By default, ports connected to end-user devices (PCs, printers) send BPDUs as part of the Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) process.
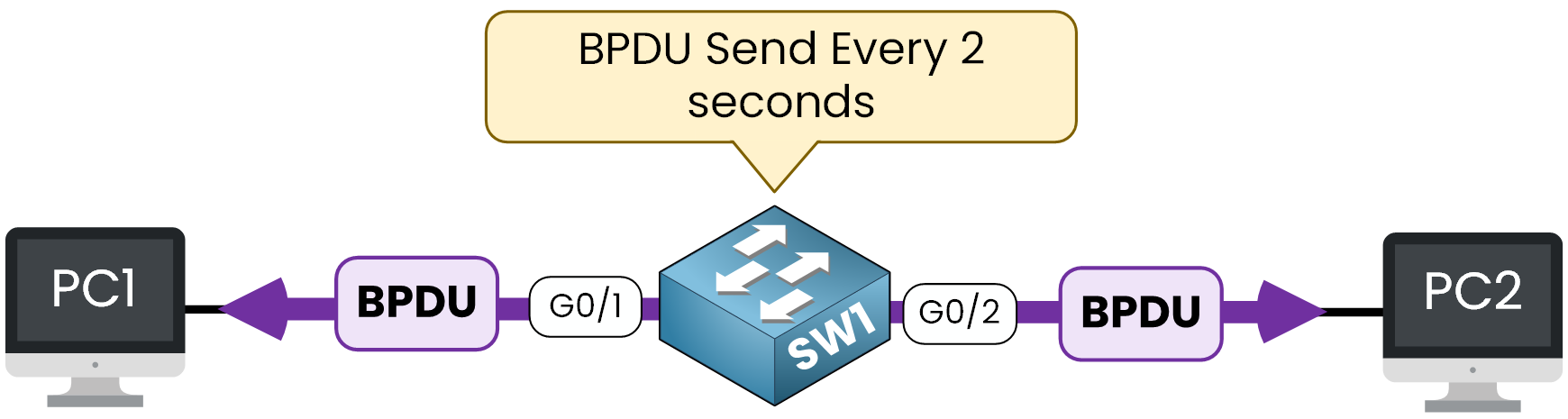
Figure 1 – Switches send BPDUs every 2 seconds by default
However, in most cases, sending BPDUs on these ports is unnecessary and can expose sensitive STP topology information.
BPDU Filter is an STP feature that disables sending and receiving of BPDUs on ports, enhancing security and preventing unwanted BPDU exchanges.
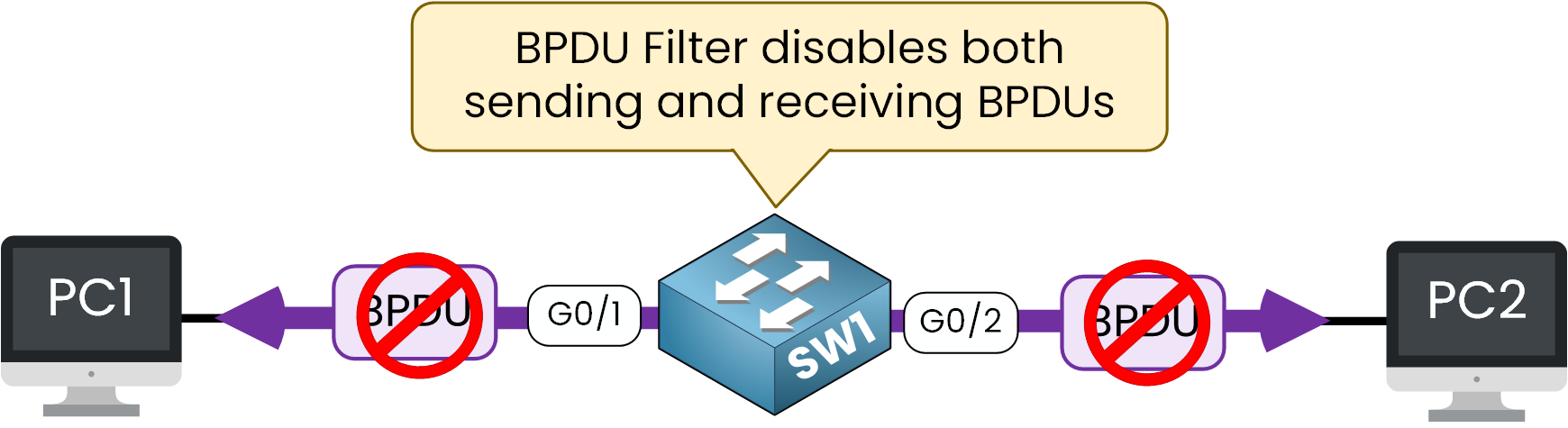
Figure 2 – BPDU Filter blocks both sending and receiving of BPDUs
Real-World Use Case
BPDU Filter is especially useful in scenarios like company mergers, where two networks with separate STP topologies are interconnected.
