In a routing table, each destination network (identified by its prefix and prefix length) can appear only once. Yet, it’s common for a router to learn about the same destination from multiple routing sources.
Administrative Distance (AD) is the value that helps the router decide which of those sources is more trustworthy. It assigns a reliability score to each route, allowing the router to prefer one source over another when multiple options exist.
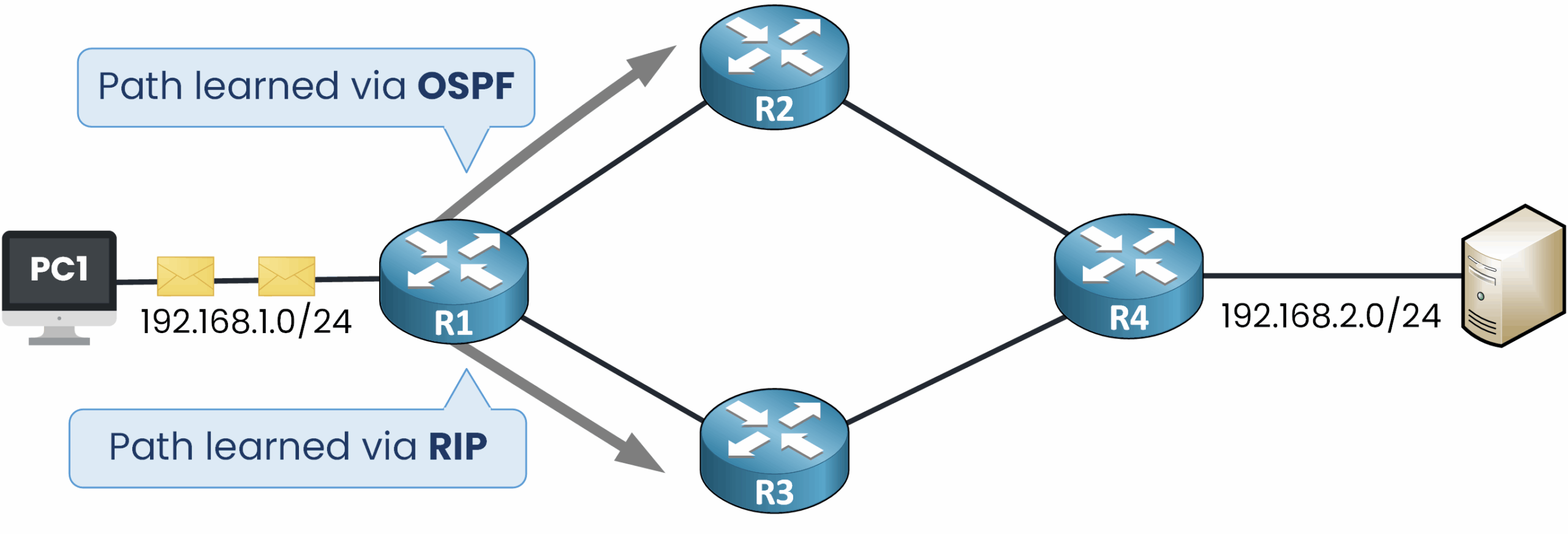
Figure 1 – Router learns paths to the same network via OSPF and RIP
To see why this matters, let’s consider a practical example. In the network below, we have four routers, and PC1 needs to send traffic to a server in the 192.168.2.0/24 network.
When the traffic reaches the first router, R1 discovers two possible paths to reach 192.168.2.0/24:
One path learned through the OSPF dynamic routing protocol
Another path learned through the RIP dynamic routing protocol
Since OSPF and RIP each use their own metric to select the best path, this raises an important question:
Which path should be installed in the routing table?
Which routing source should R1 trust?
