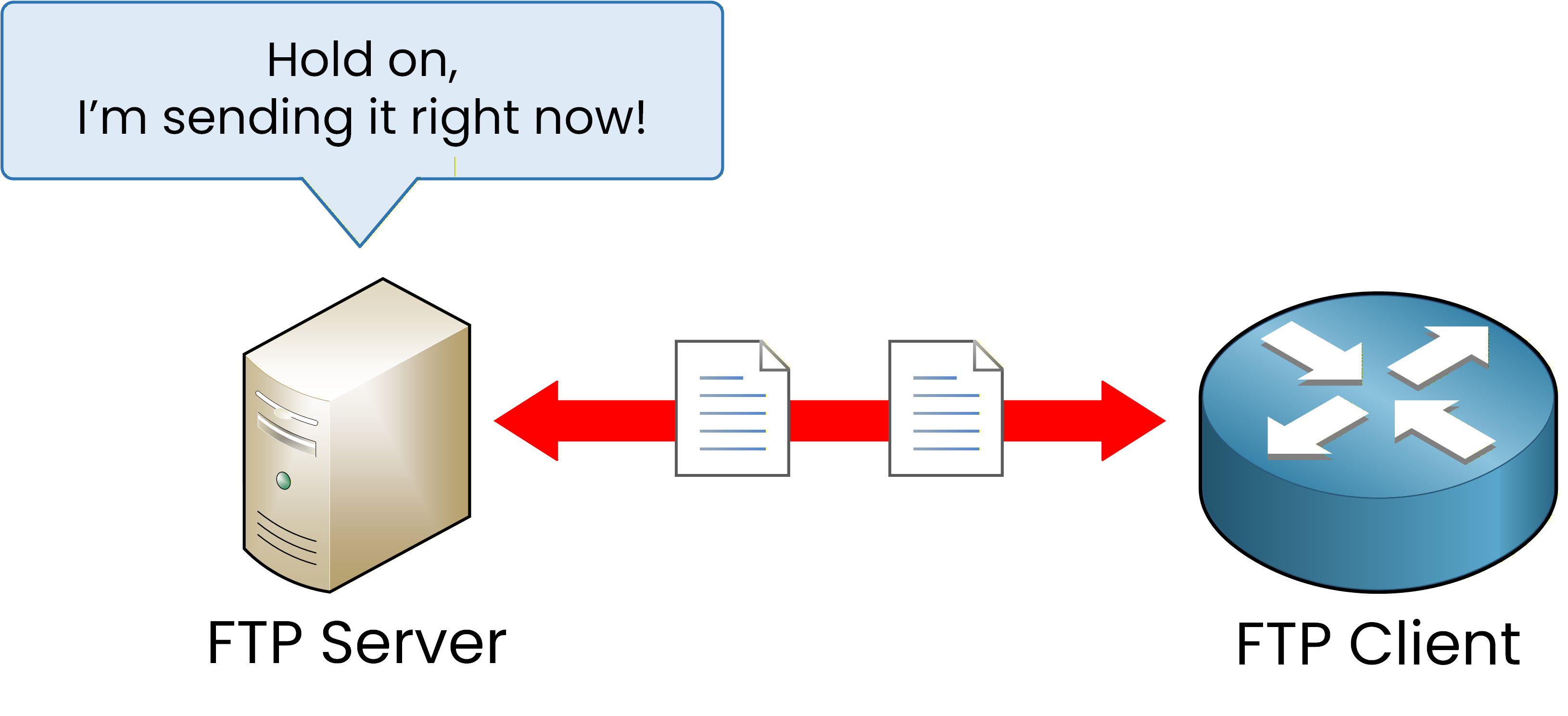
Figure 2 – The FTP server sends the startup configuration file to the client.
After receiving the request, the server sends the file to the client. This demonstrates the client–server communication model that both FTP and TFTP follow. In Cisco networks, these protocols are commonly used for IOS upgrades or when restoring configurations from backups.
The Client-Server Model
Both FTP and TFTP operate using a client–server model.
