How does a switch learn MAC addresses? It’s a core concept for anyone preparing for the CCNA exam. A switch is described as an intelligent device, but what exactly happens when it receives a frame?
Let’s find out together by looking at a simple example.
Step 1 – Topology Overview
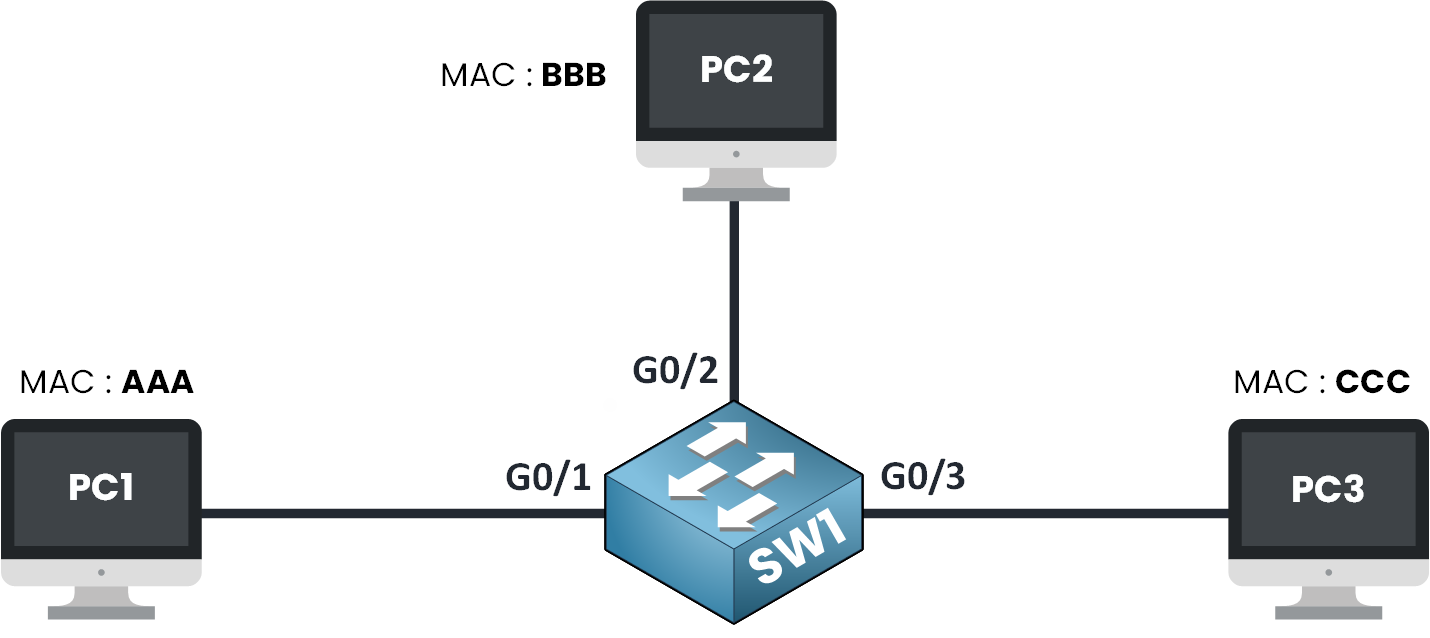
Figure 1 – Switch Learning MAC Addresses (Initial Topology)
In the diagram above, we have three devices connected to a switch called SW1.
Each device has a simplified MAC address:PC1 → MAC address AAA
PC2 → MAC address BBB
PC3 → MAC address CCC
To understand how the switch learns MAC addresses, let’s say PC1 wants to send a frame to PC3.
