Imagine if you had to manually set an IP address, subnet mask, gateway, and DNS servers on your computer every time you joined a network. It would quickly become tedious and prone to mistakes.

Figure 1 – DHCP client requesting IP configuration from the DHCP server.
DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol) is a network protocol that solves this issue by automatically assigns all necessary network settings. This means you can connect to a network and start communicating immediately without manual input.
What does DHCP provide?
When your device connects to a network, DHCP typically assigns:
An IP address: Identifies your device on the network
A subnet mask: Defines the local network range
A default gateway: Allows communication with external networks, including the internet
DNS servers: Resolves domain names like google.com into IP addresses
This automatic process ensures that devices such as computers, smartphones, and printers are correctly configured without human intervention.
Answer the question below
What does DHCP prevent when joining a network?
Understanding DHCP in Action
When your device (the DHCP client) connects to a network, it sends out a request to find a DHCP server which is usually your router, or a dedicated server in larger networks.

Figure 2 – DHCP client requesting IP configuration from the DHCP server.
The server responds by assigning all the necessary IP settings for a specific time period, called a lease.

Figure 3 – DHCP server sending IP configuration to the client.
Even though everything happens automatically, you can still check whether your device is using DHCP.
Answer the question below
What is the time period for DHCP settings?
How to Verify DHCP on Windows
Method 1: Through the Control Panel
Open the Control Panel and go to Network and Sharing Center.
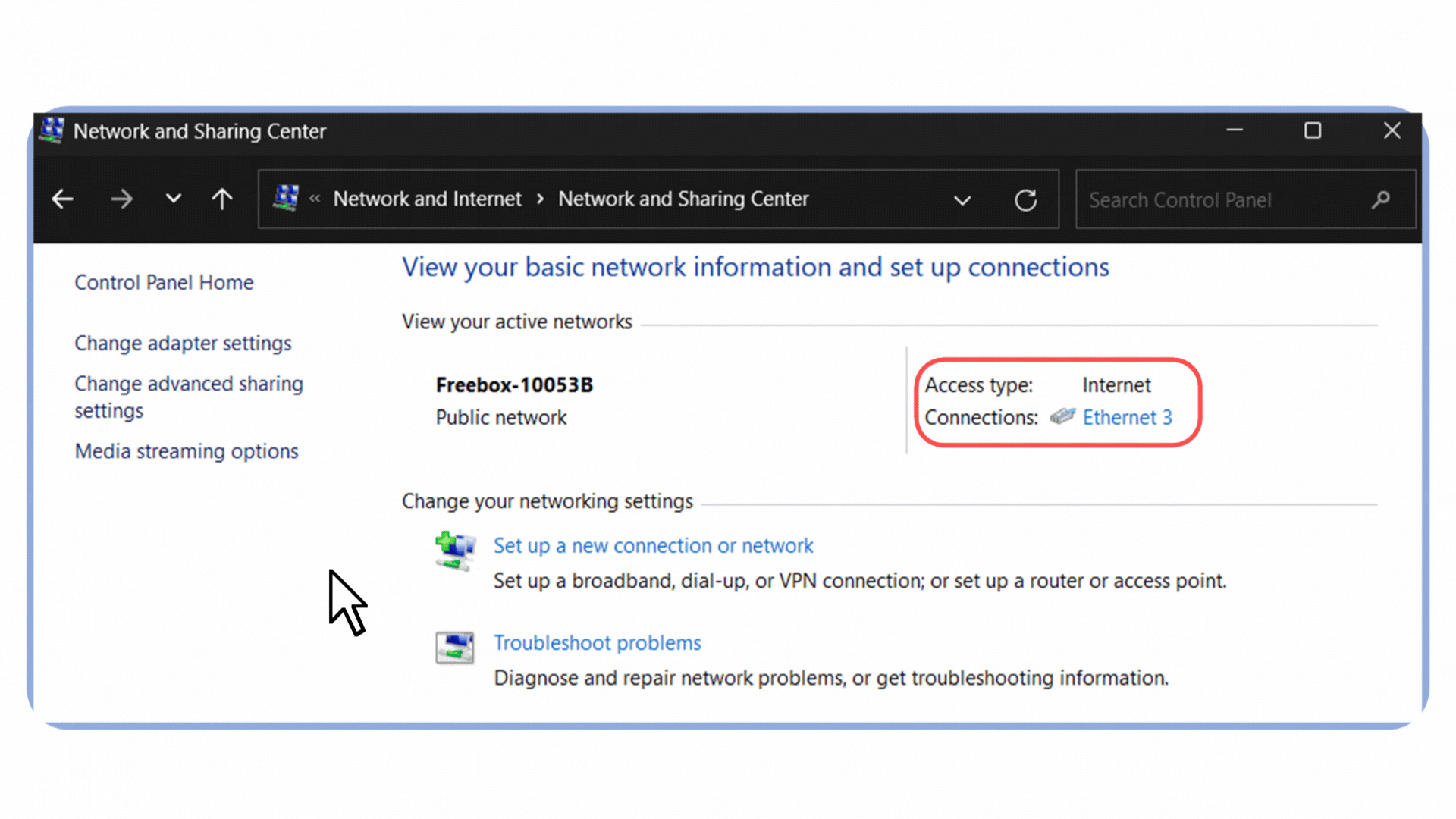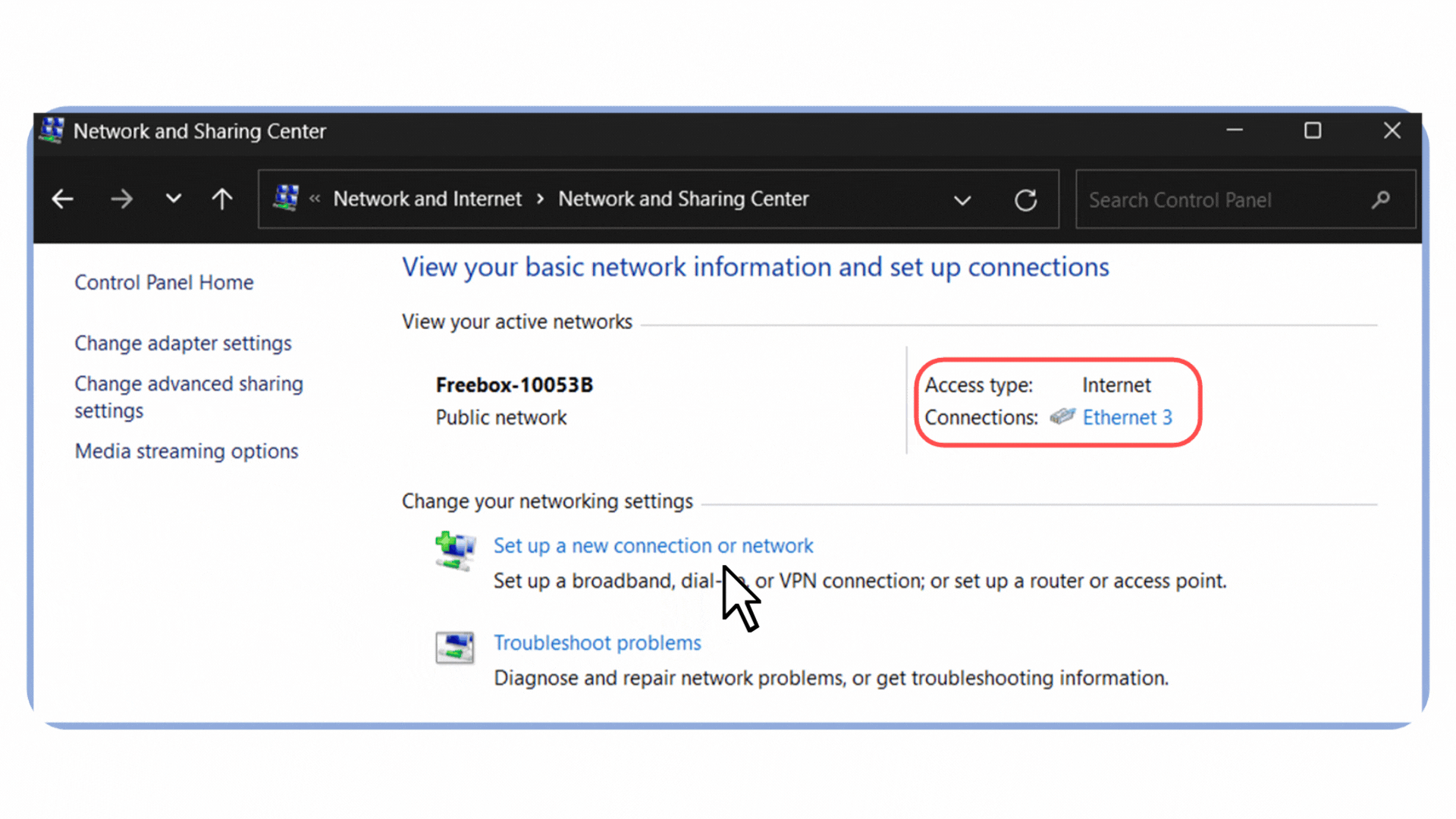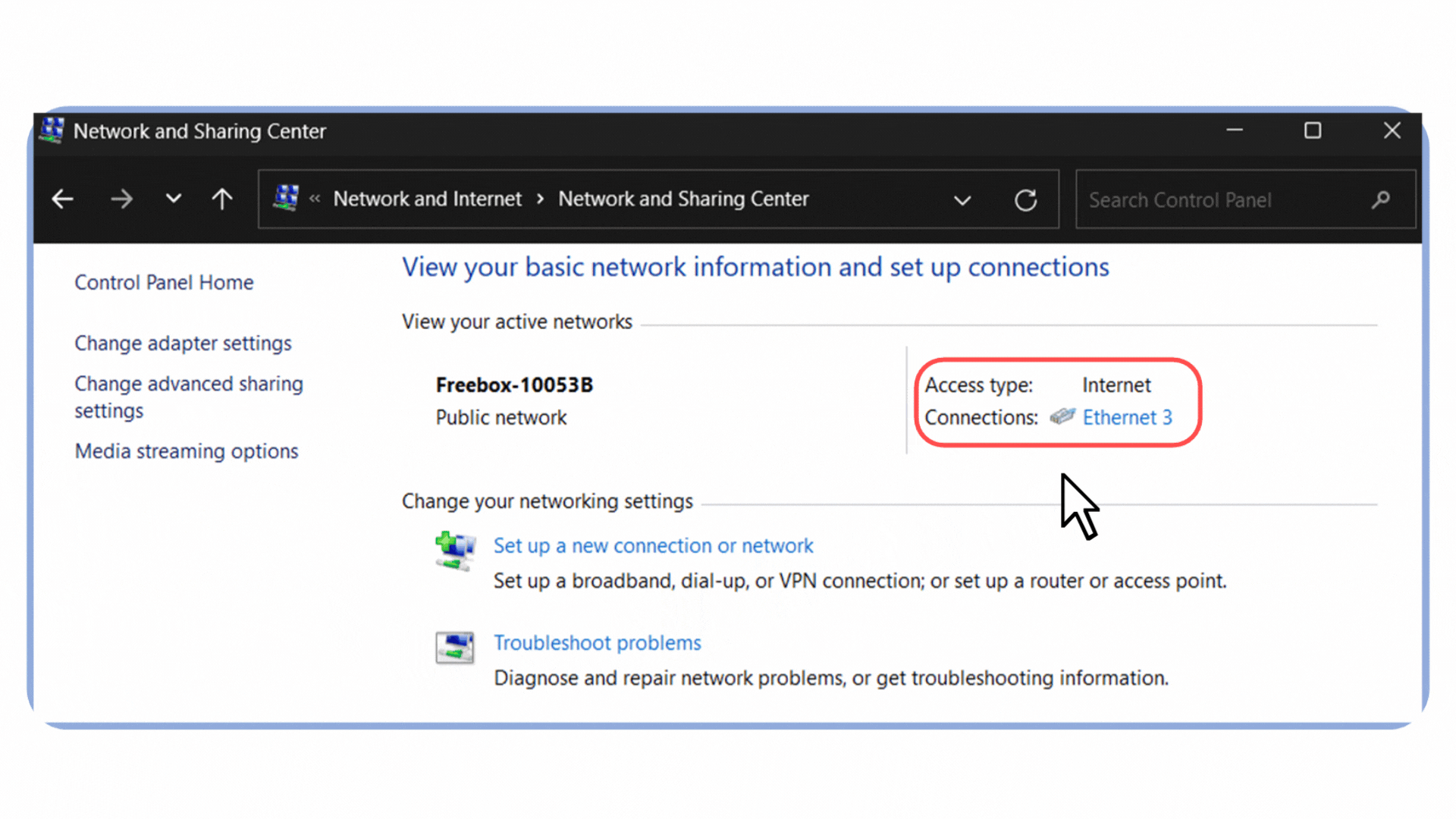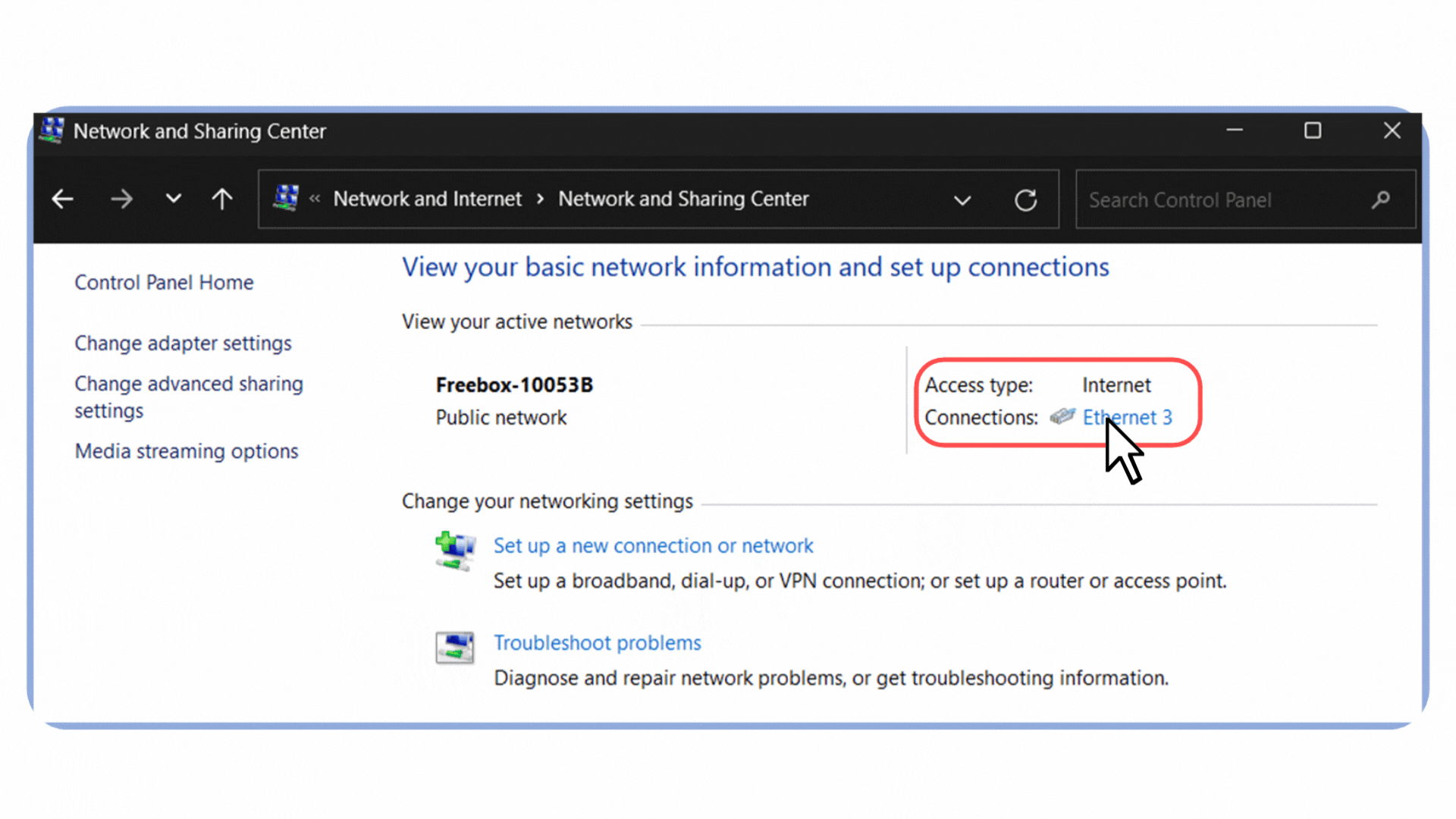
Figure 4 – Accessing the Network and Sharing Center from the Control Panel in Windows.
Click on your active connection. In my case, it’s labeled Ethernet 3 because I’m connected via an Ethernet cable.
Select Properties.
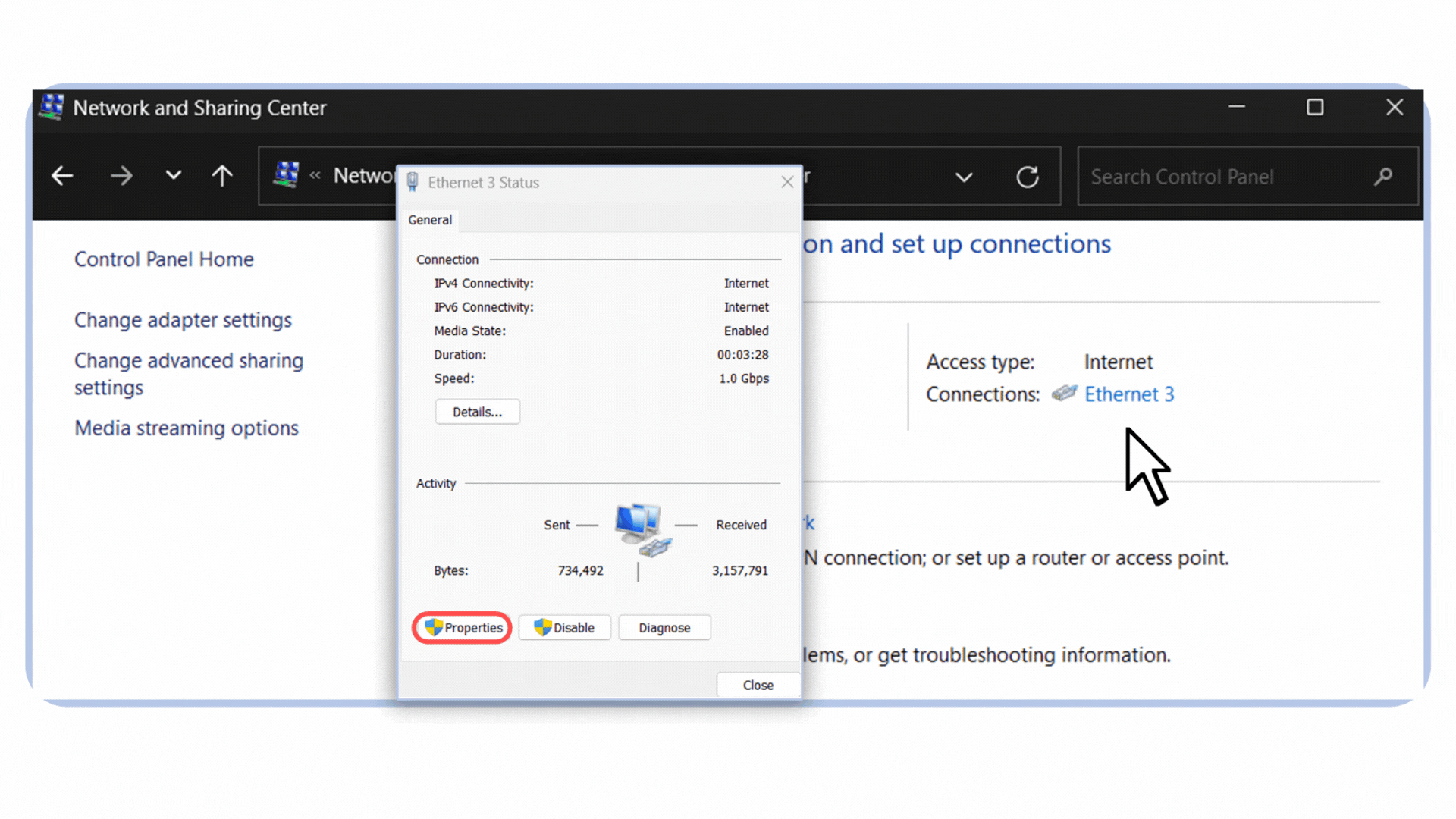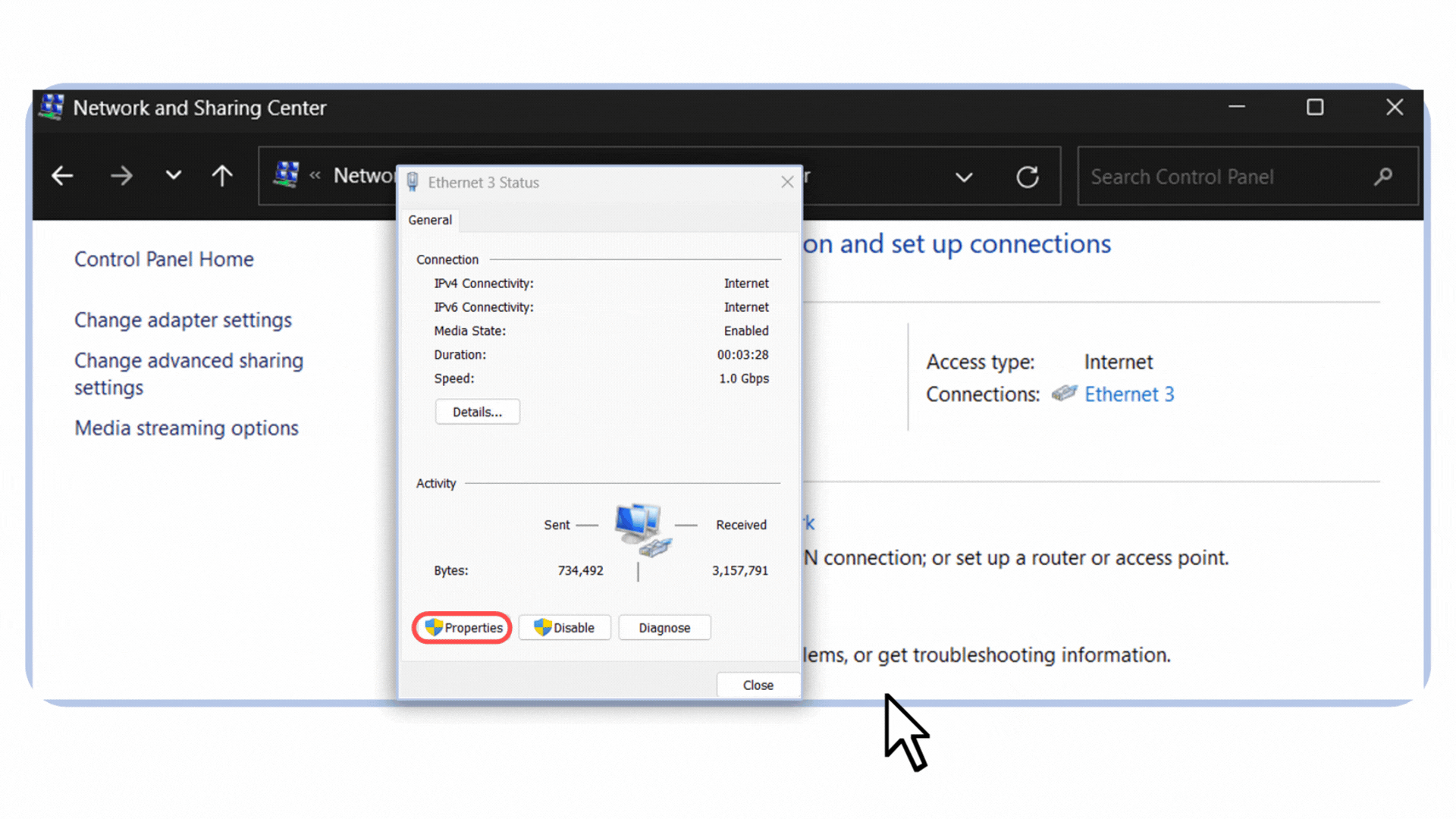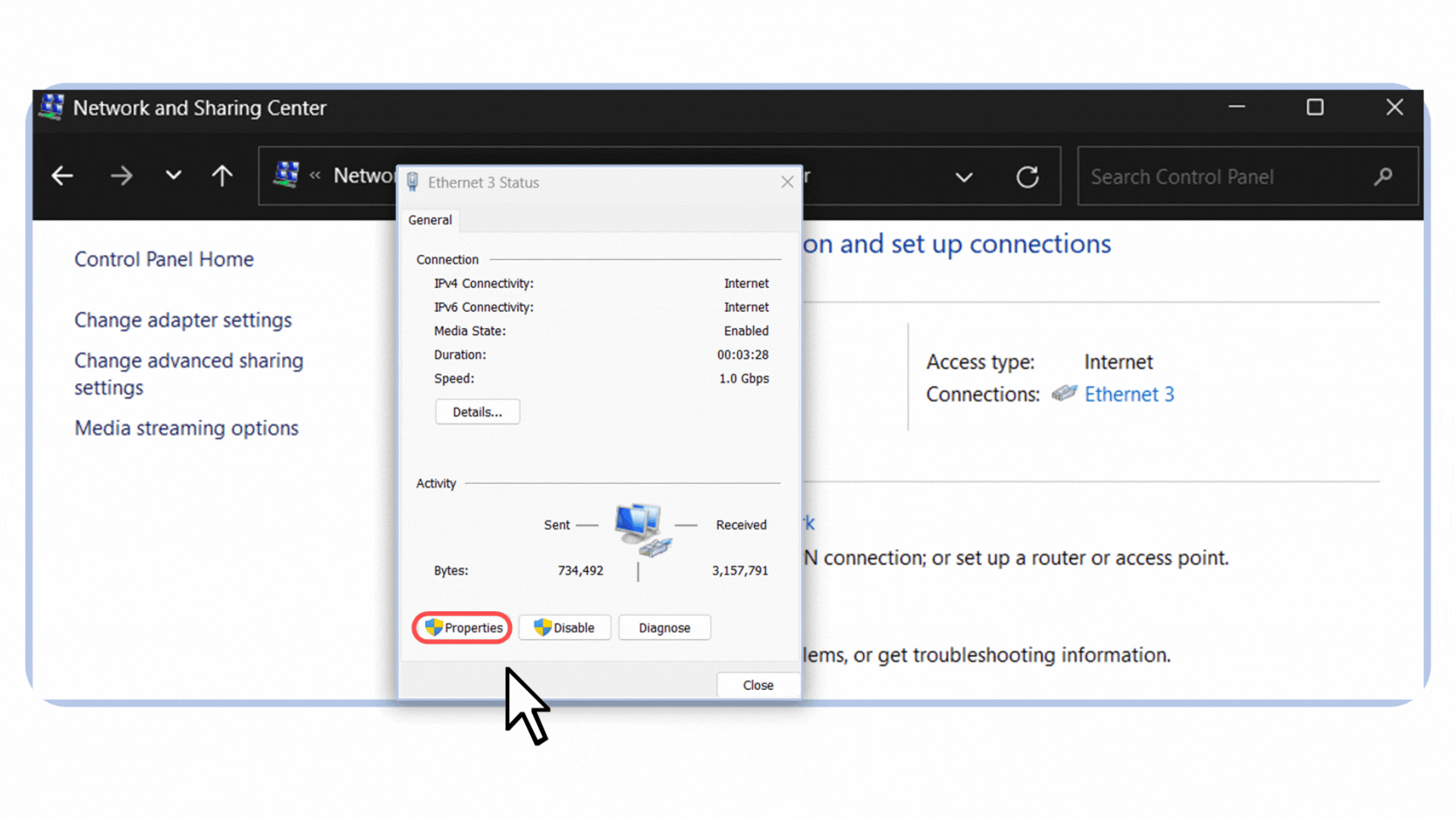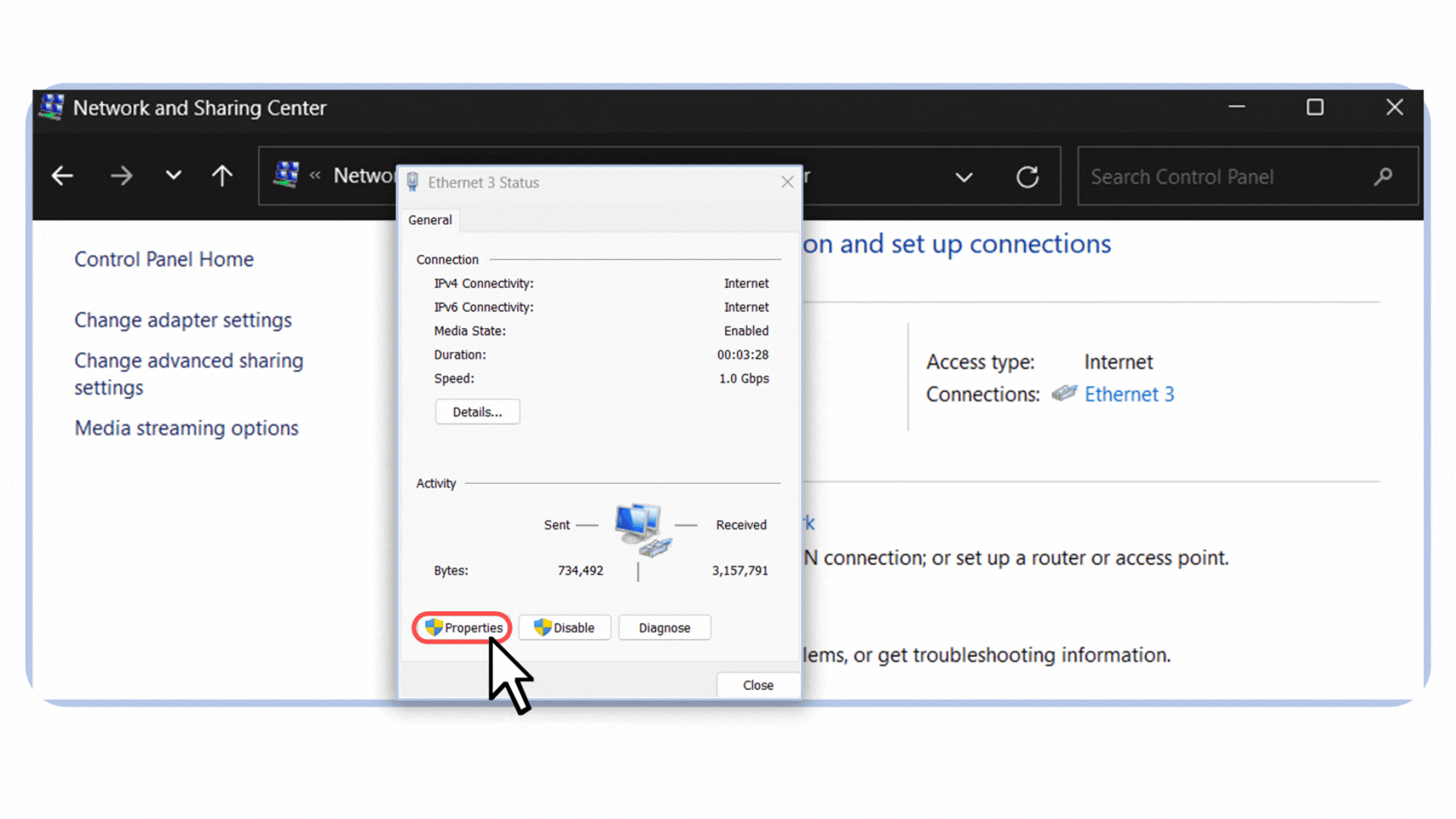
Figure 5 – Opening the Ethernet connection properties in Windows.