The server stores the files. The client, which can be a router, switch, or admin workstation, connects to download or upload them.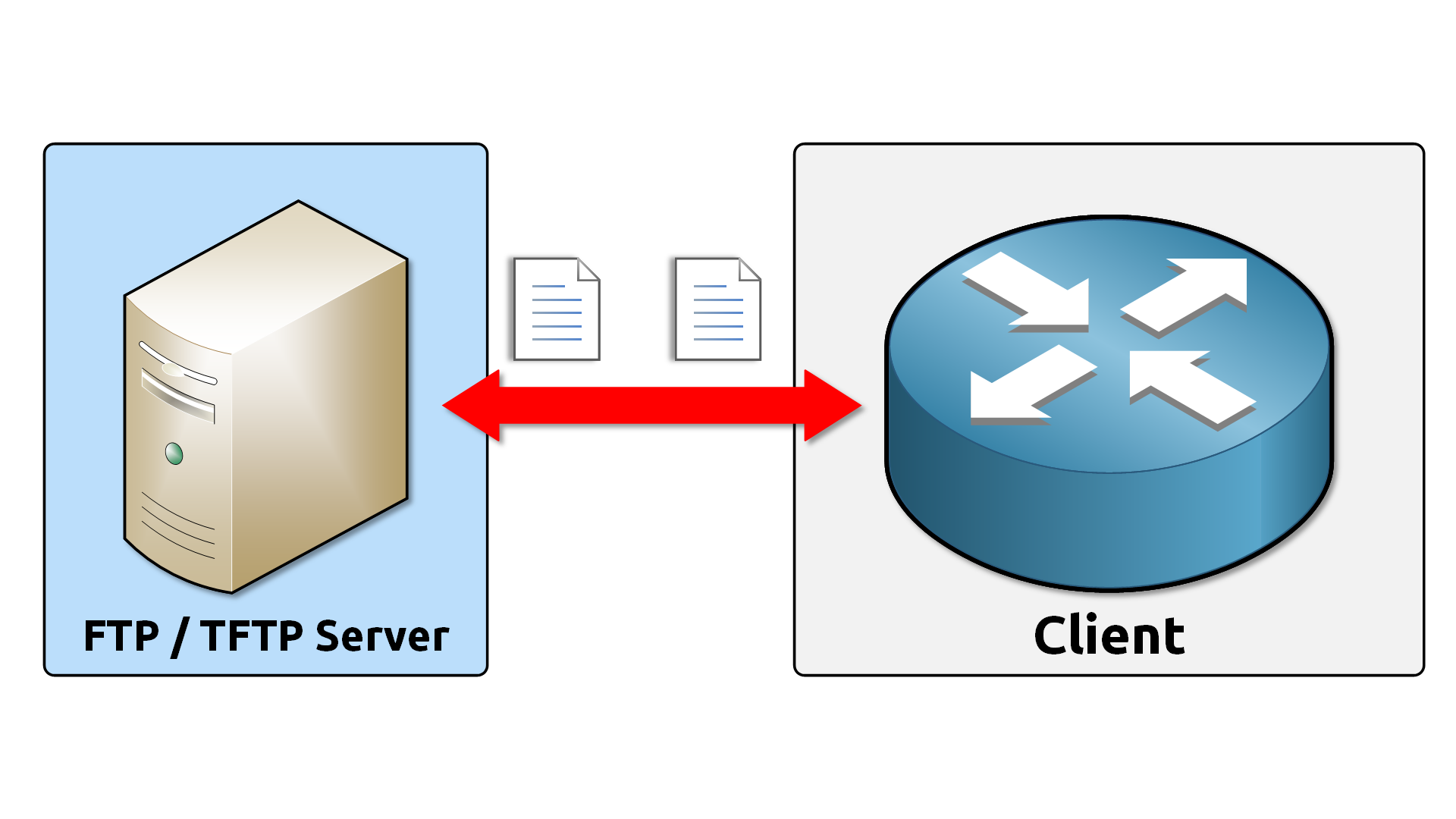
Figure 3 – FTP and TFTP client–server model.
This model centralizes file management and makes network maintenance much easier.
Instead of configuring each device individually, you can perform updates and backups from a single location.
That saves time and ensures consistency across the network.In both FTP and TFTP, the client can upload (send) or download (receive) files from the server, depending on the command used. For example, a router might upload its running configuration to a TFTP server or download a new IOS image during an upgrade.
Overview of FTP and TFTP
Although both protocols aim to transfer files between devices, they differ in reliability and control.
FTP uses TCP, which guarantees reliable delivery and supports authentication with usernames and passwords.
TFTP uses UDP, which is faster and simpler, but does not include authentication or encryption.
Both are effective in their own contexts.
Use FTP when you need reliability and user control, and TFTP when you need quick transfers in a trusted environment.Now that you understand their general purpose, let’s explore how FTP works in practice.
Answer the question below
Which protocol uses TCP and supports authentication?
FTP (File Transfer Protocol) was standardized in 1971 (RFC 114). It is still widely used for transferring files between network devices.
Unlike TFTP, FTP relies on TCP, which means each session begins with a 3 Way handshake that ensures reliable communication.All FTP communication happens in two distinct phases:
The Control Connection is used to exchange commands between devices.
The Data Connection is used to transfer the actual files.