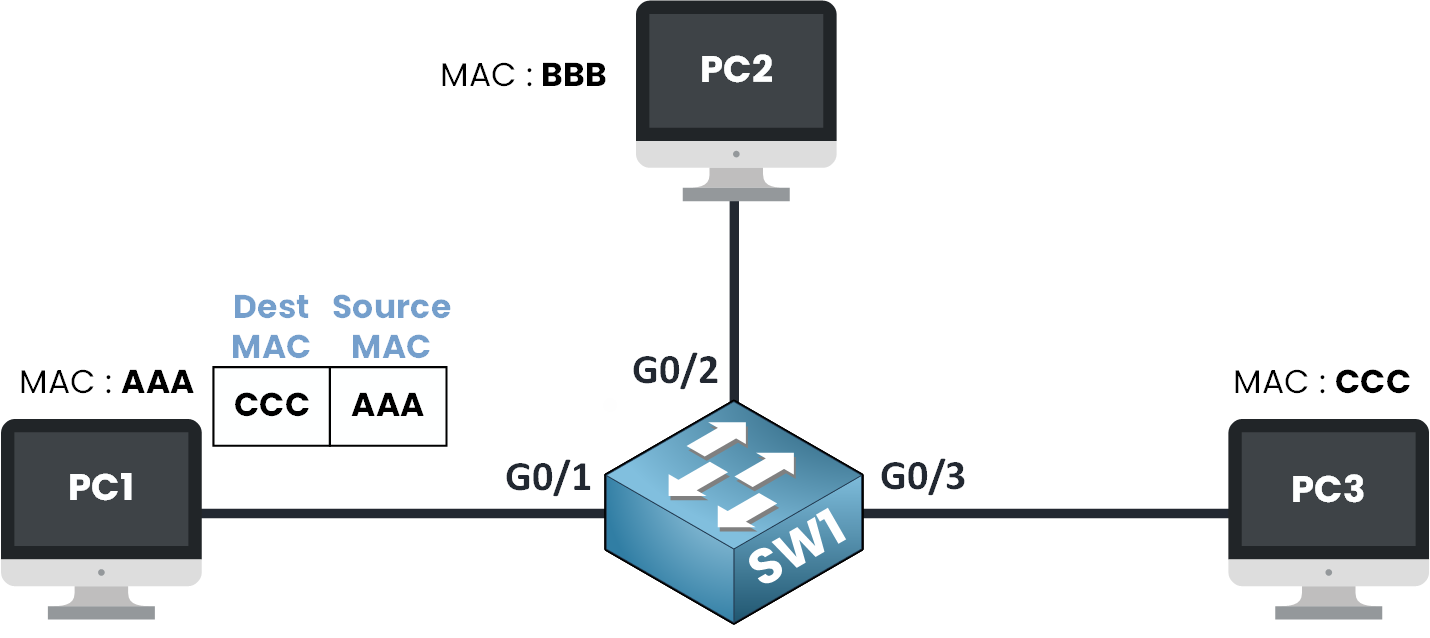
Figure 2 – Switch Learns the Source MAC Address
PC1 will create an Ethernet frame with:
Source MAC: AAA (its own address)
Destination MAC: CCC (the MAC address of PC3)
When this frame arrives at the switch on port G0/1, the switch reads the Ethernet header and sees that MAC AAA was received on interface G0/1.
Step 2 – MAC Address Table Check
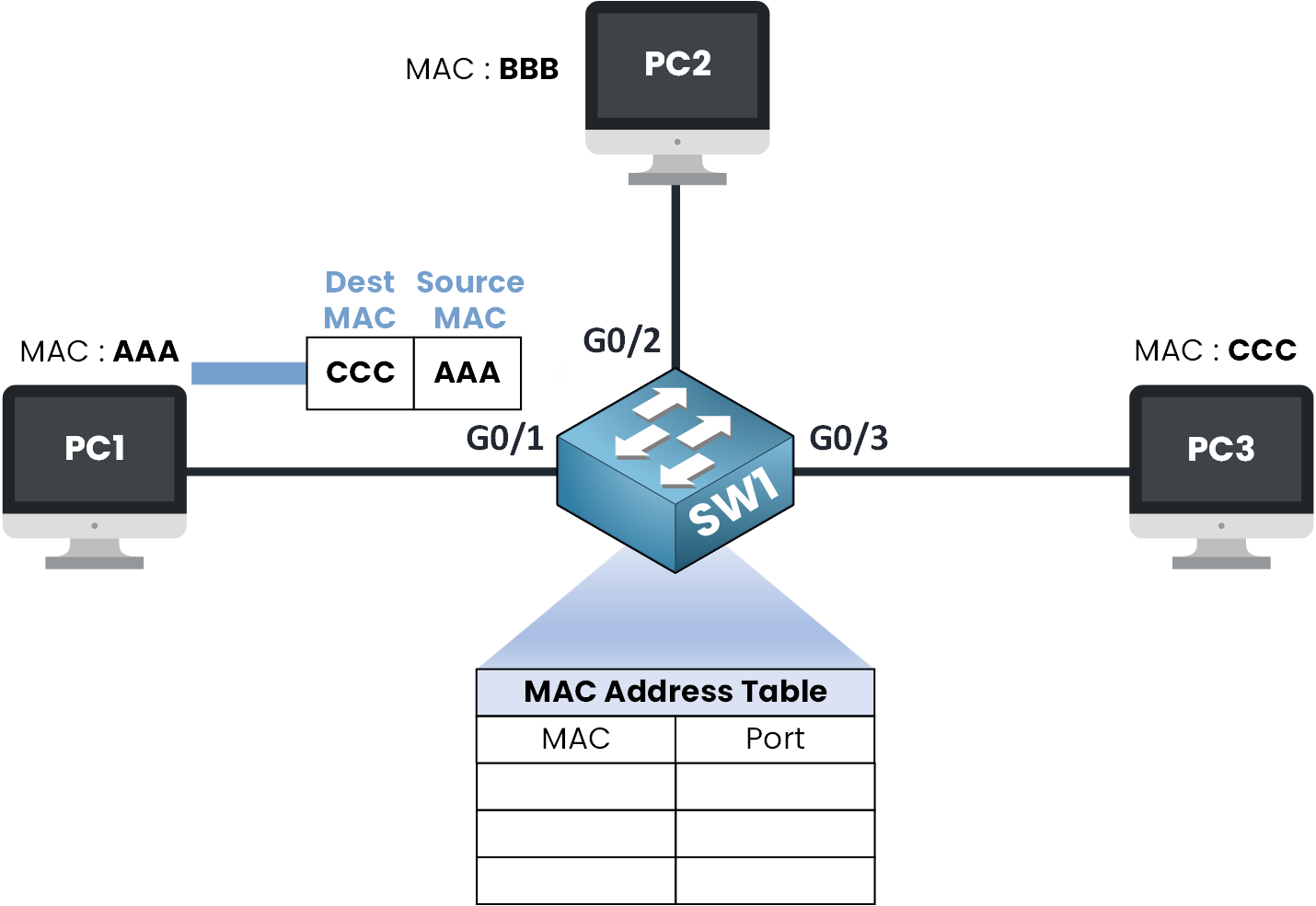
Figure 3 – MAC Address Table Check
At this point, the switch checks its MAC address table.
This table stores MAC addresses and the ports they are associated with.This table is basically a list that tells the switch:
"This MAC address is connected to this port.”
But for now, the table is empty the switch hasn’t learned anything yet !
So what does it do?
It reads the Ethernet frame sent by PC1 and looks at the source MAC address: it's AAA.
And since it’s the first time the switch sees this MAC address, it says:“Okay, I don’t know this one yet… but I just received it on G0/1, so I’ll remember that!”
So the switch adds an entry to its table:
MAC address AAA → G0/1
This is exactly how a switch learns MAC addresses: by associating the source MAC of incoming frames with the port they arrive on.
This way the switch can learn mac address, the switch search the source mac address in the ethernet header and will verify if the switch already know it's address.
The switch doesn’t need to be told where the devices are, it figures it out by looking at the source MAC address, that’s the key to understanding how does a switch learn MAC addresses dynamically.
