A default static route is a manually configured route that forwards traffic when no more specific route matches the destination.
Think of the default static route as a route used when no other routes in your router can be used to send the packet to the destination. (If you’re not yet familiar with regular static routes, see our Static Route lesson first.)
Let’s look at this example together: we have a packet with destination IP 8.8.8.8, and our router needs to find a route to send this packet to its destination.
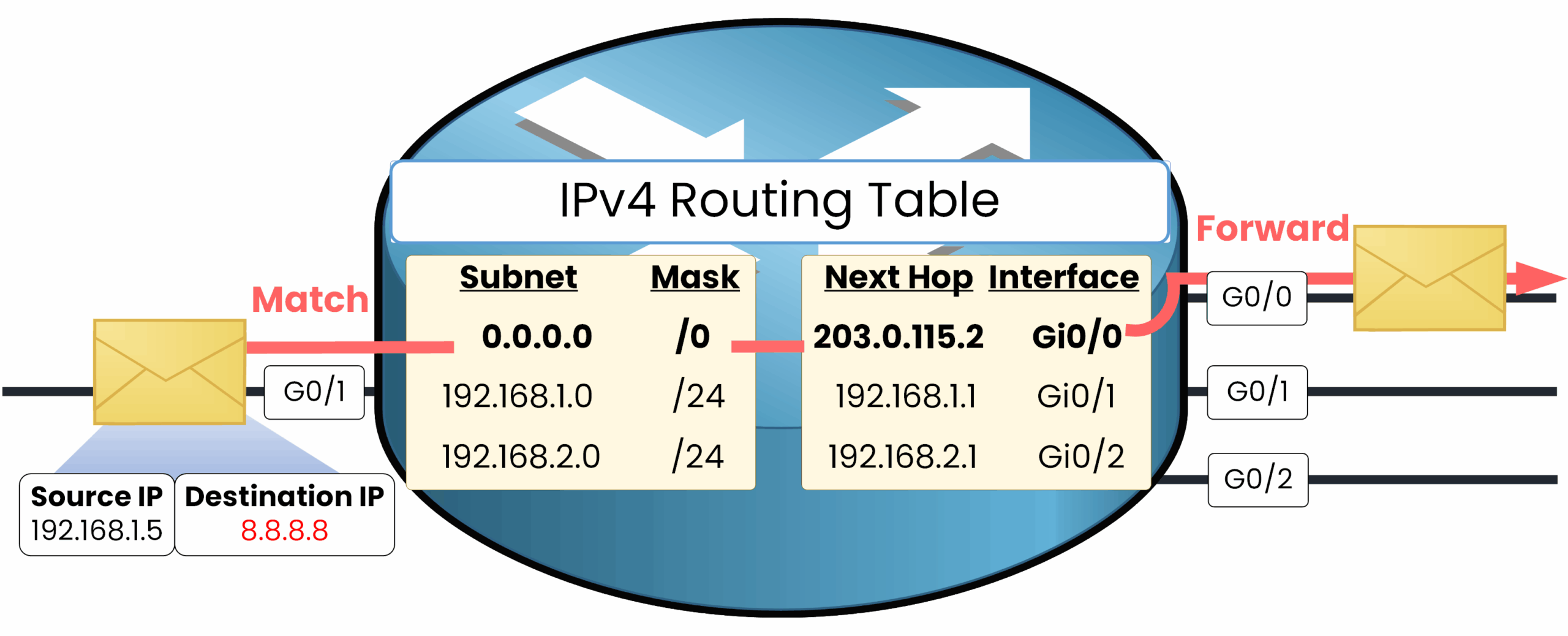
Figure 1 – Default Static Route Lookup
There are three routes in this routing table. The first route is the default route with subnet 0.0.0.0 and mask /0, which means: "you can use this route when no other route matches the destination IP," because 0.0.0.0/0 includes all IP addresses.
The second route is 192.168.1.0/24, which does not match the destination IP.
The third route is 192.168.2.0/24, which also does not match.Longest Prefix Match (LPM)
The router always prefers the most specific route (longest prefix match).
0.0.0.0/0is used only if no other route matches the destination.Since no other route matches, the router will use the default static route and forward the packet to the next hop 203.0.115.2 via G0/0.
