As you know, a VLAN creates a separate Subnet and Broadcast Domain. Devices inside the same VLAN can communicate directly at Layer 2, but as soon as a host in a VLAN needs to talk to a host in another VLAN, a problem appears: VLANs cannot communicate with each other without a Layer 3 device.
That’s where InterVLAN Routing comes in. It allows traffic to move between VLANs using either a router or a multilayer switch.
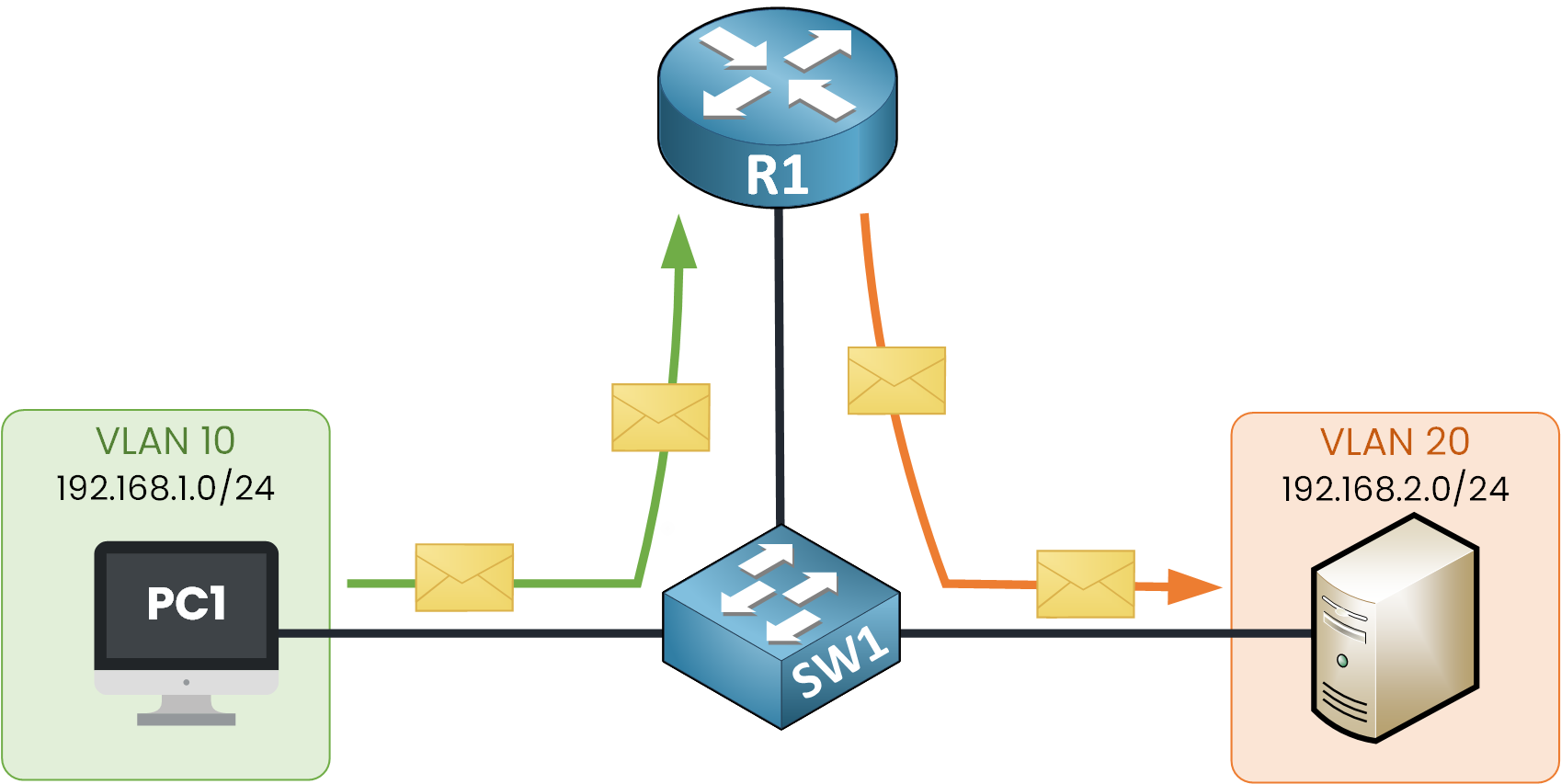
Figure 1 – InterVLAN Routing Process
In this lesson, we’ll explore the three main methods of InterVLAN Routing:
Legacy InterVLAN Routing – the old way, limited and no longer used today.
Router-on-a-Stick – a simple solution for small to medium networks.
Layer 3 Switch with SVIs – the modern, scalable solution for enterprises.
Answer the question below
The first method to look at is Legacy InterVLAN Routing.
This solution uses a router with multiple physical Ethernet interfaces. Each router interface connects to a switch port assigned to a different VLAN. This interfaces acts as that VLAN’s default gateway (R1 G0/1 for VLAN 10, R1 G0/3 for VLAN 20).