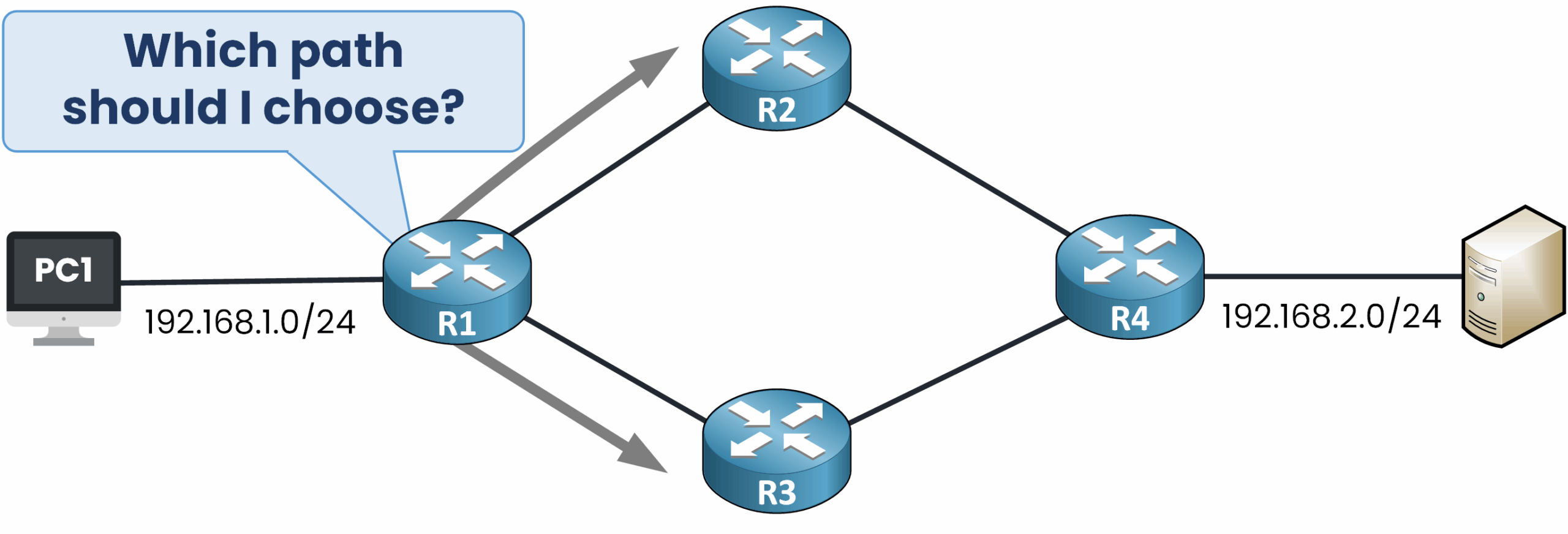
Figure 2 – Router faces a choice between two different network paths
This is exactly where Administrative Distance comes into play. In our example, it allows the router to make a choice when different routing sources point to the same destination.
The AD is a number assigned to each route that indicates how reliable the source is. The lower the value, the more the router will trust that route.
Administrative Distance is used first to select the most trusted routing protocol when multiple protocols advertise the same destination. Once the protocol is chosen, its metric is used to determine the best path within that protocol.
Answer the question below
Below is a table showing the default Administrative Distance values for different types of routes.
