HSRP (Hot Standby Router Protocol) is a Cisco redundancy protocol that allows multiple routers to share a single virtual default gateway.
It ensures that your devices always have a reachable gateway even if the main router fails.
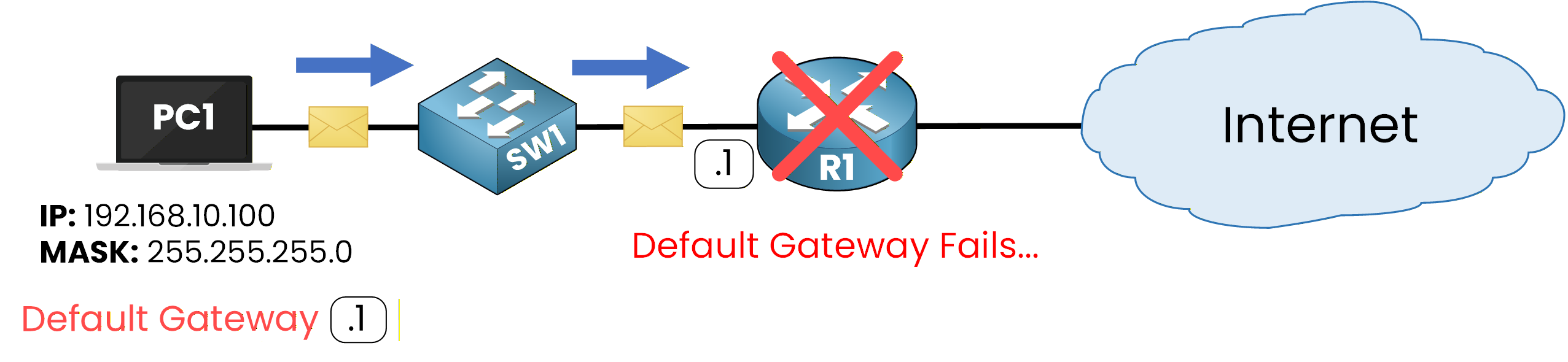
Figure 1 - Default Gateway Fails
In a normal network, when the default gateway goes down, all devices lose connectivity outside their subnet.
HSRP solves this problem by creating a virtual router shared between several physical routers.
With this setup, your network continues to operate normally even if one router fails.HSRP Overview
HSRP is the first protocol from the First Hop Redundancy Protocol (FHRP) family that you’ll learn about.
By the end of this lesson, you’ll understand how HSRP keeps your gateway alive and what happens behind the scenes when a router fails.Let’s start by exploring the concept of the HSRP Group.
HSRP Group
HSRP groups routers into logical units called HSRP groups, each identified by a unique group number.
Routers in the same group work together to maintain the same virtual gateway for connected hosts.In the example below, routers R1 and R2 belong to HSRP Group 1.