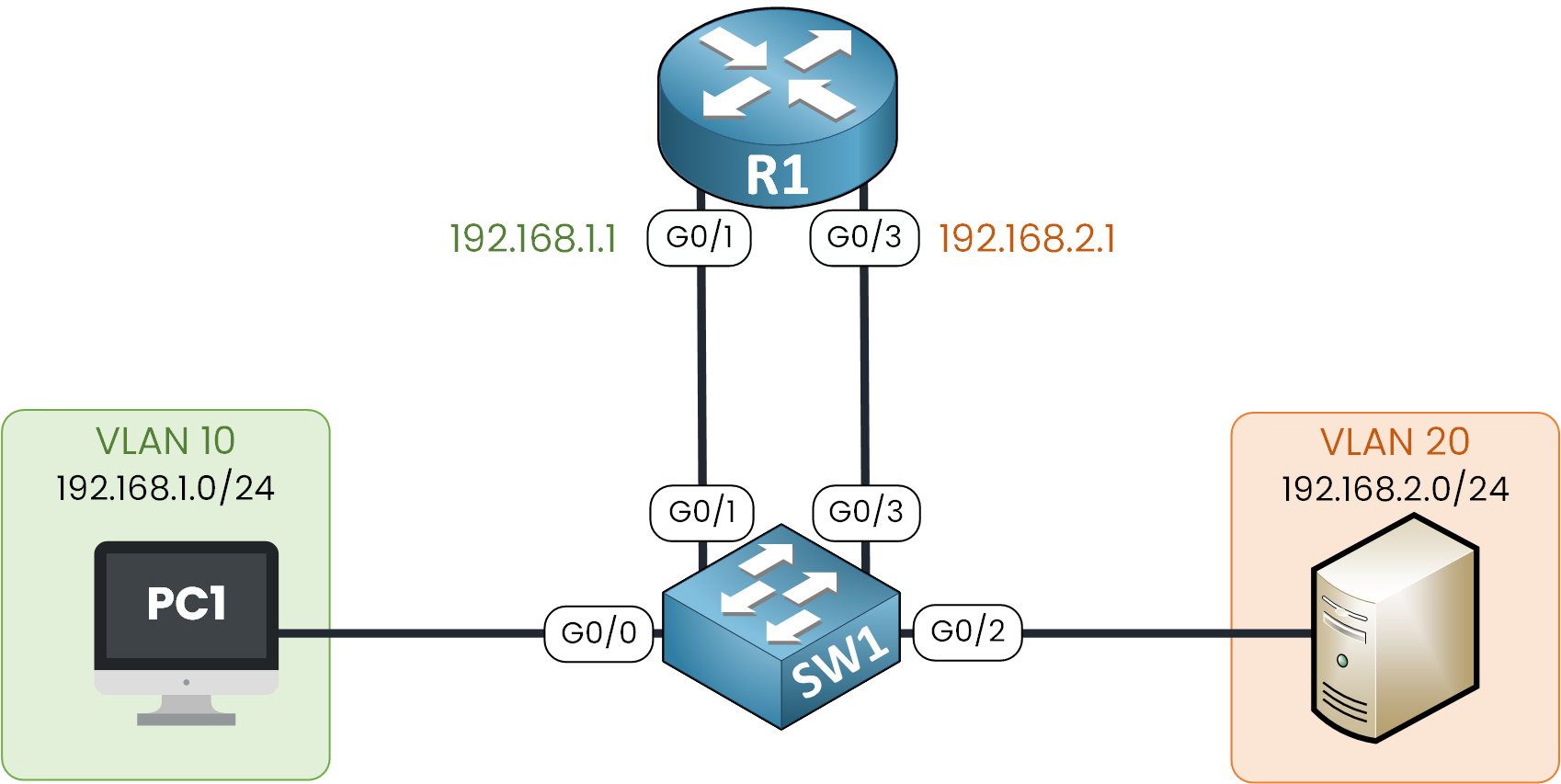
Figure 2 – Legacy InterVLAN Routing Topology
In our example, we have two VLANs:
VLAN 10 (192.168.1.0/24) with PC1
VLAN 20 (192.168.2.0/24) with the Server
On switch SW1 :
Interfaces G0/0 and G0/1 are associated with VLAN 10
While Interfaces G0/2 and G0/3 are associated with VLAN 20
When PC1 sends a packet to the server in VLAN 20, since the destination is on another subnet, PC1 forwards the packet to its default gateway 192.168.1.1.