BPDU Filter ensures that BPDUs are not exchanged between the different STP topology preserving their independent spanning tree configurations.
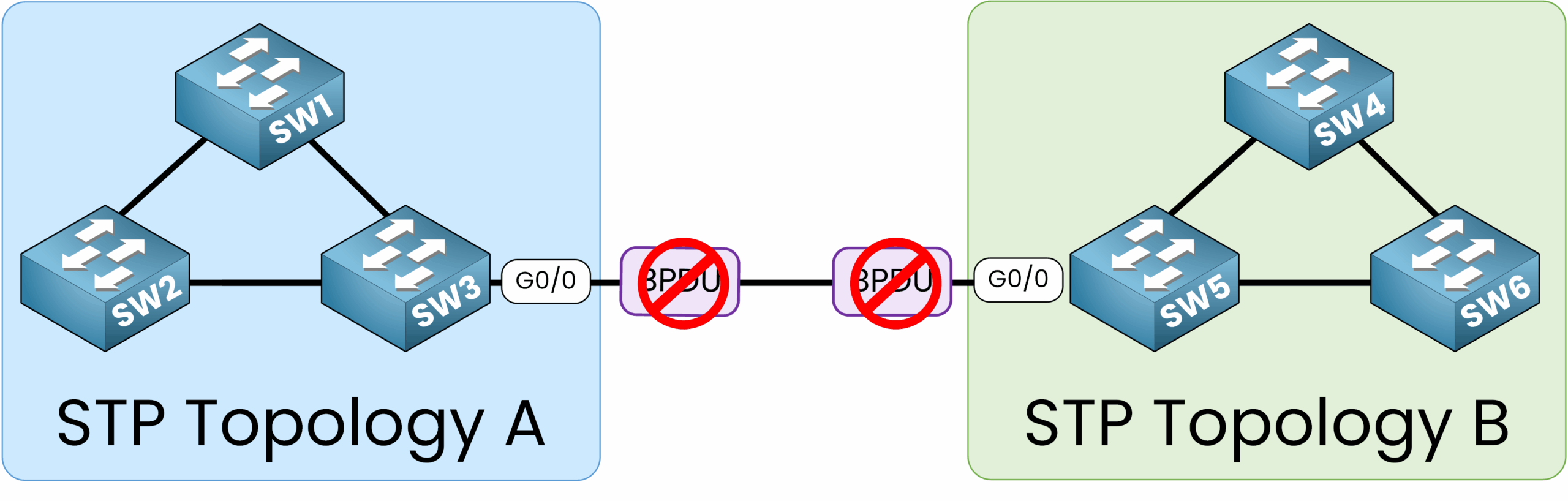
Figure 3 – BPDU Filter prevents STP topology exchanges between two networks
This ensures that each network maintains its own spanning tree configuration without sharing or disrupting the other’s topology.
Answer the question below
What does BPDU Filter block on a port?
BPDU Filter can be configured in two ways:
On Individual Ports: Apply to specific interfaces for precise control over which ports should stop sending BPDUs.
Globally: Enable across all PortFast-enabled ports on the switch.
Enabling BPDU Filter on Individual Ports
Let’s configure on interface GigabitEthernet0/0 of switch SW3 and SW5 to prevent the exchange of BPDUs between two separate STP topologies.