Step 3 – Source MAC Learned on G0/1
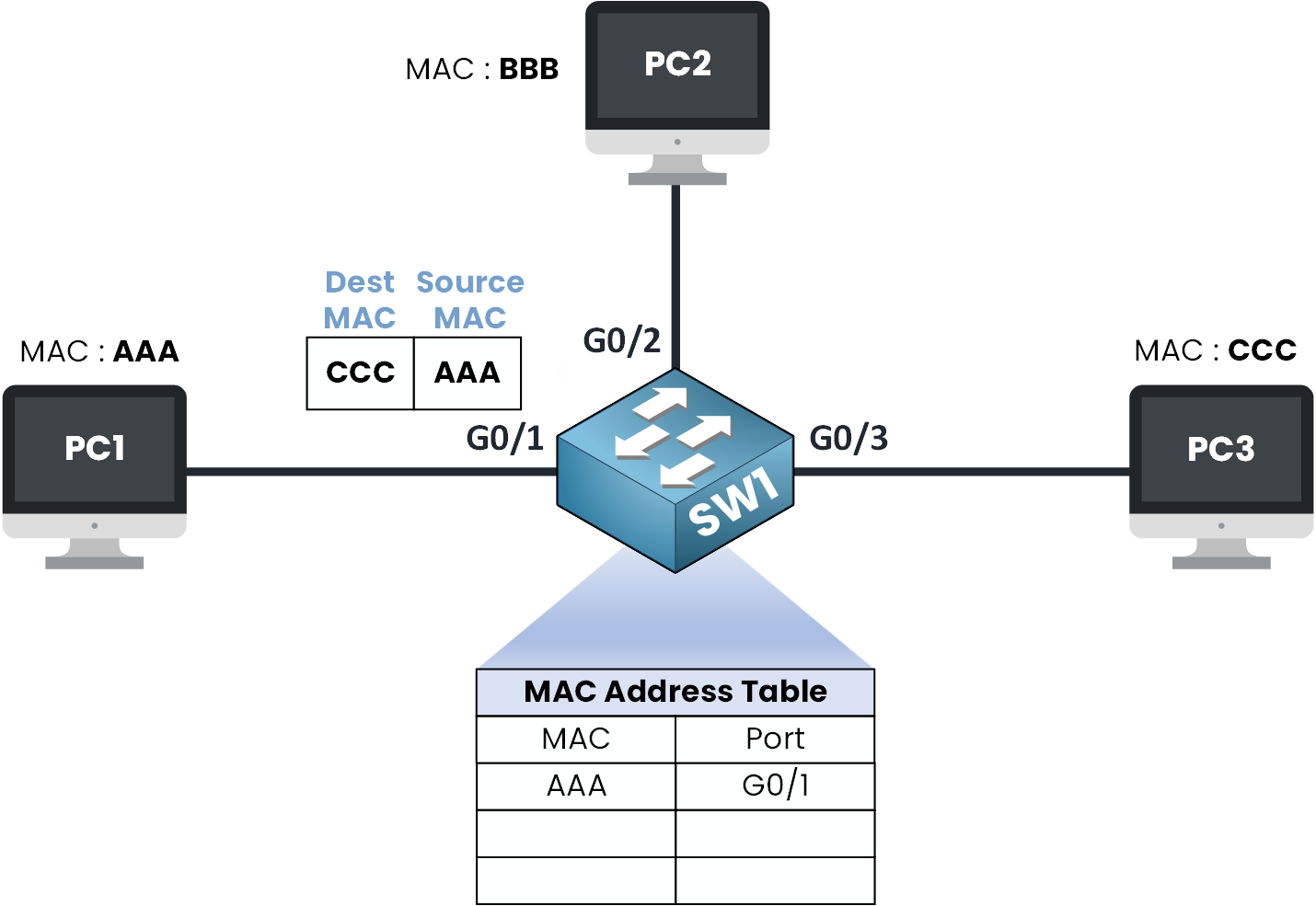
Figure 4 – Source MAC Address AAA learned on G0/1
But now the switch has to send the frame to its destination and that’s a different story.
First the switch will checks its MAC address table again, this time looking for the destination MAC address which is CCC (that’s PC3).
And here’s the problem:
The switch doesn’t know yet where CCC is.
There’s no entry for it in the table.So what does it do?
Well, when a switch doesn’t know where to send a frame, it doesn’t guess it floods the frame.
This means the switch will sends the frame out of all other ports except the one it came from.
At that moment, the switch is basically saying:
“I don’t know where CCC is, so I’ll ask everyone. Let’s see who replies.”