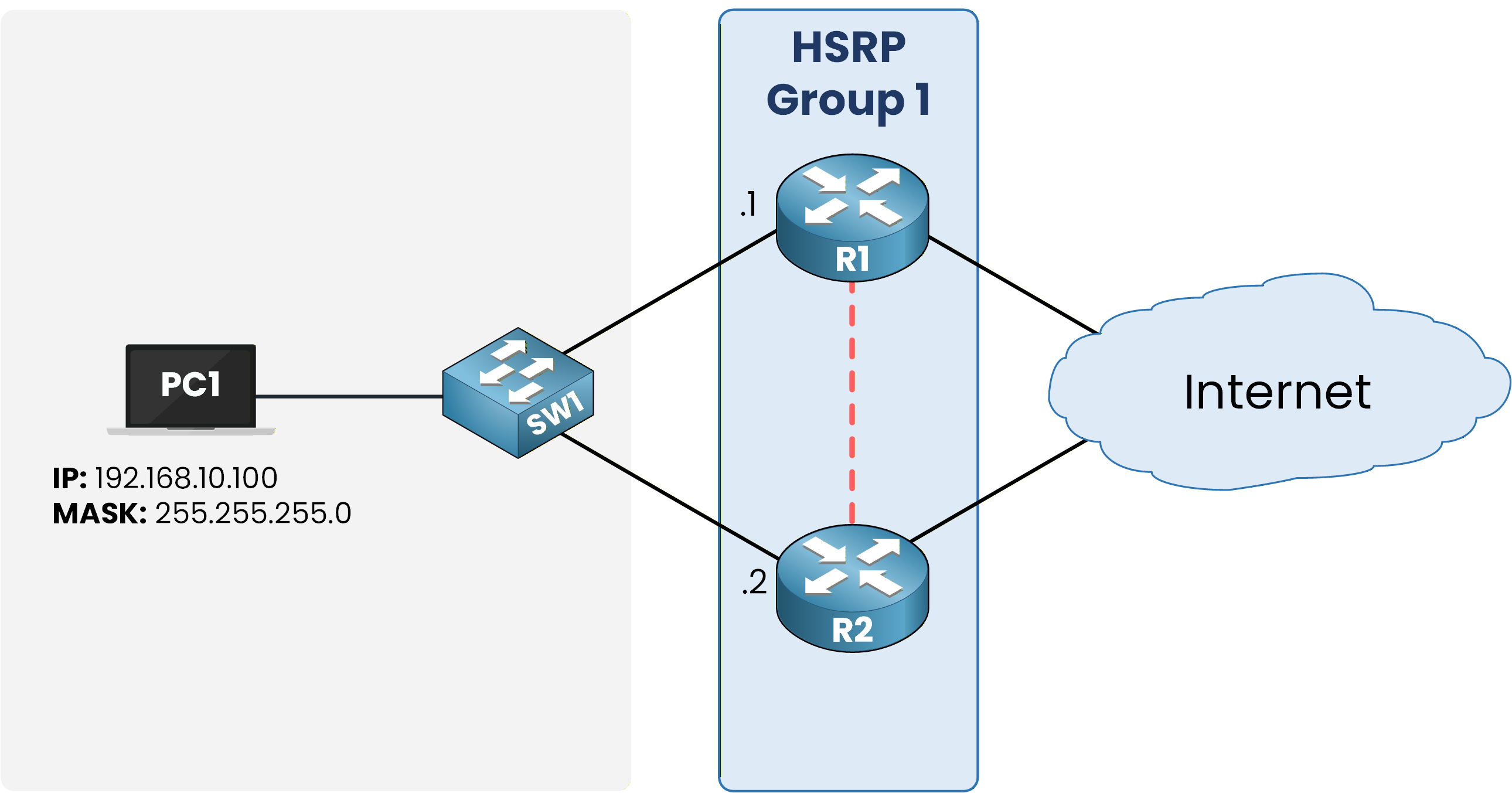
Figure 2 – HSRP Group Topology
Once you decide which routers belong to the same group, you assign them a Virtual IP Address (VIP).
This address acts as the default gateway for all devices in your network.Answer the question below
Which protocol keeps the default gateway available if a router fails?
The Virtual IP Address, or VIP, is the IP address shared by the HSRP group.
It acts as the default gateway for all devices in the network.VIP as the Default Gateway
In our example network 192.168.10.0/24, the routers in HSRP Group 1 share the VIP 192.168.10.3.
Hosts in this subnet use 192.168.10.3 as their default gateway.PC1> ipconfig Ethernet adapter Ethernet: IPv4 Address. . . . . . . . . . . : 192.168.10.100 Subnet Mask . . . . . . . . . . . : 255.255.255.0 Default Gateway . . . . . . . . . : 192.168.10.3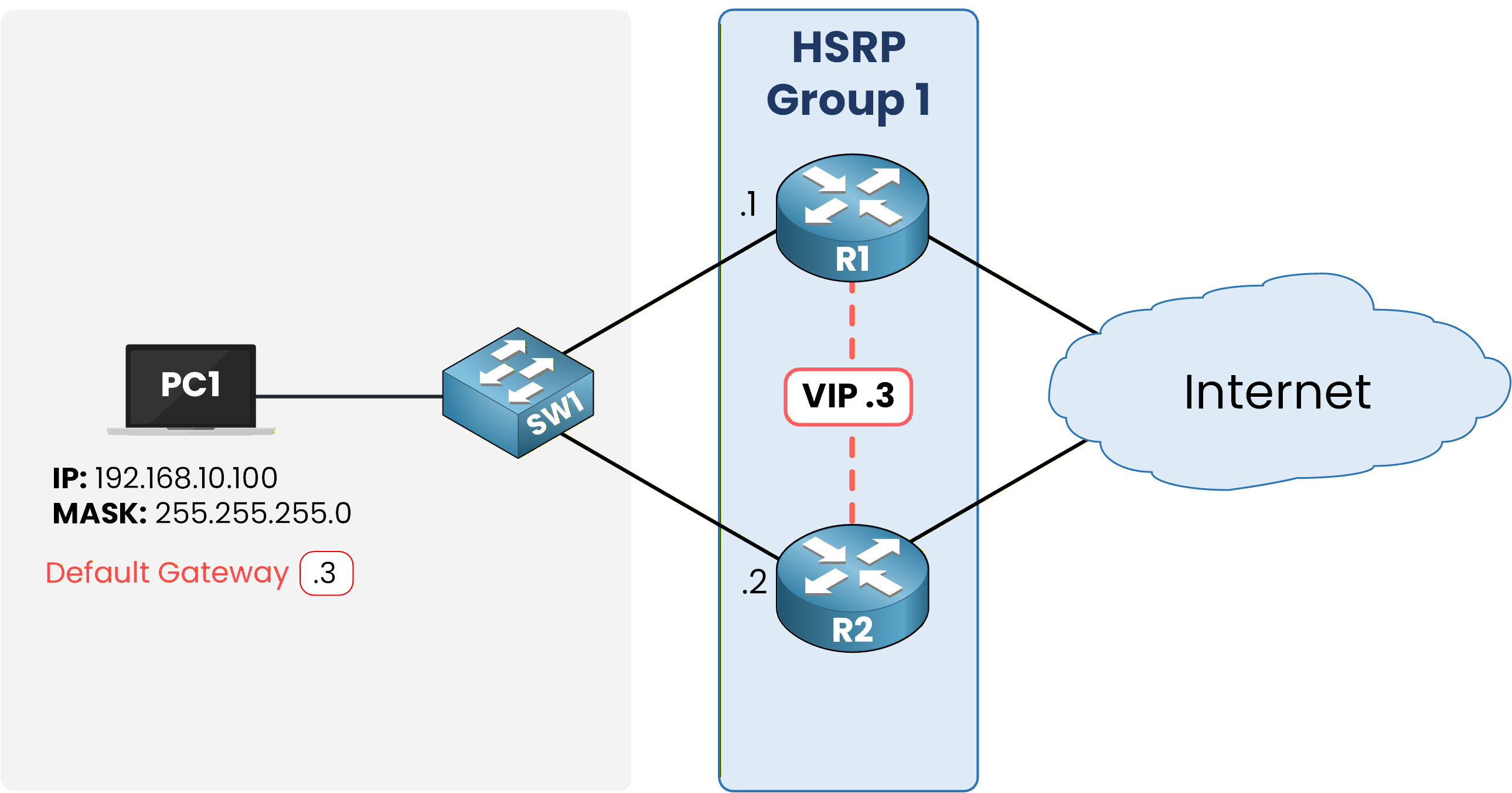
Figure 3 – HSRP Virtual IP (VIP) Assigned as Default Gateway
The HSRP group and the virtual IP address are simple to configure.
Let’s take a look together.Basic HSRP Configuration
First, select one interface on each router and assign it an IP address.
Then, group these interfaces under the same HSRP group and define the shared VIP.By using the command
standbyip R1 Configuration
R1# conf t Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z. R1(config)# interface g0/0 R1(config-if)# ip address 192.168.10.1 255.255.255.0 R1(config-if)# standby 1 ip 192.168.10.3R2 Configuration
R2# conf t Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z. R2(config)# interface g0/0 R2(config-if)# ip address 192.168.10.2 255.255.255.0 R2(config-if)# standby 1 ip 192.168.10.3Here’s what each command does:
standby starts the HSRP process.
1 identifies the HSRP group number.
ip 192.168.10.3 defines the shared Virtual IP Address (VIP).
Once configured, the routers start communicating to keep the virtual gateway active and ready for use.
Let’s now see how HSRP manages the routers within the group.
Answer the question below
What address do hosts use as their HSRP default gateway?
In order to choose which router will actually forward the packets, you need to understand the concept of HSRP roles.
In every HSRP group, routers are assigned specific roles: the Active Router and the Standby Router.