4. In the list, select Internet Protocol Version 4 (TCP/IPv4).
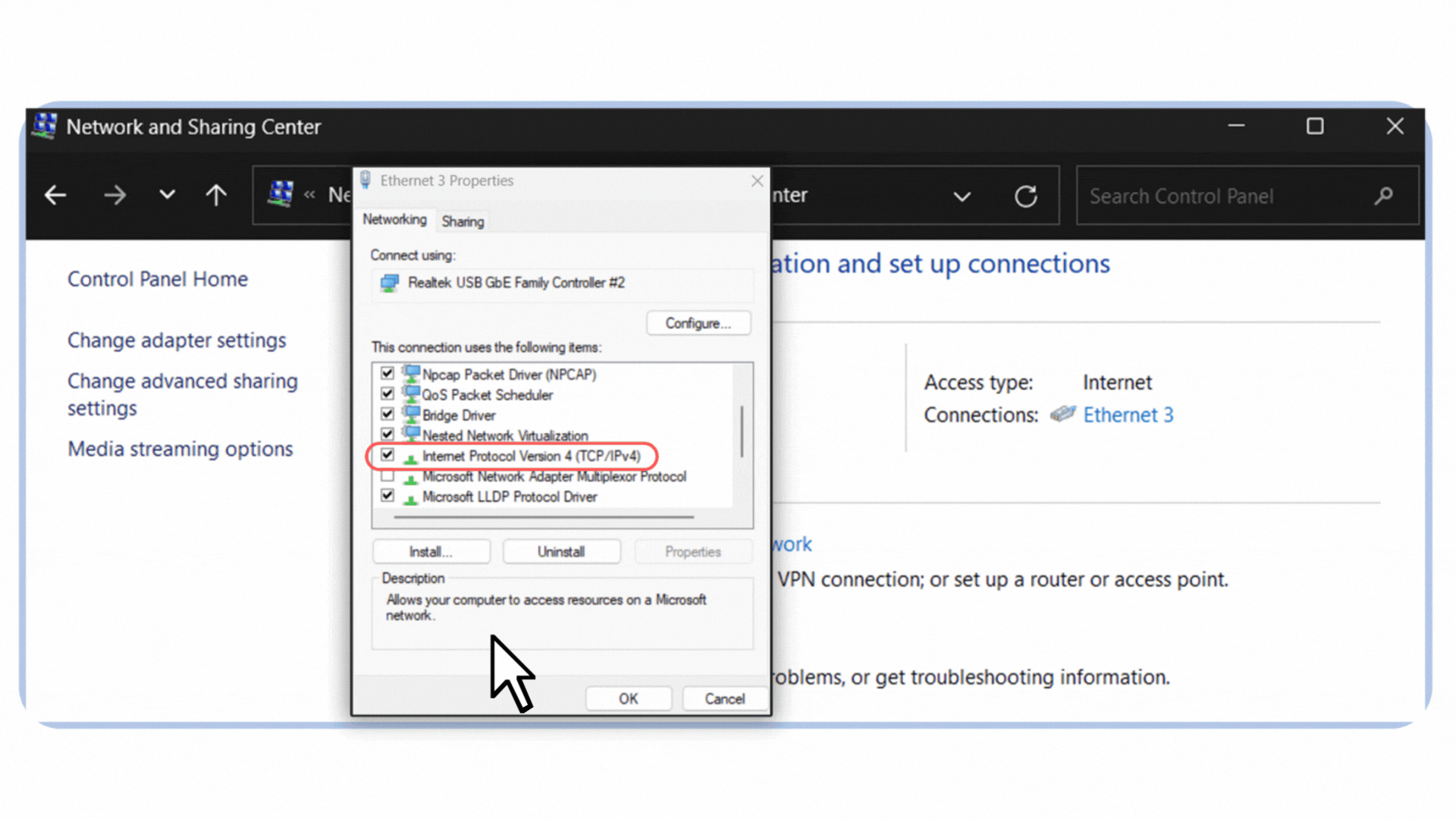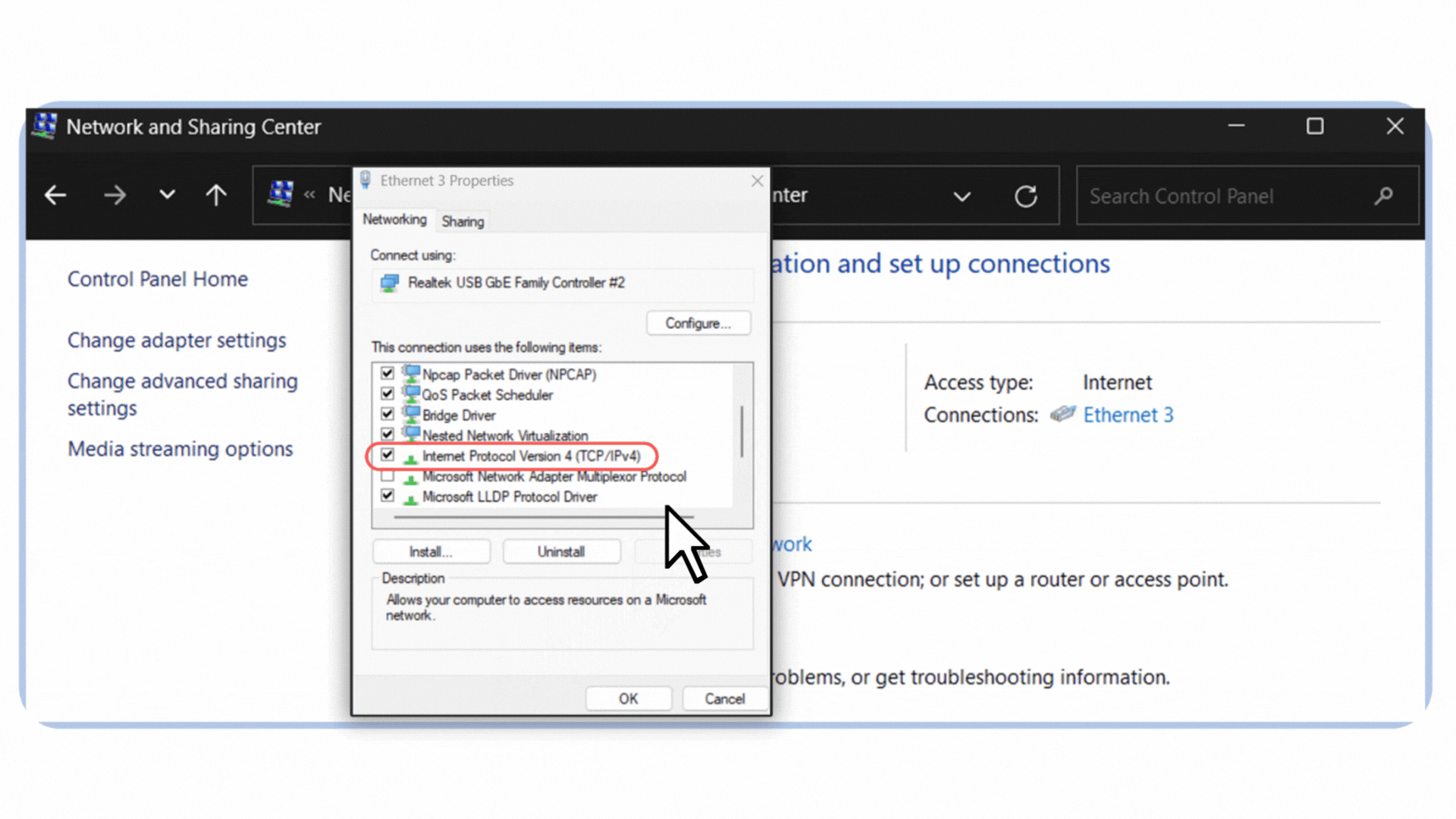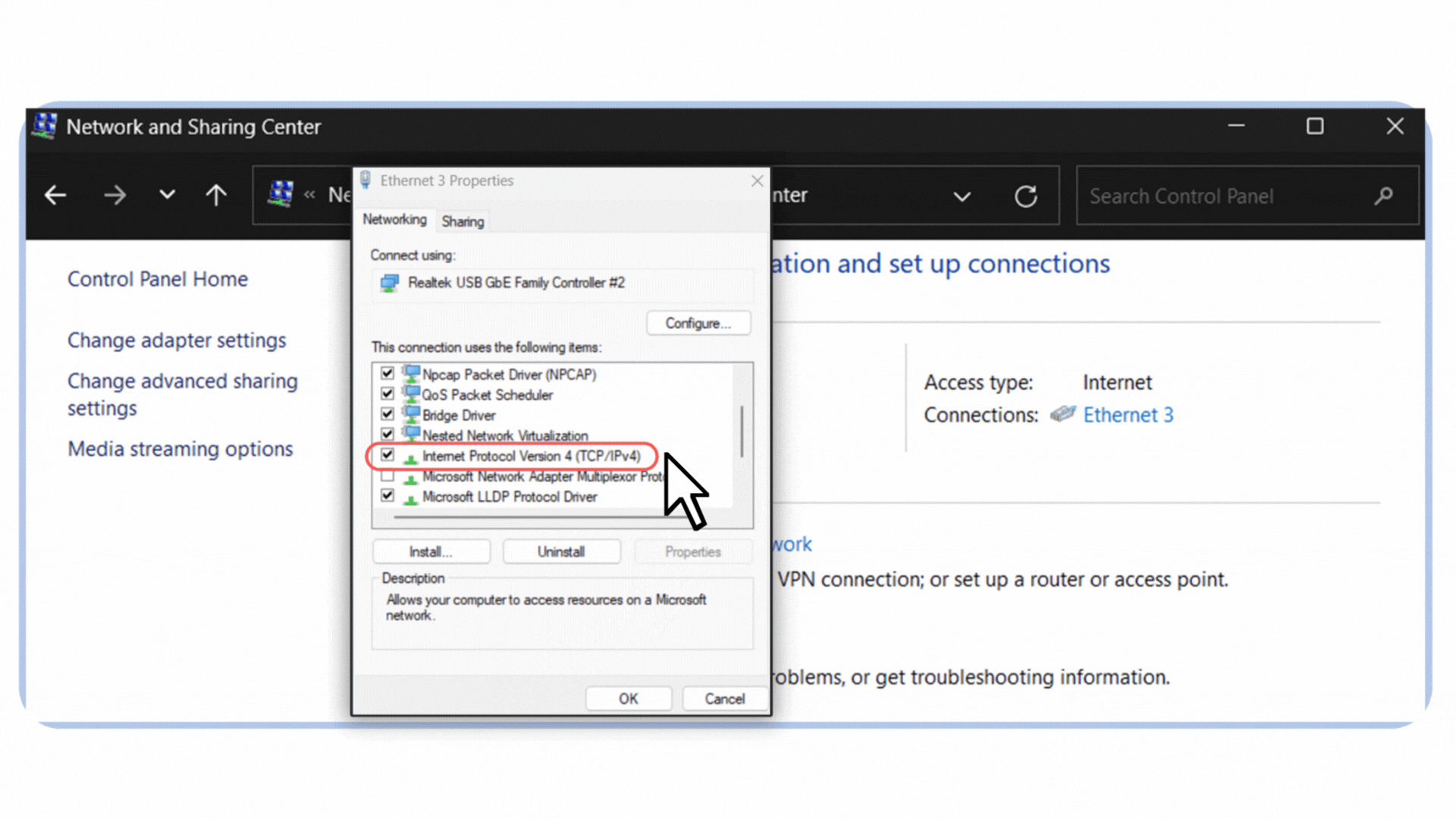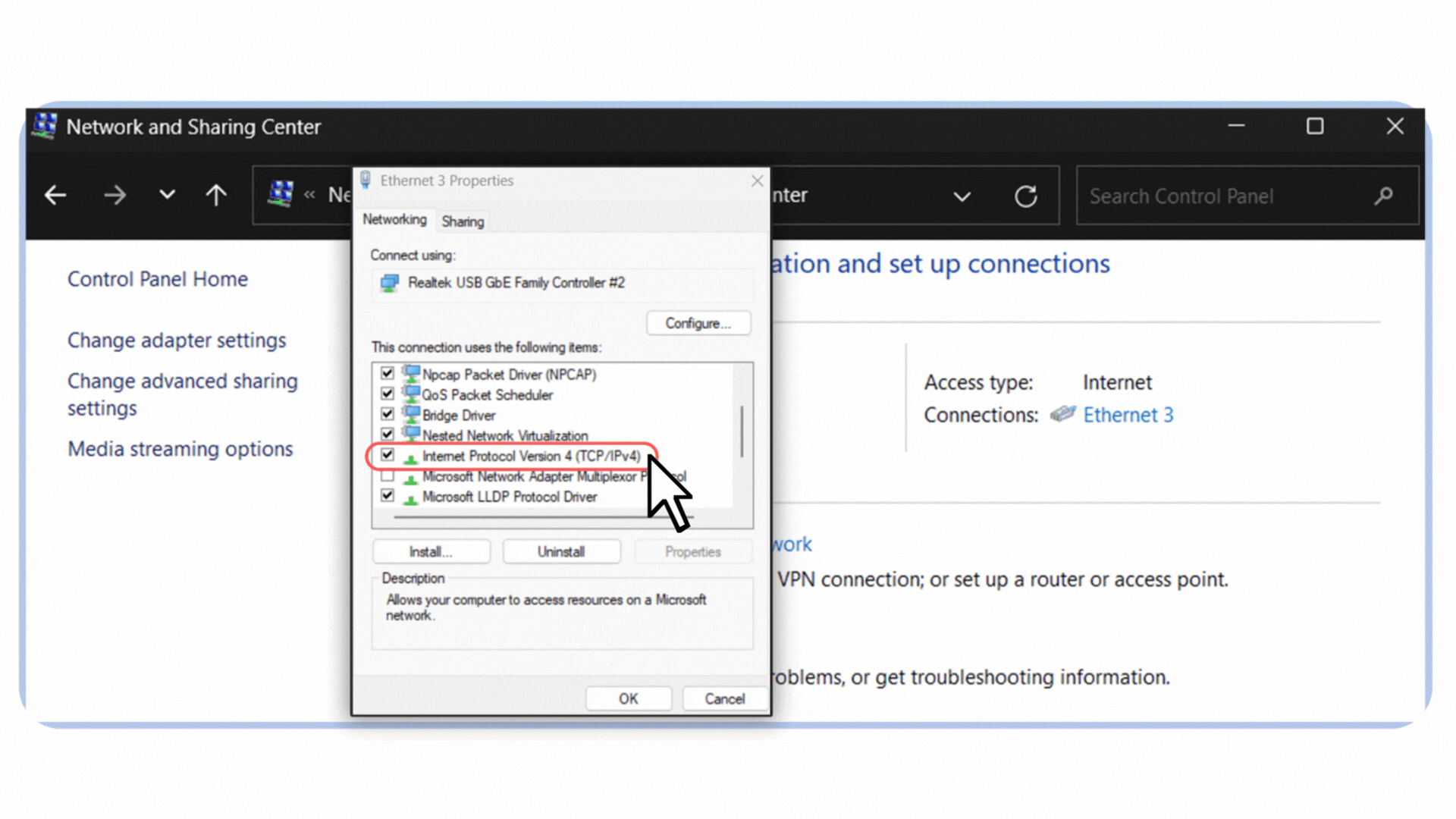
Figure 6 – Selecting Internet Protocol Version 4 (TCP/IPv4) in the Ethernet properties.