Step 4 – Frame Flooding
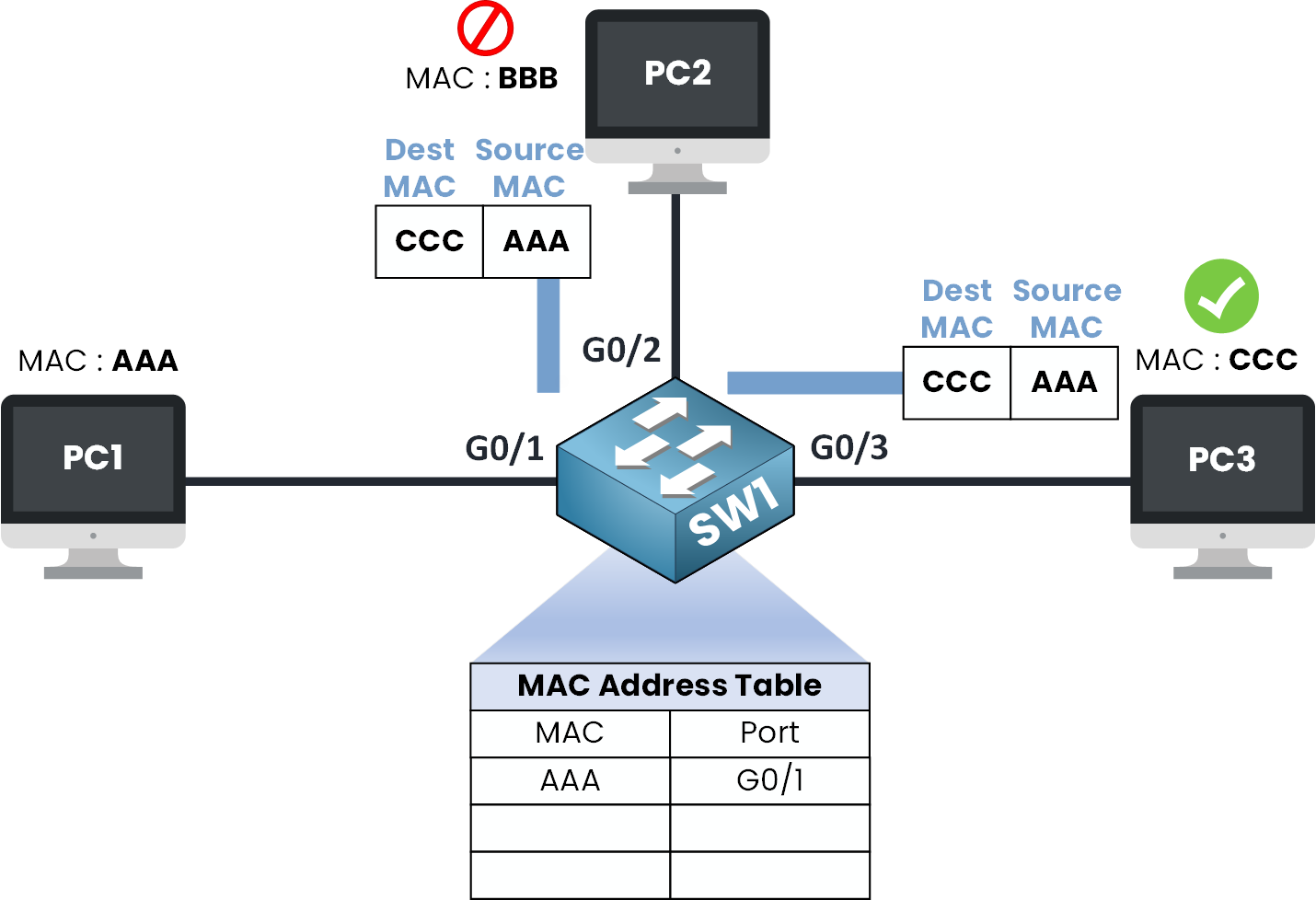
Figure 5 – Frame Flooding and Delivery
At this point, both PC2 and PC3 receive the Ethernet frame.
PC2 looks at the frame, checks the destination MAC address and thinks:
“Hmm… this is for CCC, but my MAC address is BBB, not for me.”
So PC2 just drops the frame.PC3 will respond because he sees that the destination MAC address in the frame matches his own.