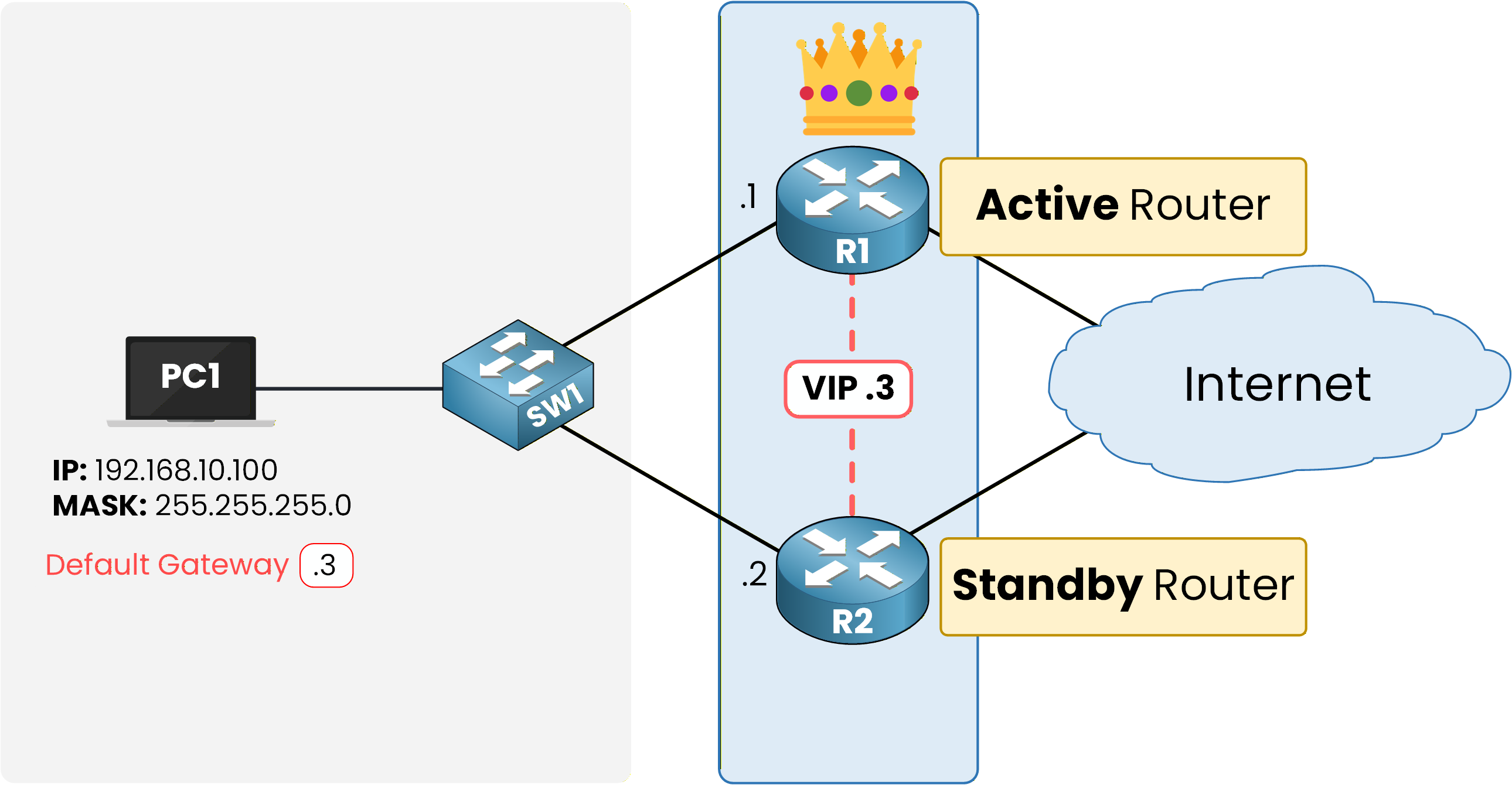
Figure 4 – HSRP Roles: Active and Standby Routers
Active Router
The Active Router is the one currently forwarding the traffic. It:
Responds to ARP requests for the Virtual IP Address (VIP).
Forwards all packets sent to the VIP.
Acts as the default gateway for all devices in the network.
Standby Router
The Standby Router is the backup device. It:
Monitors its status to detect any failure.
Instantly takes over if the Active Router goes down.
This simple role division ensures that one router is always in control while the other is ready to replace it instantly.
Answer the question below
Which router handles traffic destined for the VIP?
At this point, you know that one router becomes Active and the other stays Standby.
But how do they decide which one takes each role?
Figure 5 – How Active and Standby are elected ?
This is an excellent question and the answer is straightforward.
Routers use two main parameters to determine their roles: Priority and IP Address.
Figure 6 – HSRP Election Criteria: Priority and IP Address
1 - Priority
The router with the highest priority becomes the Active Router.
By default, all routers have a priority of 100.
You can manually adjust this value to influence the election.
The range goes from 0 to 255, with 255 being the highest possible priority.
Changing the priority lets you control which router should take the Active role and which one should remain on standby.
2 - Highest IP Address
If two routers have the same priority, the router with the highest IP address on the HSRP interface becomes the Active Router.
This acts as a simple tiebreaker when priorities are equal.
Configuring HSRP Priority
To control which router becomes Active, you can manually set the priority value for each router.