5. Make sure both options are set to:
"Obtain DNS server address automatically”
“Obtain an IP address automatically”
If both are selected, DHCP is enabled.
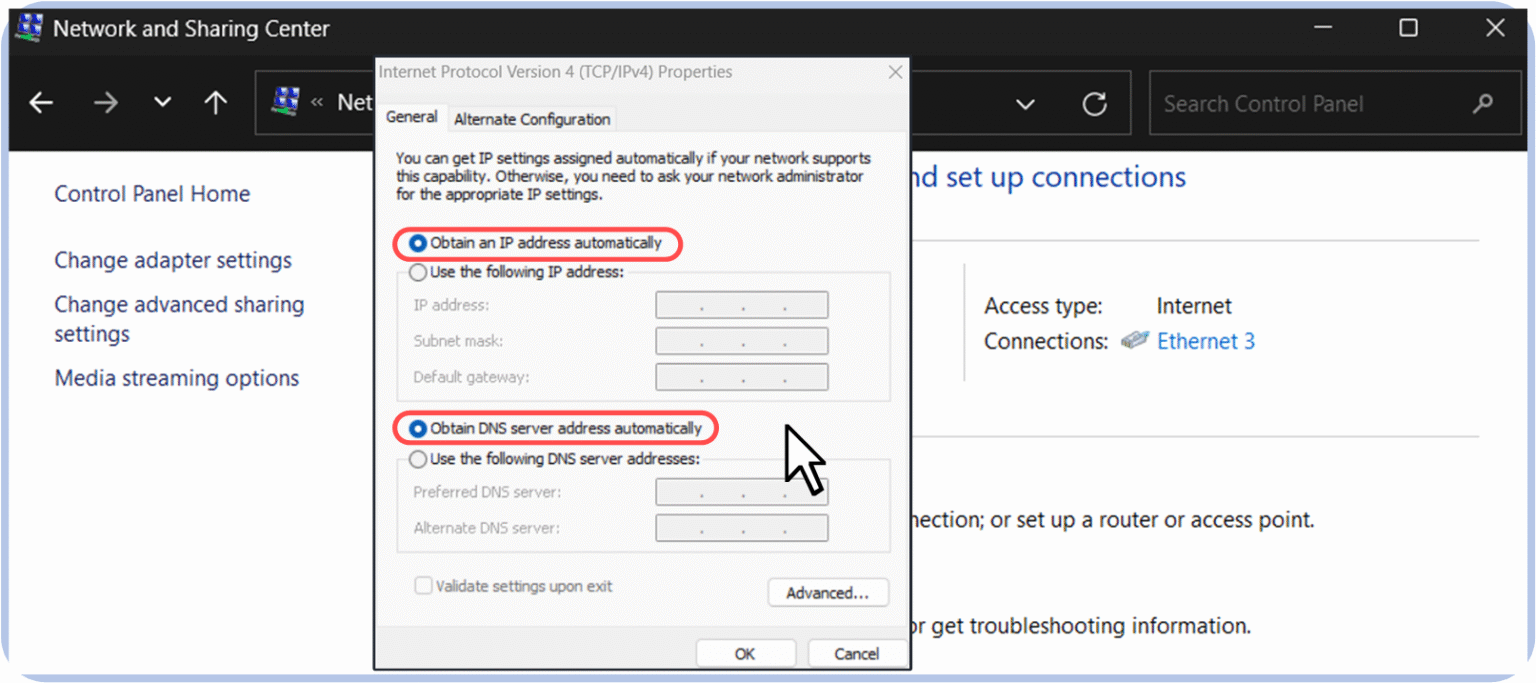
Figure 7 – DHCP enabled with automatic IP and DNS server address configuration.
Method 2: Using Command Prompt
You can also check if DHCP is enabled using the ipconfig /all command.
Open Command Prompt and type:
C:\Users\PingMyNetwork>ipconfig /all /Output Omitted/ Ethernet adapter Ethernet 3: Connection-specific DNS Suffix . : Description . . . . . . . . . . . : Realtek USB GbE Family Controller #2 Physical Address. . . . . . . . . : 38-7C-76-11-B0-70 DHCP Enabled. . . . . . . . . . . : Yes Autoconfiguration Enabled . . . . : Yes IPv4 Address. . . . . . . . . . . : 192.168.1.19(Preferred) Subnet Mask . . . . . . . . . . . : 255.255.255.0 Lease Obtained. . . . . . . . . . : Monday, January 27, 2025 10:47:39 PM Lease Expires . . . . . . . . . . : Tuesday, January 28, 2025 10:47:39 AM Default Gateway . . . . . . . . . : 192.168.1.254 DHCP Server . . . . . . . . . . . : 192.168.1.254 DNS Servers . . . . . . . . . . . : 192.168.1.254 NetBIOS over Tcpip. . . . . . . . : Enabled /Output Omitted/What to Look For
DHCP Enabled: Yes
This confirms that your device uses DHCP to obtain its configuration.DHCP Server
This shows the IP address of the server that assigned your settings (often your home router).
IPv4 Address, Subnet Mask, Default Gateway
These are the parameters your device received automatically.
Lease Obtained / Lease Expires
These lines indicate the duration of the DHCP lease.
Answer the question below
Which field in ipconfig /all tells you that DHCP is enabled?
What is a DHCP Lease?
Lease Obtained: When the DHCP server assigned the IP address.
Lease Expires: When the address is no longer valid unless renewed.
When the lease expires, the client must request a new lease. If not, the IP is returned to the available pool for reuse by other devices.
This lease system prevents unused IPs from staying assigned forever. It helps the DHCP server manage addresses efficiently, especially on networks with many clients.
Answer the question below
We’ve seen that DHCP automatically assigns IP settings to devices.
But how does it actually work behind the scenes?
Let’s break it down together.
DHCP Ports
The DHCP protocol uses specific ports to communicate:
UDP port 68 — used by the DHCP client
UDP port 67 — used by the DHCP server
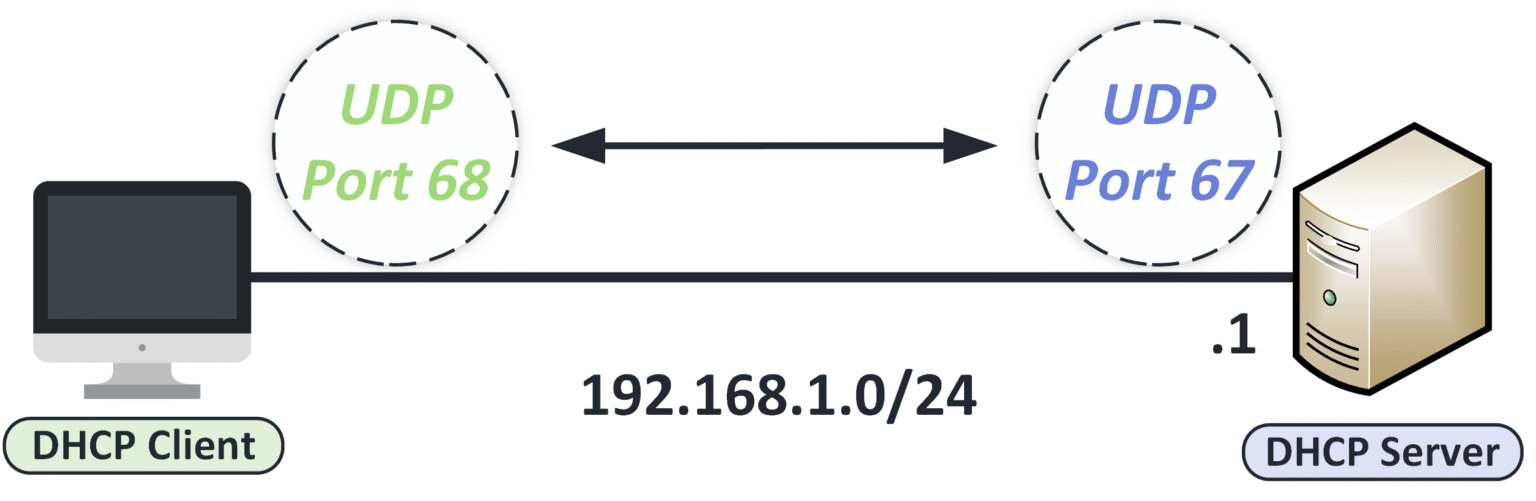
Figure 8 – DHCP communication using UDP port 68 for the client and UDP port 67 for the server.
These ports are used throughout the DHCP process.
Make sure to remember them for your CCNA exam.
The DHCP Process (Step by Step)
When a device connects to a network without an IP address, it uses DHCP to automatically obtain its network configuration.
This happens through a 4-step process often referred to as DORA:
Discover, Offer, Request, Acknowledge
Let’s go through each step.