When PC3 replies, the new Ethernet frame will have:
Source MAC: CCC
Destination MAC: AAA
Step 5 – Switch Learns the MAC Address of PC3
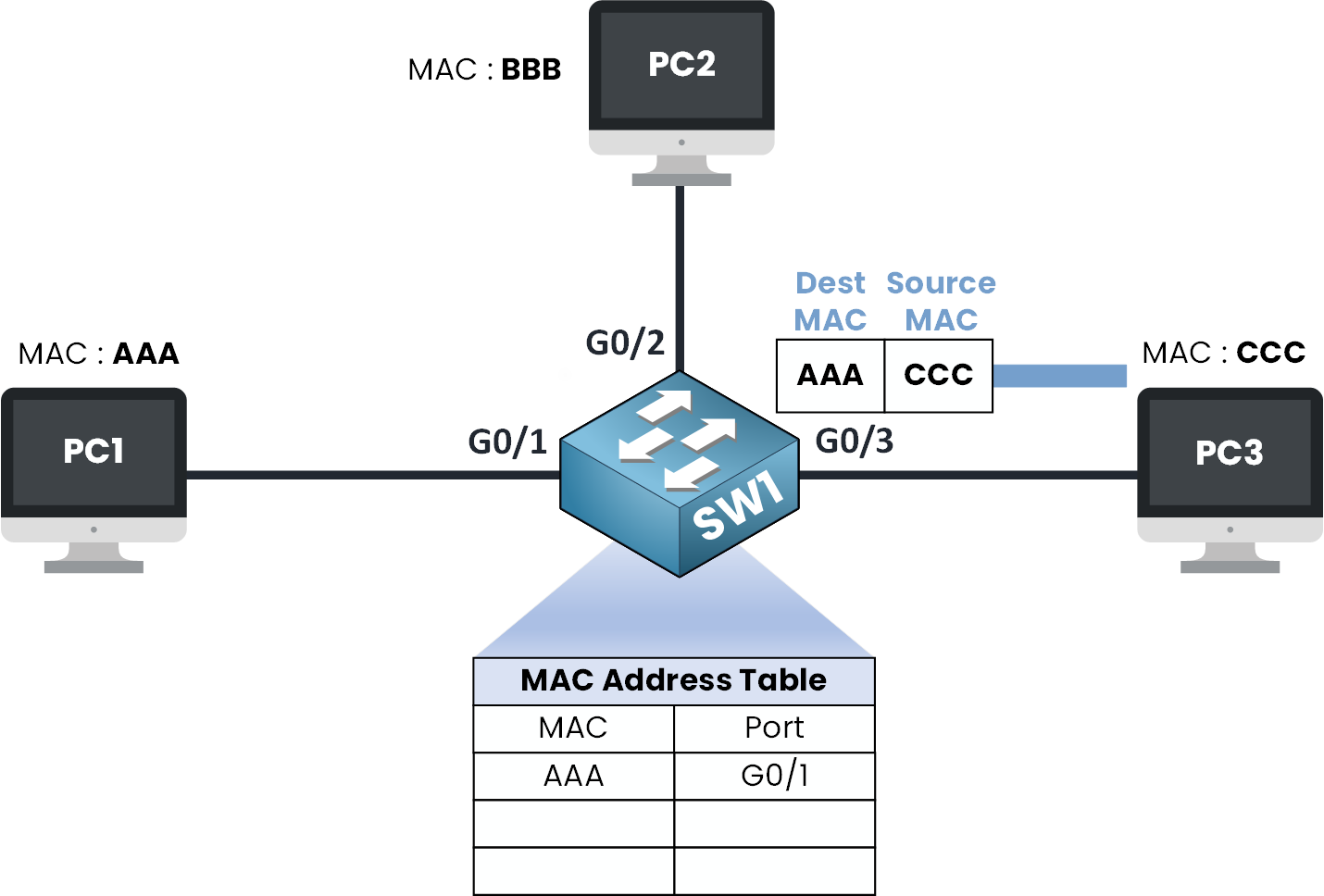
Figure 6 – Switch Learns the MAC Address of PC3
The switch receives this new frame on G0/3.
It takes a look at the source MAC address which is CCC and thinks:
“Alright, I don’t know this MAC yet… but I just got it on G0/3 let me save that in my MAC Address Table.”