A higher priority means the router will take the Active role.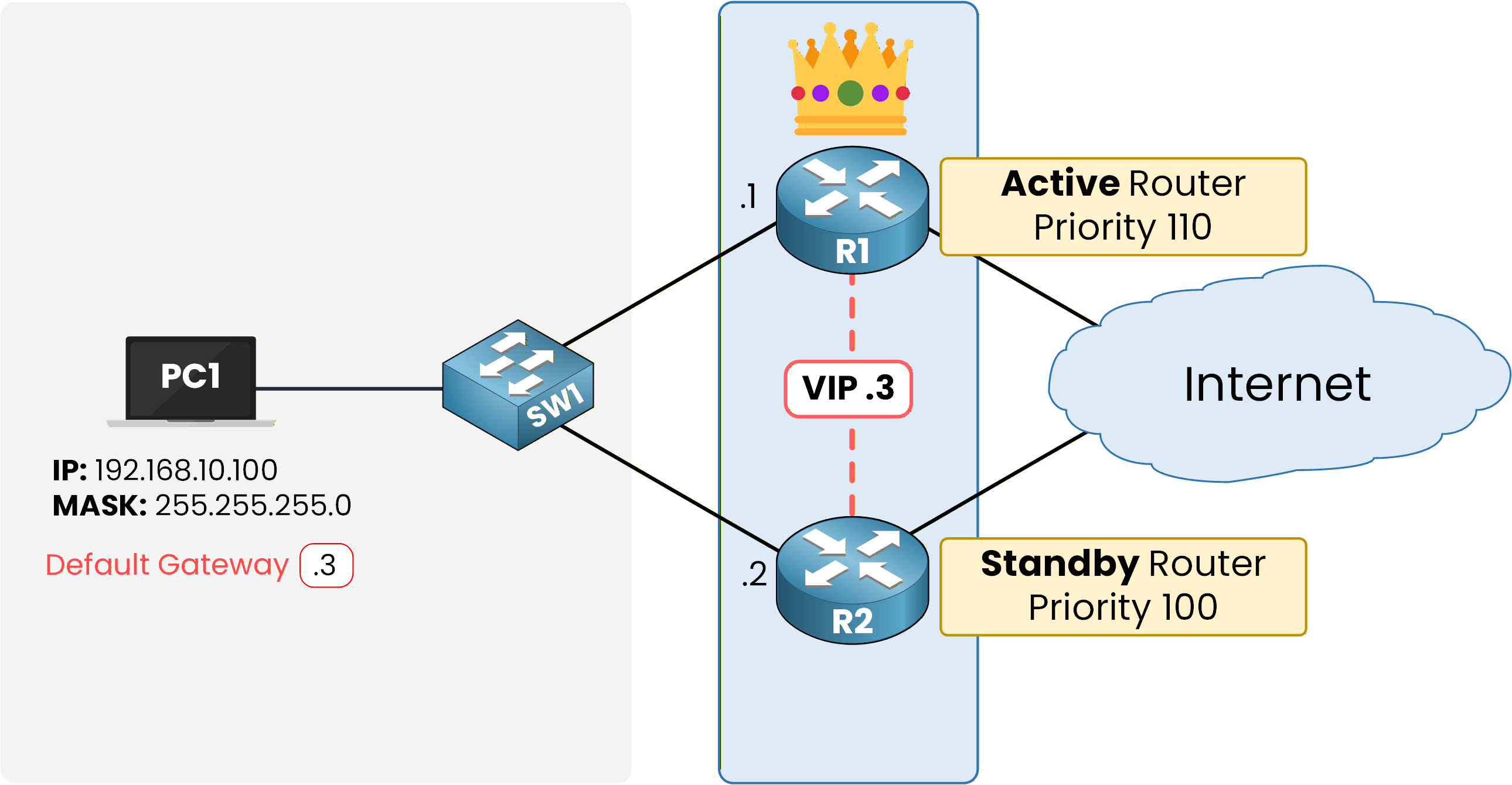
Figure 7 – Manual Configuration of Active and Standby Roles in HSRP
40 % Complete: you’re making great progress
Unlock the rest of this lesson
If you’d like to continue your CCNA journey, simply create your free account.
Access all CCNA lessons
Practice with hands-on labs
Train with Practice exams and Quizzes
Progress tracking in your dashboard
Made by network engineers - CCNP certified
learners globally
Hot Standby Router Protocol (HSRP)
In the previous course, you learned the importance of First Hop Redundancy Protocols (FHRPs) in ensuring network reliability and availability. Now, we’ll explore what is HSRP in networking and why it’s one of the most widely used FHRPs developed by Cisco.