🔻 What Happens Without a Default Route
Let's consider a realistic scenario in which no default route has been configured. If PC1 were to send a packet to the destination IP address 8.8.8.8, our router R1 would discard it because there is no matching route in its routing table.
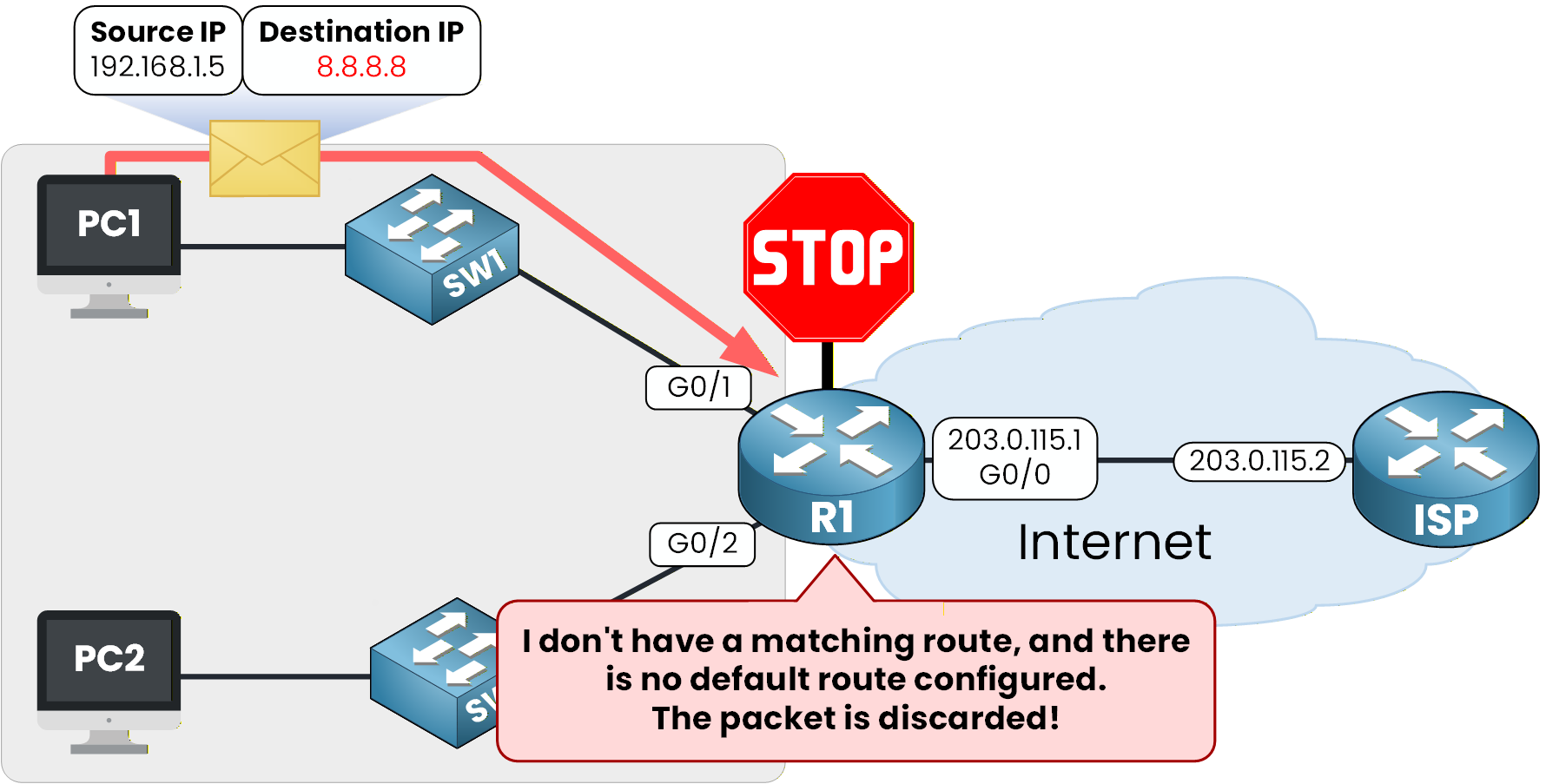
Figure 2 – Packet discarded due to missing route
In Cisco IOS routers, configuring a default static route is pretty easy, the command is
ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0.In the example below, R1 is connected to the Internet Service Provider and a default static route can be used to send the unknown destination to the ISP. To do this, we specify the next hop as the IP interface of the internet service provider.