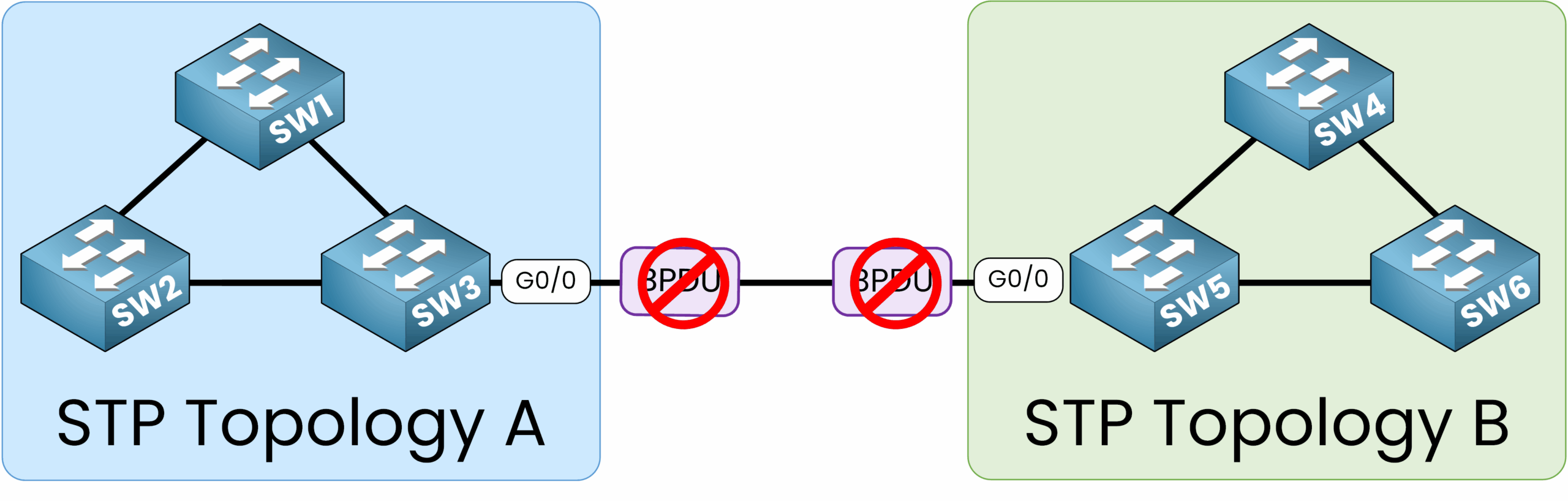
Figure 4 – STP Topology Used to Configure BPDU Filter
Configuring BPDU Filter on SW3
Enable BPDU Filter on the interface:
SW3# conf t Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z. SW3(config)# interface g0/0 SW3(config-if)# spanning-tree bpdufilter enable SW3(config-if)# endVerify the configuration:
SW3# show spanning-tree interface g0/0 detail Port 1 (GigabitEthernet0/0) of VLAN0001 is designated forwarding Port path cost 4, Port priority 128, Port Identifier 128.1. Designated root has priority 32769, address 5030.9804.6800 Designated bridge has priority 32769, address 5030.9804.6800 Designated port id is 128.1, designated path cost 0 Timers: message age 0, forward delay 0, hold 0 Number of transitions to forwarding state: 1 Link type is point-to-point by default Bpdu filter is enabled BPDU: sent 63, received 2As shown above, BPDU Filter is enabled on GigabitEthernet0/0 of SW3. This interface no longer participates in BPDU transmission or processing.
40 % Complete: you’re making great progress
Unlock the rest of this lesson
If you’d like to continue your CCNA journey, simply create your free account.
Access all CCNA lessons
Practice with hands-on labs
Train with Practice exams and Quizzes
Progress tracking in your dashboard
Made by network engineers - CCNP certified
learners globally
BPDU Filter
BPDU Filter is a Spanning Tree feature that prevents ports from sending or receiving BPDUs, protecting the topology from unwanted exchanges. This lesson explains when to use BPDU Filter, how to configure it, and why it matters for securing STP.