Step 1 — DHCP Discover
When a device joins a network for the first time, it has no IP address and doesn’t know where the DHCP server is.
Figure 9 – DHCP client wondering where the DHCP server is to request an IP address.
To find one, it sends a DHCP Discover message as a broadcast on the network.

Figure 10 – DHCP client sending a Discover message to locate available DHCP servers.
This way, any DHCP server listening can respond with an offer.
In this capture, we can observe: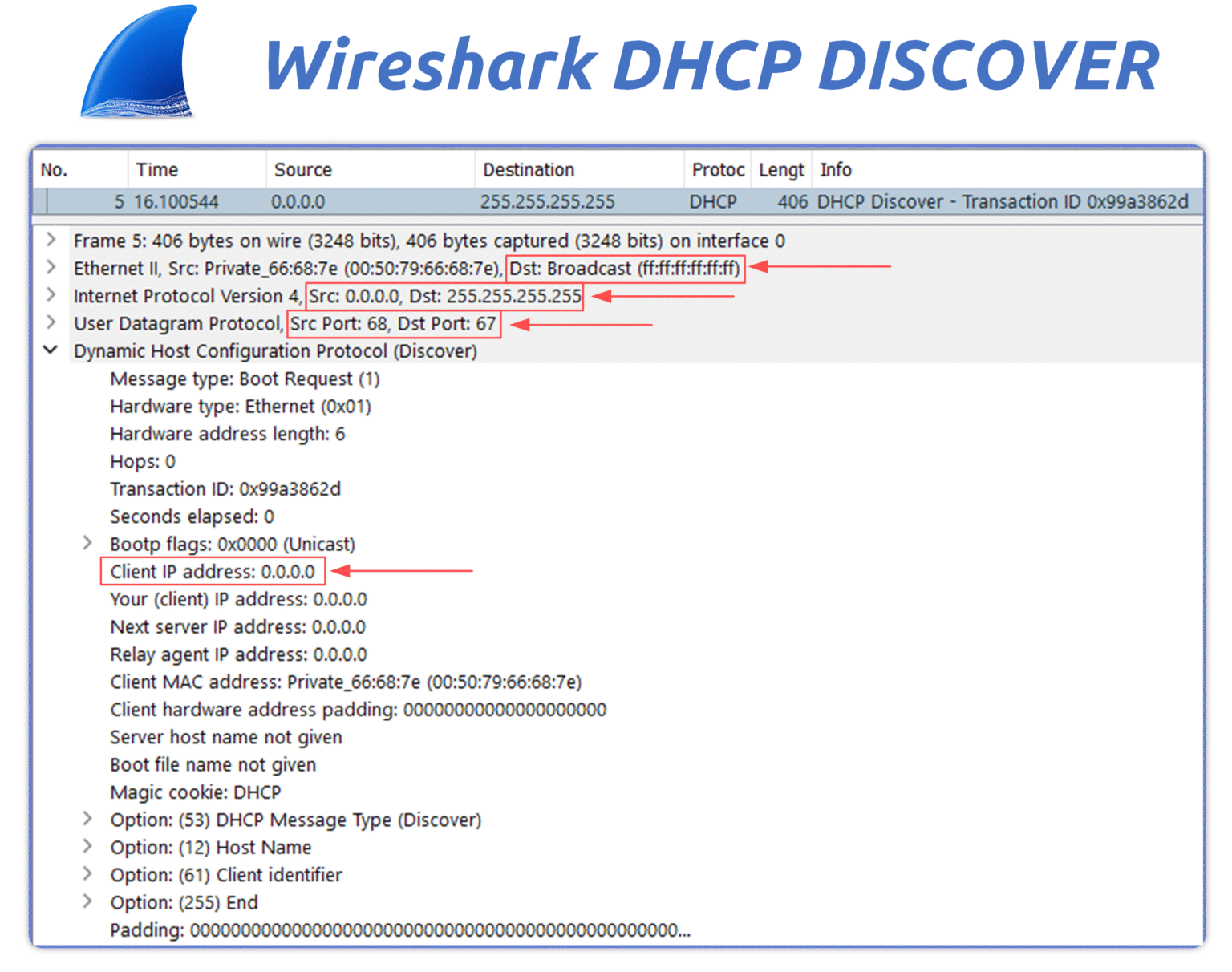
Figure 11 – Wireshark capture of a DHCP Discover broadcast using UDP ports 68 and 67.
Destination MAC: FF:FF:FF:FF:FF:FF — unknown server MAC, so broadcast.
Source IP: 0.0.0.0 — the client doesn't have an IP address yet.
Destination IP: 255.255.255.255 — broadcast to the entire subnet.
UDP Ports: source port 68 (client), destination port 67 (server).
This broadcast is essential because the client has no prior information about the server’s address.
Answer the question below
What message does the client send first?
Step 2 — DHCP Offer
When a DHCP server receives the Discover message, it replies with a DHCP Offer, proposing an IP address and configuration settings to the client.
This message is usually sent as a unicast directly to the client’s MAC address.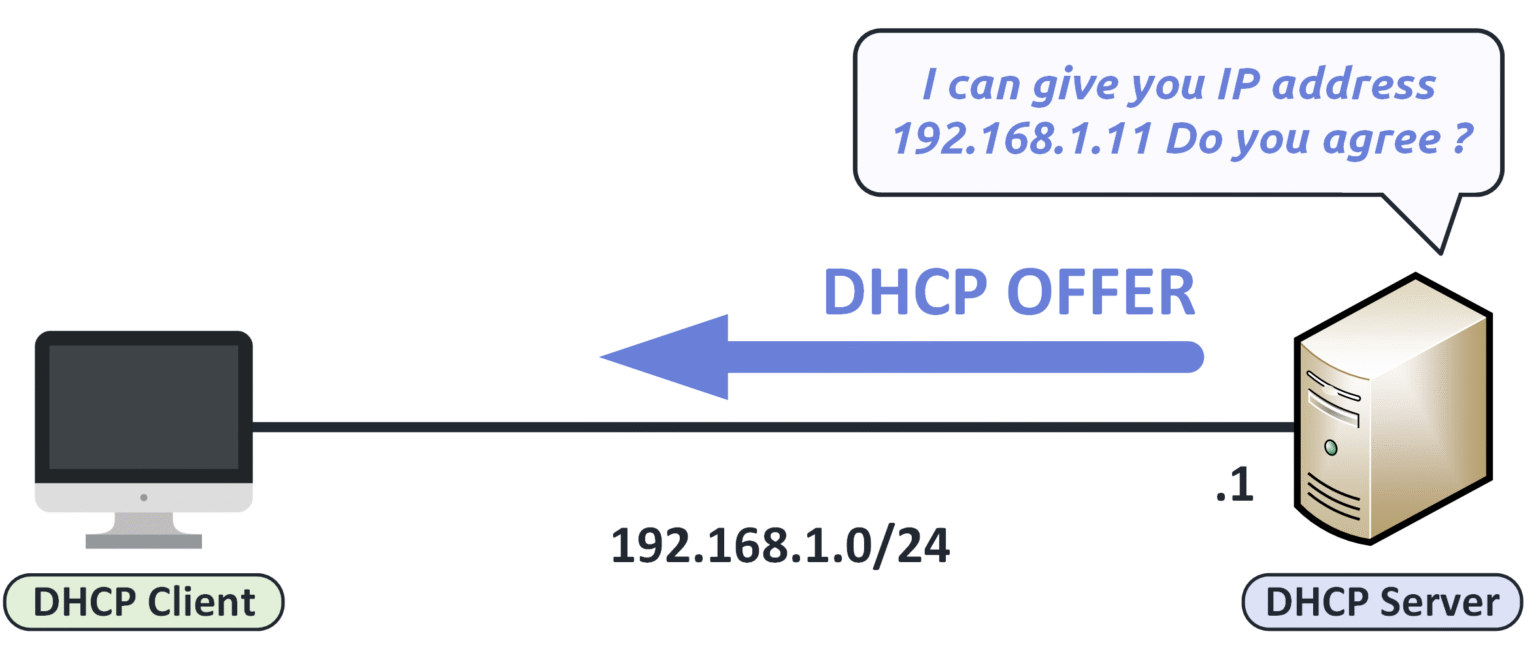
Figure 12 – DHCP server sending an Offer with an IP address to the client.
In this capture, we can observe:
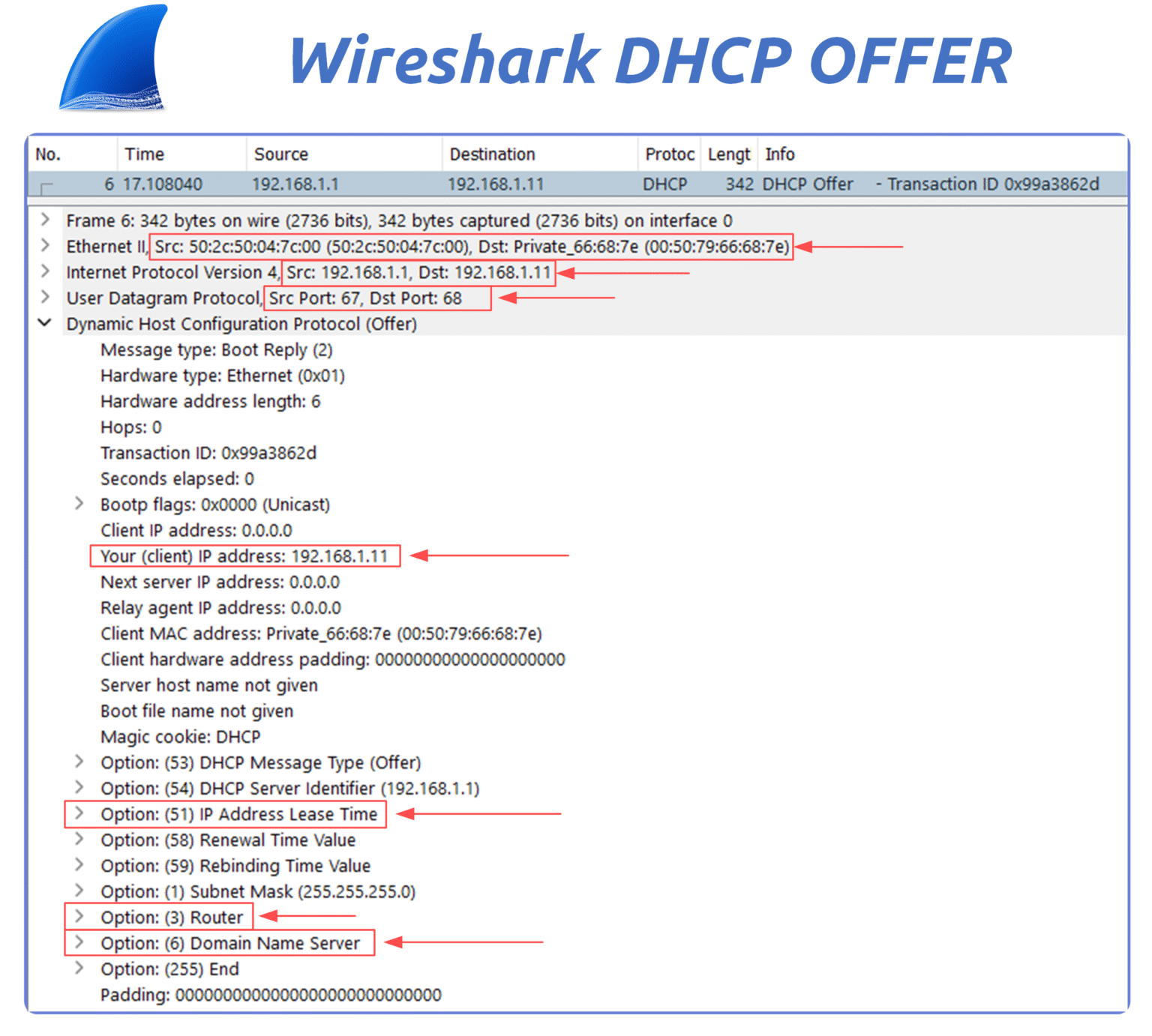
Figure 13 – Wireshark capture of a DHCP Offer proposing IP 192.168.1.11 to the client.