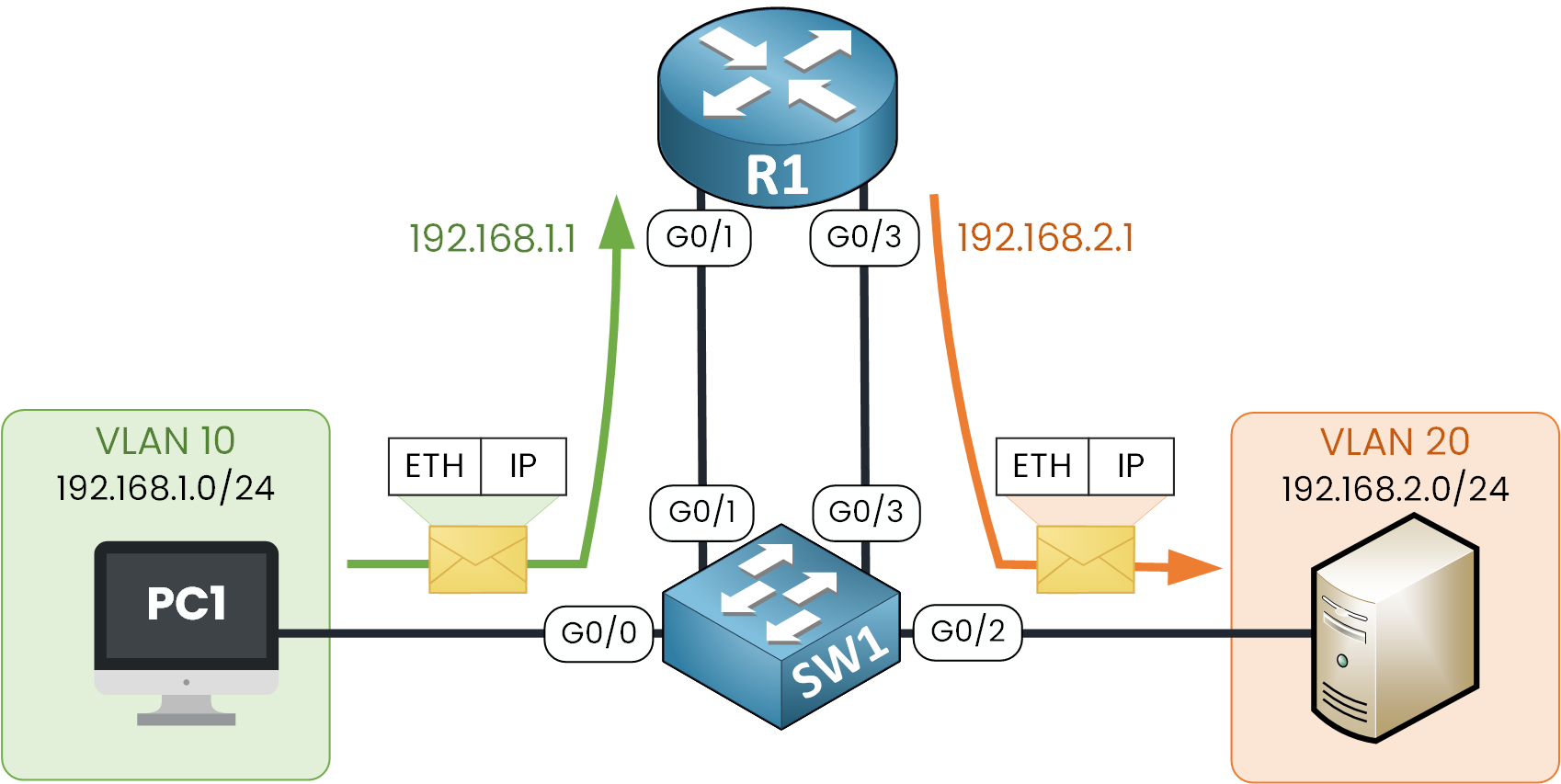
Figure 3 – Legacy Router-on-a-Stick Packet Flow
R1 receives the packet on interface G0/1, examines the destination IP, and routes the packet out interface G0/3 to reach the server in VLAN 20. SW1 then forwards the frame to the server.
Limitations
Since legacy interVLAN routing uses one physical interface per VLAN, this solution is not scalable because routers have a limited number of physical interfaces. Using one physical router interface per VLAN could quickly exhaust the router’s capacity.
In our example, R1 used two separate Ethernet interfaces to route the traffic between VLAN 10 and VLAN 20.
Now imagine we need to add 10 VLANs: it would require 10 more physical interfaces between R1 and SW1, which is obviously not scalable.
This method of interVLAN routing is no longer implemented in production networks nowadays but keep in mind this was the first method ever created.
Answer the question below
In legacy interVLAN routing, how many router interfaces are required per VLAN?
Router on a Stick method overcomes the limitation of Legacy interVLAN Routing. in this method the router only needs one physical Ethernet interface to route traffic between multiple VLANs.
40 % Complete: you’re making great progress
Unlock the rest of this lesson
If you’d like to continue your CCNA journey, simply create your free account.
Access all CCNA lessons
Practice with hands-on labs
Train with Practice exams and Quizzes
Progress tracking in your dashboard
Made by network engineers - CCNP certified
learners globally
InterVLAN Routing
InterVLAN Routing is the process that allows communication between devices in different VLANs by using a router or a Layer 3 switch. In this lesson, you will learn the three main methods, Legacy InterVLAN Routing, Router-on-a-Stick, and SVIs and understand their advantages and limitations.