FTP Control Connection
The FTP session starts with the control connection. This connection exchanges commands between the client and the server.
This connection uses TCP port 21 and stays open throughout the entire session.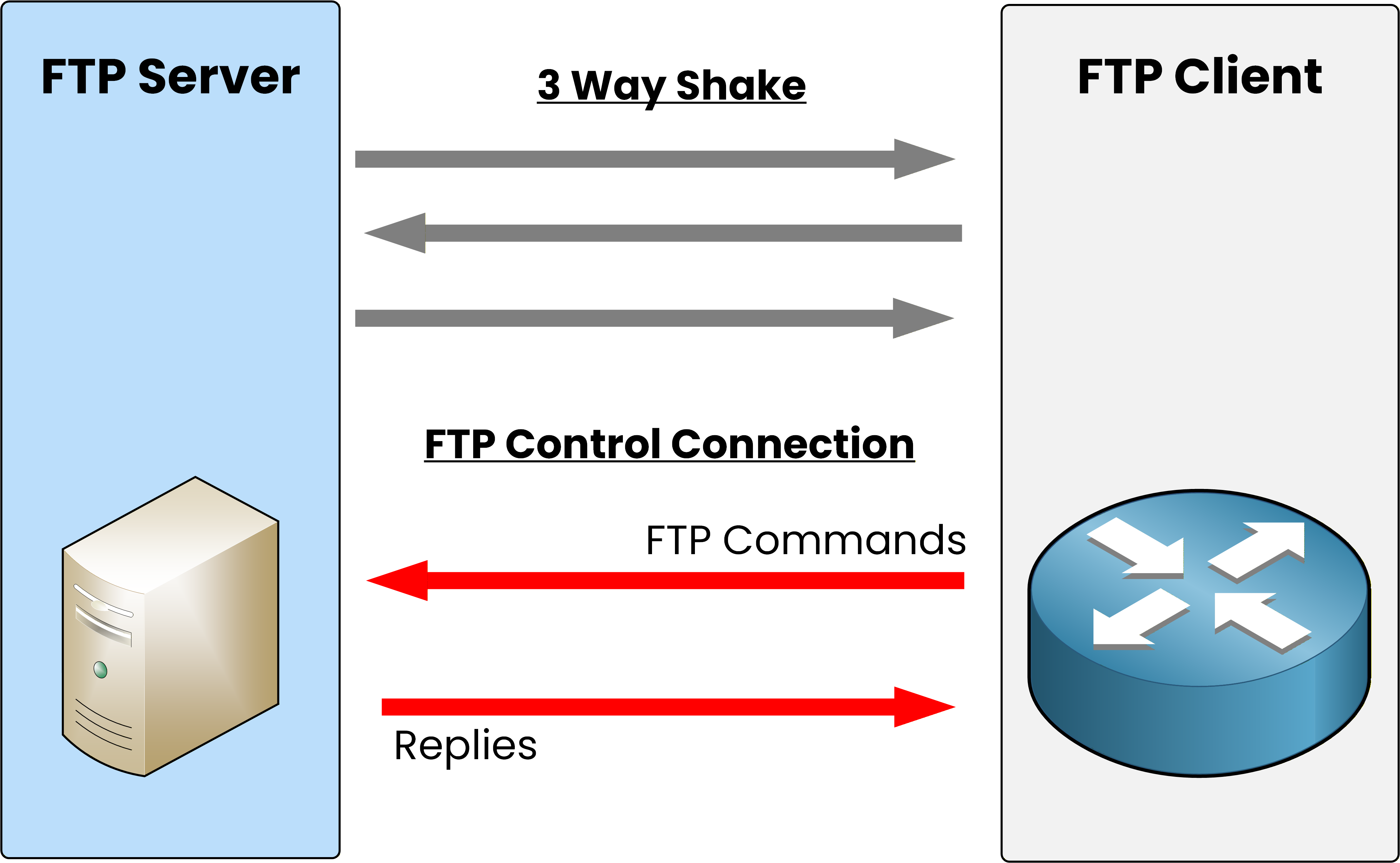
Figure 4 – The FTP control connection is established after the TCP three-way handshake.
Once the handshake is complete, the client can start sending FTP commands to the server, for example, to request a file.
The server replies to acknowledge these commands and confirm that it is ready.
At this stage, no data is transferred yet, the control channel only carries instructions.When it is time to send or receive a file, a second connection called the data connection must be created.
40 % Complete: you’re making great progress
Unlock the rest of this lesson
If you’d like to continue your CCNA journey, simply create your free account.
Access all CCNA lessons
Practice with hands-on labs
Train with Practice exams and Quizzes
Progress tracking in your dashboard
Made by network engineers - CCNP certified
learners globally