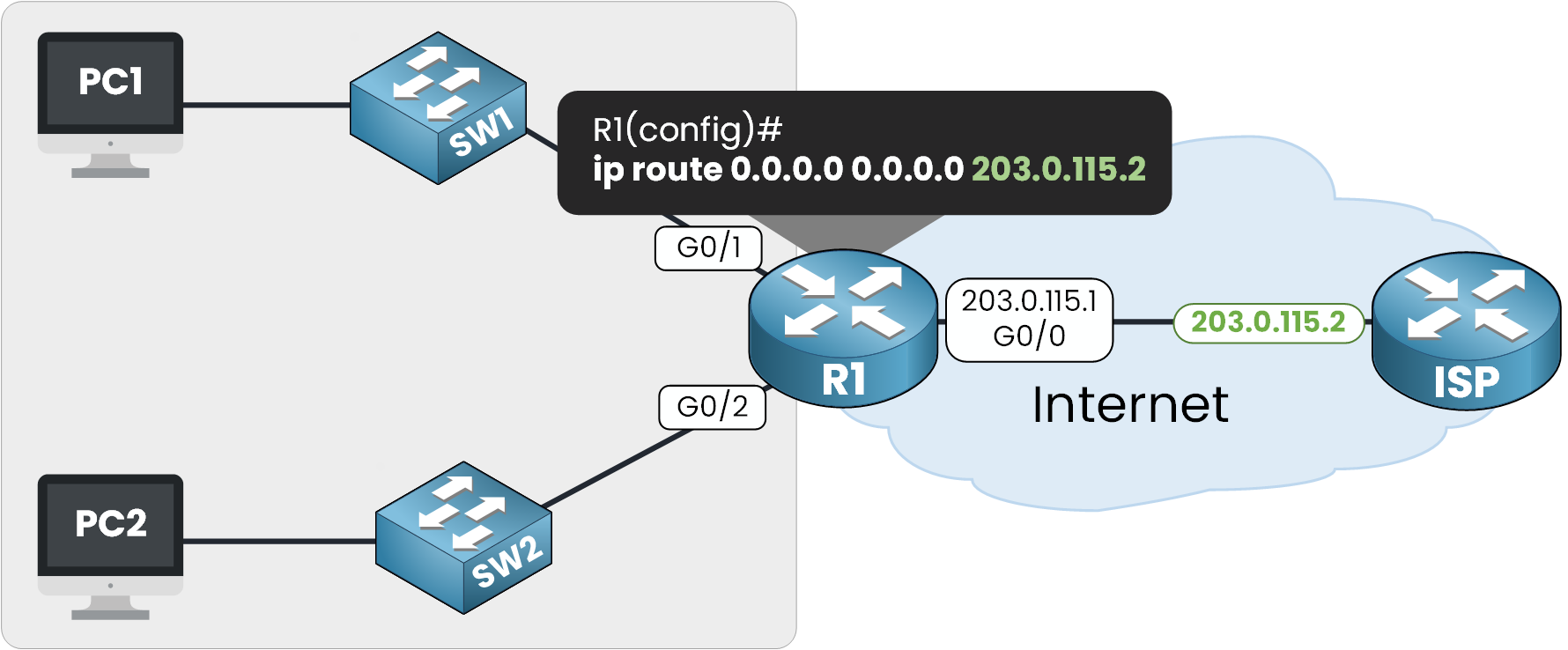
Figure 3 – Configuring the Default Static Route on R1
✅ With Default Static Route
Since the default static route is created, our router R1 is now able to forward traffic to unknown destinations to the next hop 203.0.115.2 by using interface G0/0. If we retake our example, PC1 sends a packet to destination IP 8.8.8.8. R1 doesn't have a specific IP route to this destination, the default static route is matched.
40 % Complete: you’re making great progress
Unlock the rest of this lesson
If you’d like to continue your CCNA journey, simply create your free account.
Access all CCNA lessons
Practice with hands-on labs
Train with Practice exams and Quizzes
Progress tracking in your dashboard
Made by network engineers - CCNP certified
learners globally
Default Static Route
A default static route acts as a fallback path when no specific route exists in the routing table. In this lesson, you’ll learn how it works, how to configure it on Cisco routers, and why it’s essential for reaching external networks like the Internet.