The switch adds a new entry to its MAC address table:
MAC address CCC → G0/3
Step 6 – Updated MAC Address Table
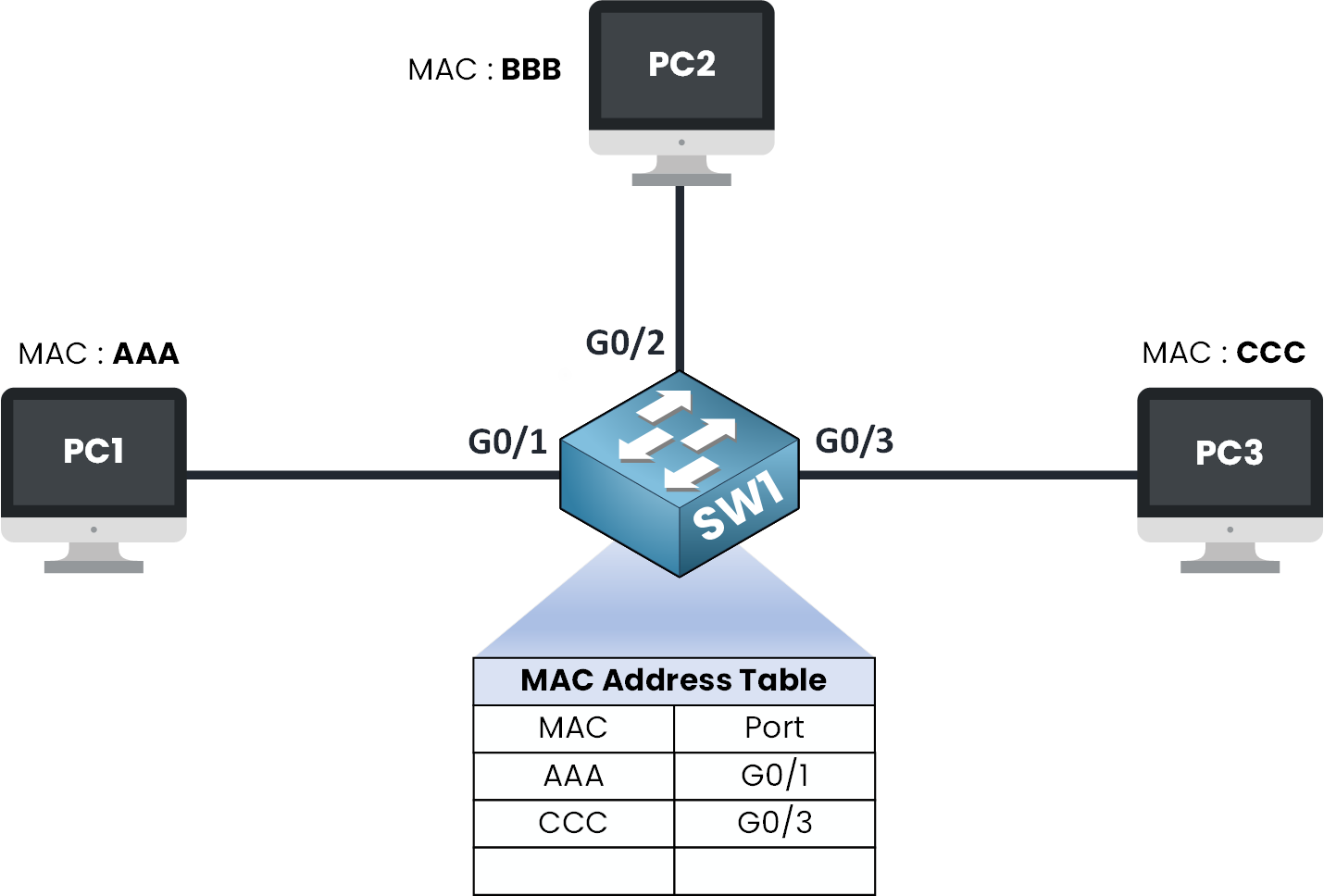
Figure 7 – MAC Address Table
Now the switch knows :
PC1 (AAA) is on Gi0/1
PC3 (CCC) is on Gi0/3
So when the switch sees that the destination MAC address is AAA, it checks its table, finds that AAA is linked to G0/1.
The Ethernet frame is forwarded to PC1 through that port.