Source IP: DHCP server IP (192.168.1.1)
Destination IP: proposed IP for the client (192.168.1.11)
Destination MAC: MAC address of the client (learned from Discover)
UDP Ports: source port 67 (server), destination port 68 (client)
Your (Client) IP Address field: proposed IP (192.168.1.11)
DHCP Options:
Option 51: Lease time
Option 6: DNS servers
Option 3: Default gateway
The client can now decide whether to accept the proposed configuration.
Answer the question below
What message does the server send after Discover?
Step 3 — DHCP Request
After receiving the Offer, the client replies with a DHCP Request to confirm it wants to use the proposed IP address.
This message is broadcast to inform all DHCP servers that one has been selected.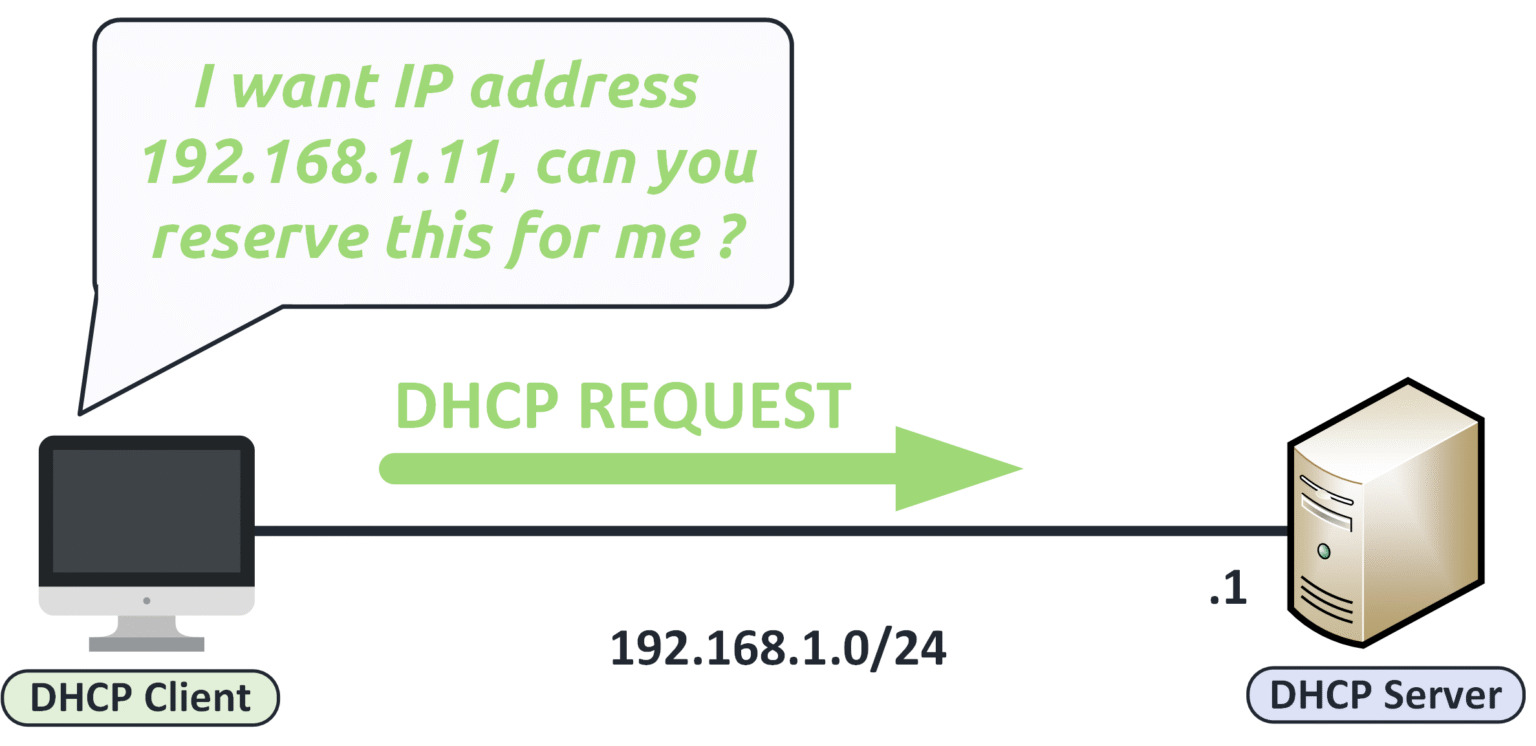
Figure 14 – DHCP client sending a Request to reserve the offered IP address.
In this capture, we can observe:
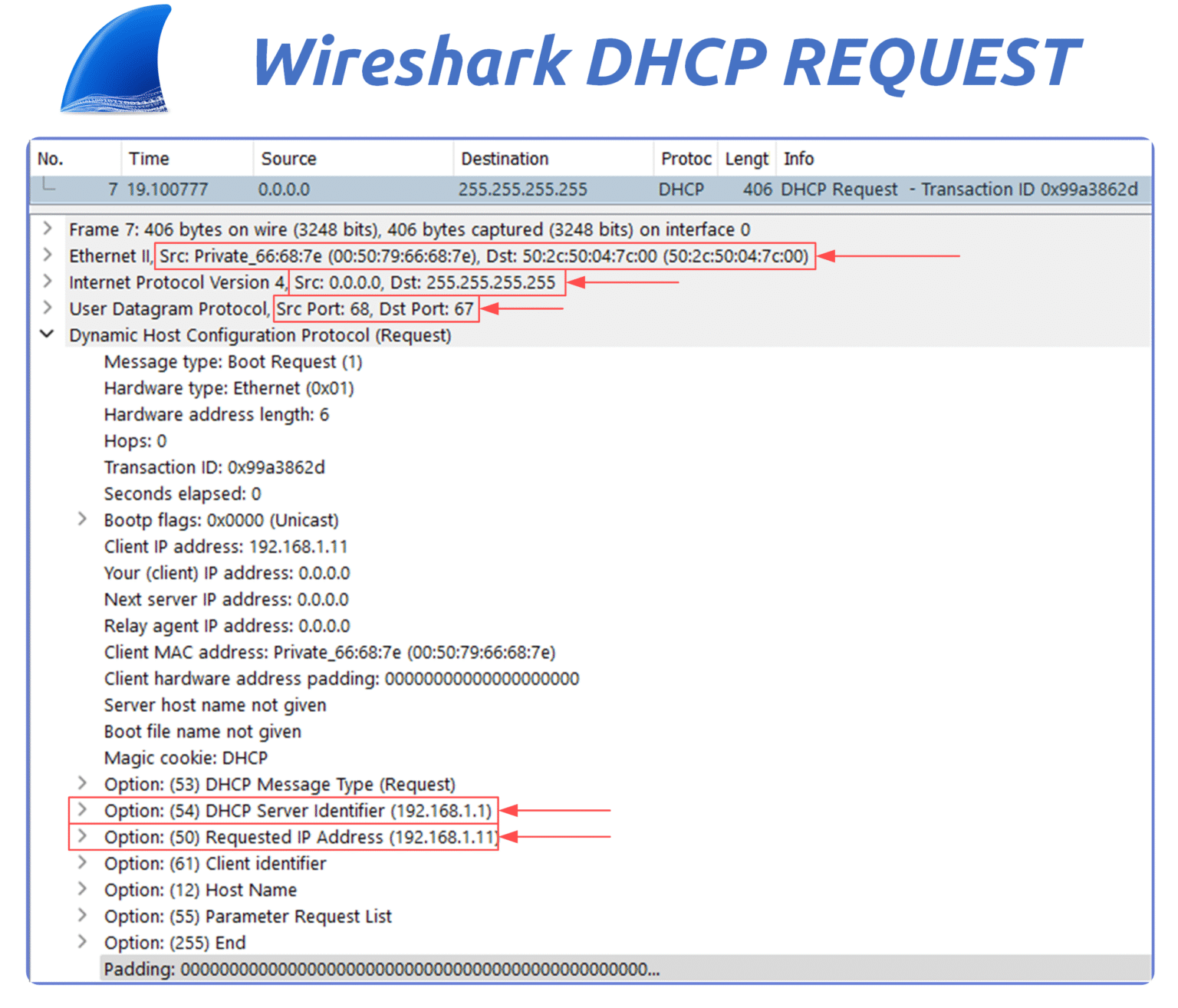
Figure 15 – Wireshark capture of a DHCP Request for IP 192.168.1.11.
Source IP: 0.0.0.0 — the client still doesn’t have an IP
Destination IP: 255.255.255.255 — broadcast
Destination MAC: FF:FF:FF:FF:FF:FF — broadcast
UDP Ports: source port 68 (client), destination port 67 (server)
DHCP Options:
Option 50: Requested IP address (192.168.1.11)
Option 54: DHCP Server Identifier (192.168.1.1)
This message tells the server:
“I accept your offer. Please assign me this IP.”
Other DHCP servers that may have sent an offer now know their proposal was declined.
Answer the question below
What message does the client send to accept the offered IP?
Step 4 — DHCP ACK
Once the client has requested the offered IP, the DHCP server replies with a DHCP ACK to finalize the process.
This message confirms that the IP address is officially assigned and provides all necessary configuration parameters.