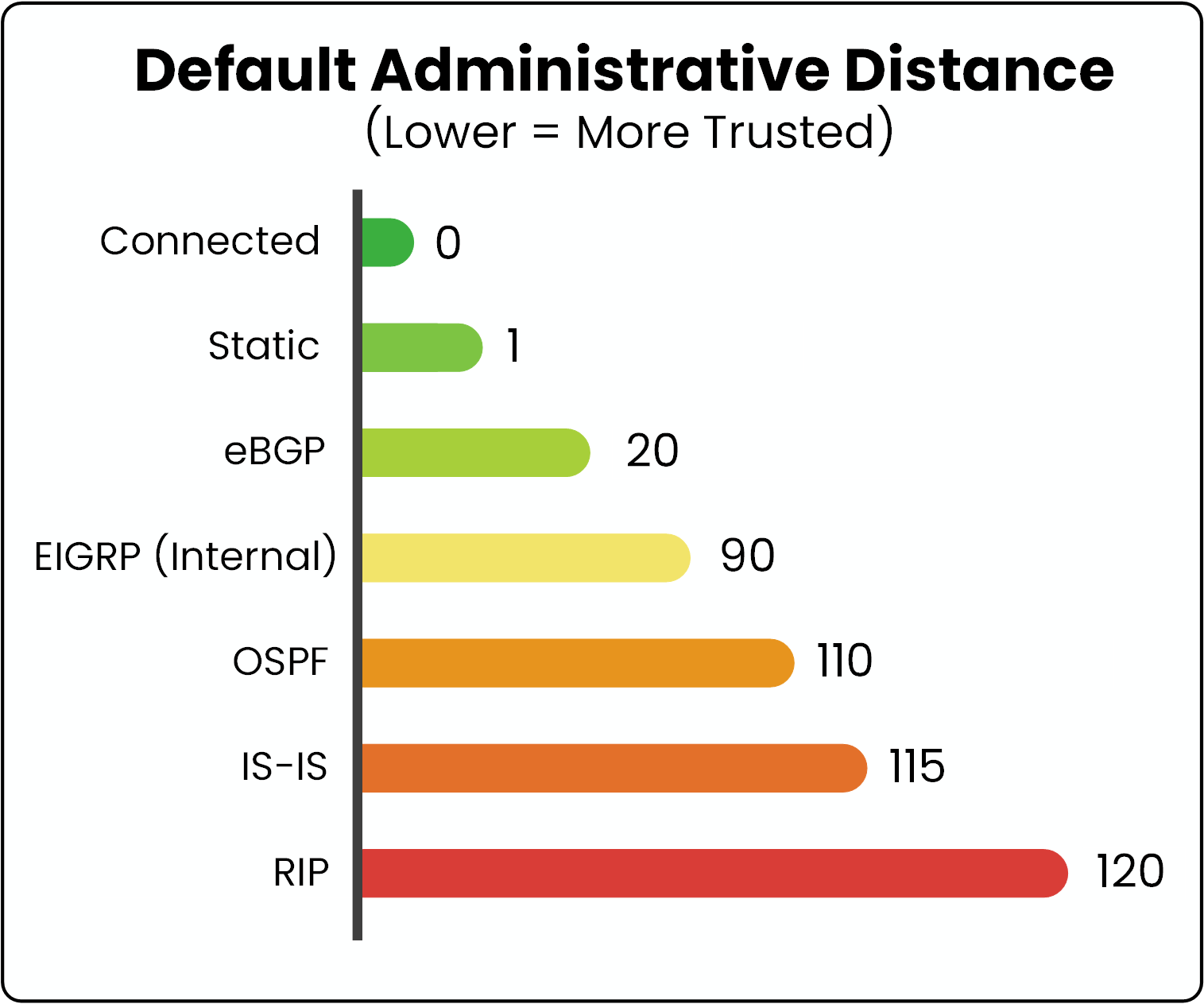
Figure 3 - Default Administrative Distance
The smaller the Administrative Distance, the more trusted the route is. At the very top, we have directly connected routes with an AD of 0. This makes sense because these networks are physically connected to the router’s interfaces, there’s no need to question their reliability.
Next, we have static routes with an AD of 1. These are configured manually by a network administrator, which means they are considered highly reliable.
Then we move on to dynamic routing protocols. Here, I’ve listed the most common ones and the values you should know for the CCNA.
For example:
40 % Complete: you’re making great progress
Unlock the rest of this lesson
If you’d like to continue your CCNA journey, simply create your free account.
Access all CCNA lessons
Practice with hands-on labs
Train with Practice exams and Quizzes
Progress tracking in your dashboard
Made by network engineers - CCNP certified
learners globally
Administrative Distance
Administrative Distance tells the router which routing source to trust when different protocols advertise the same destination. This lesson explains how AD influences the routing table and helps you troubleshoot route selection with confidence.