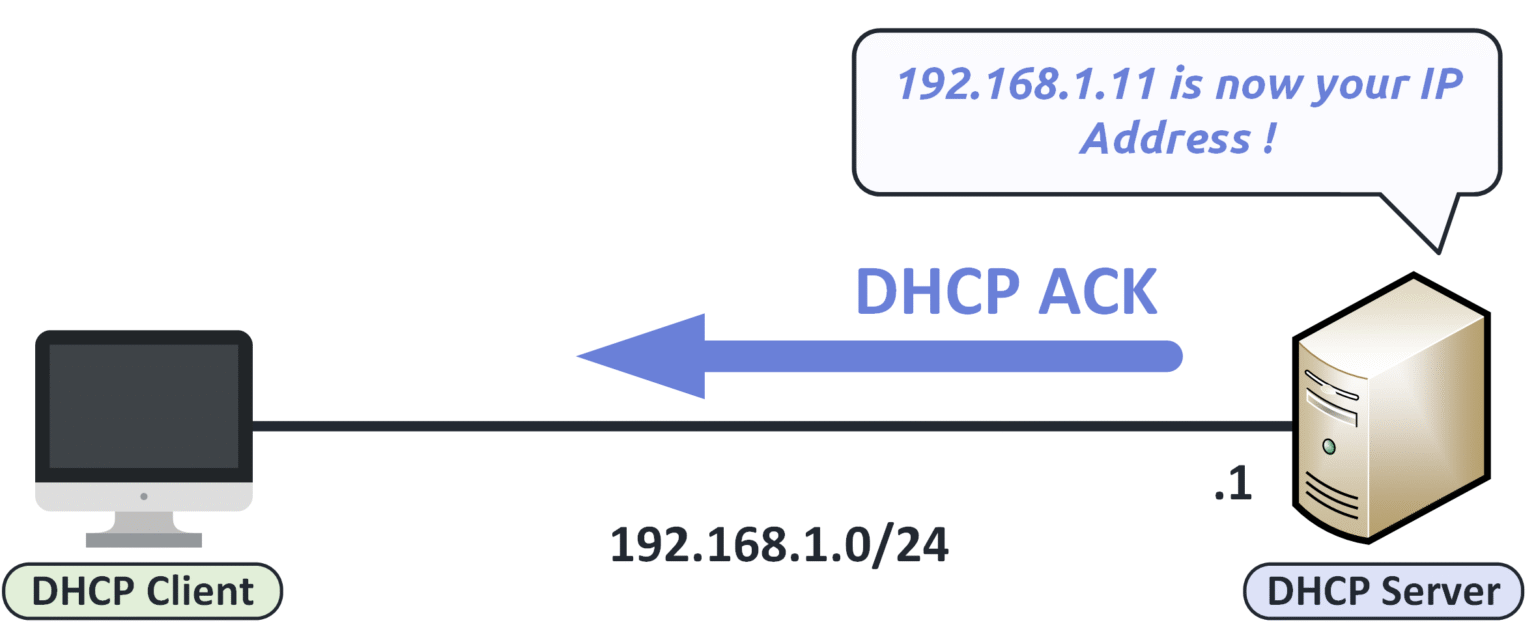
Figure 16 – DHCP server sending an ACK to confirm IP assignment to the client.
In this capture, we can observe:
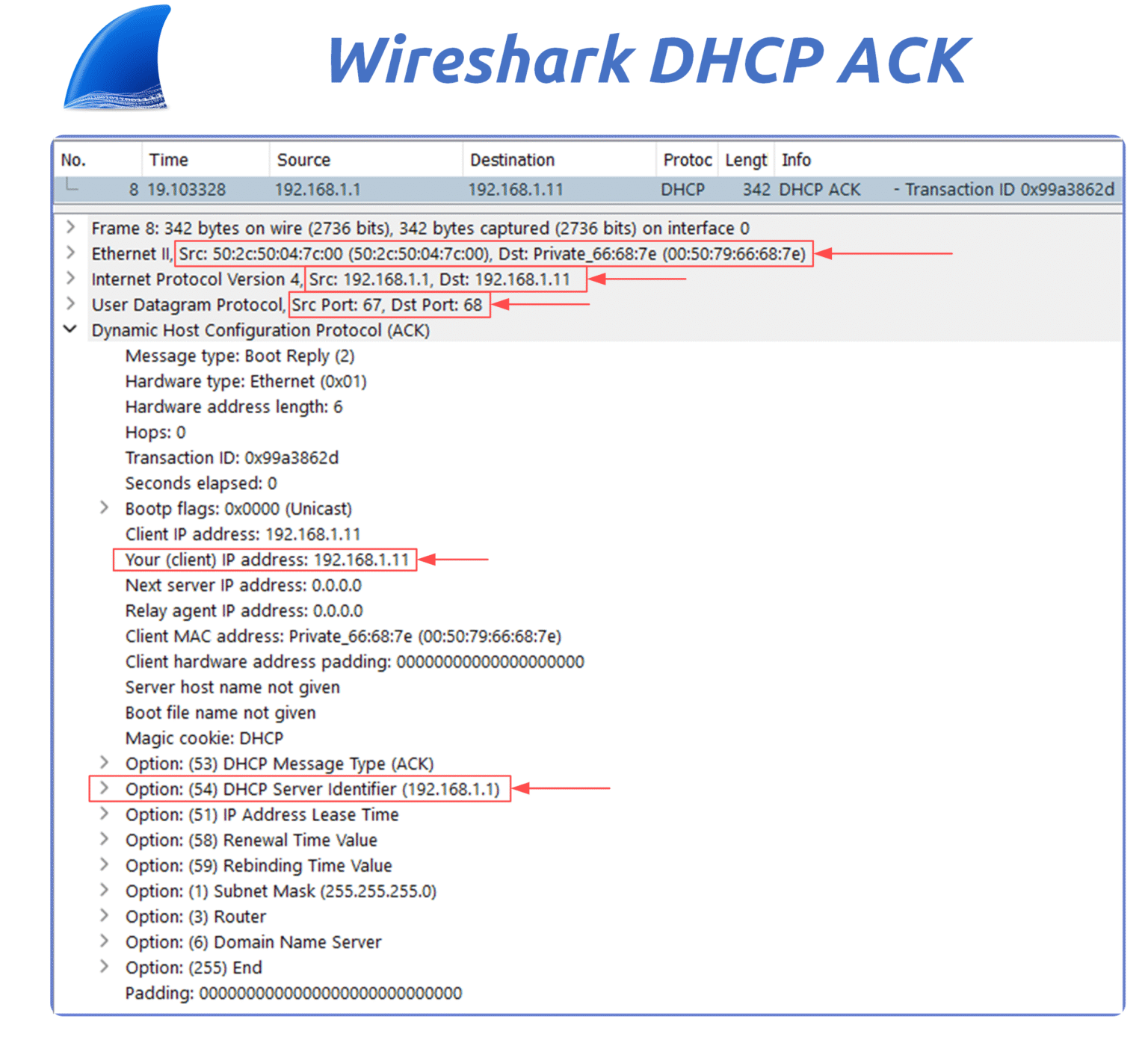
Figure 17 – Wireshark capture of a DHCP ACK confirming IP assignment to the client.
Source IP: 192.168.1.1 — the DHCP server
Destination IP: 192.168.1.11 — the client’s new IP
Destination MAC: the client’s MAC address (unicast)
UDP Ports: source port 67 (server), destination port 68 (client)
DHCP Options:
Option 51: Lease duration
Option 6: DNS servers
Option 3: Default gateway
Once the client receives this ACK, it can officially use the assigned IP address.
It is now fully configured and ready to join the network.
Figure 18 – Client fully configured with assigned IP address from the DHCP server.
Answer the question below
Which UDP port does the DHCP client use?
The DHCP process follows four key steps, known by the acronym DORA:
Discover — The client sends a broadcast to find any available DHCP server.
Offer — The server responds with an IP address and network details.
Request — The client formally requests to use the offered IP.
Acknowledge — The server confirms the lease and finalizes the configuration.
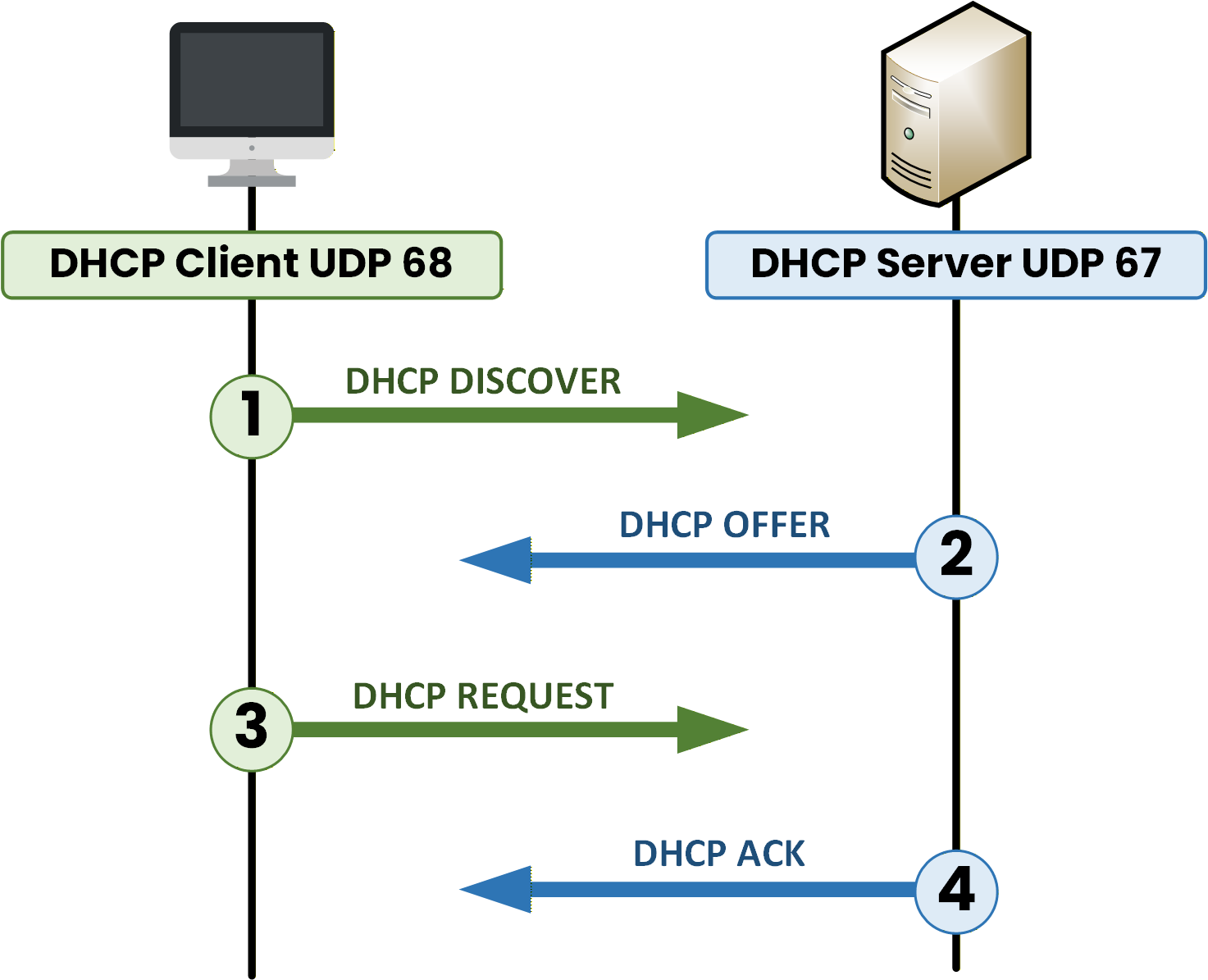
Figure 19 – The four DHCP DORA steps: Discover, Offer, Request, and Acknowledge.
Each step is essential for automatic IP configuration. Make sure you understand them well, this is a common topic on the CCNA exam.
Answer the question below
What does the “O” in the DORA process stand for?
In this lesson, you discovered how DHCP automates IP address assignment in a network.
You learned:
How to verify DHCP settings on a device
How the DORA process works (Discover, Offer, Request, Acknowledge)
The UDP ports used: 67 (server) and 68 (client)
How to analyze DHCP traffic with Wireshark
What’s Next?
In the next course, we’ll see how to configure a Cisco router as a DHCP server.
Let’s move from theory to practice!Answer the question below
DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol)
DHCP in networking is the protocol that automatically assigns IP configuration so devices can join a network without manual input. This lesson explains how DHCP operates through the DORA process and why it is essential for reliable connectivity.