Step 7 – Frame Delivery
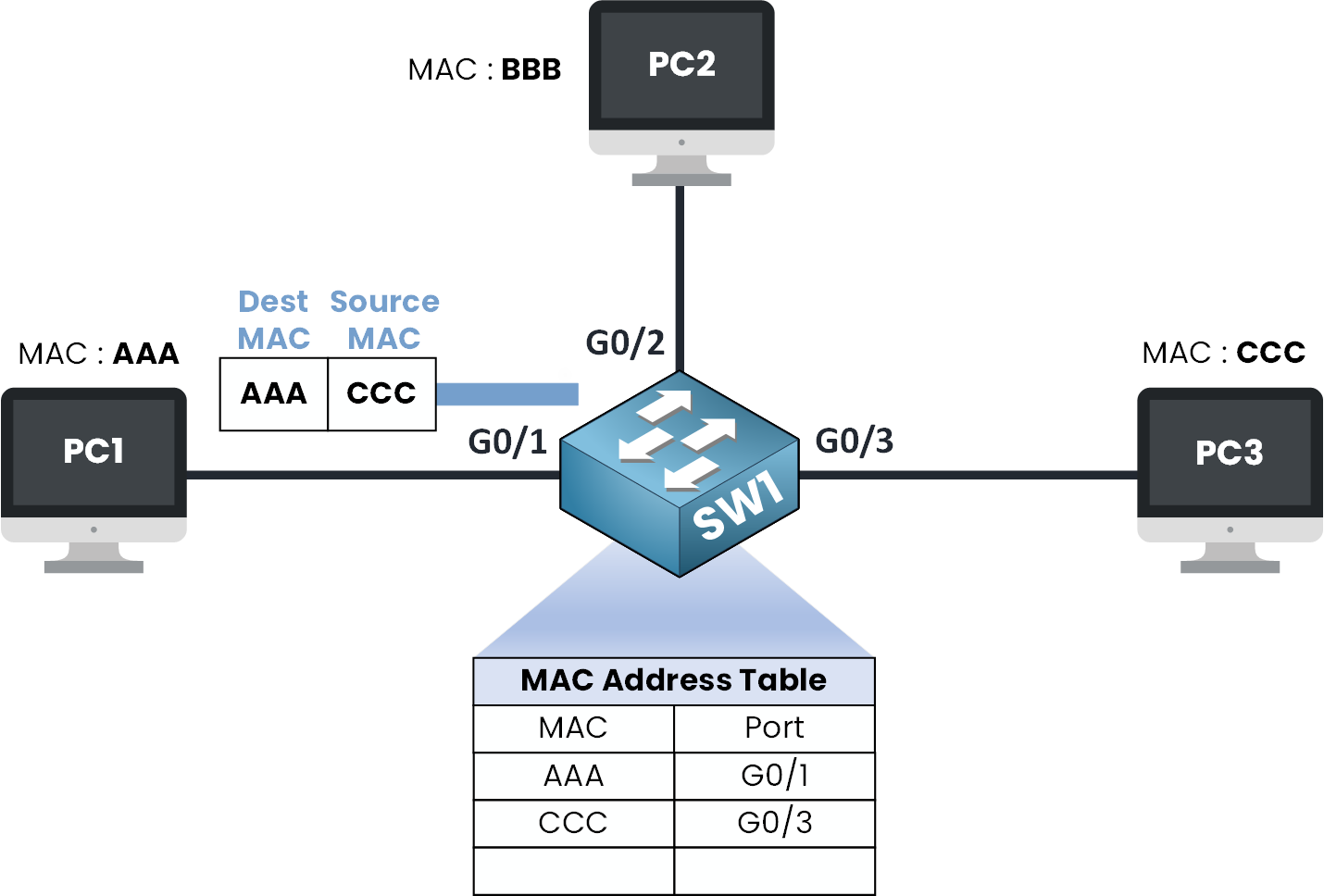
Figure 8 – Frame Delivery
What you need to remember is that the switch will remember the source MAC address and associate it with the port where it received the Ethernet frame.
Now let's take a look at some Cisco CLI commands to see how the switch builds its MAC address table
Answer the question below
In this example, we will use real MAC Addresses for PC1, PC2 and PC3.
Figure 9 – Verifying Interface Status on SW1
First, we need to make sure that all interfaces are up.
We can verify that with this command:SW1#show interfaces status Port Name Status Vlan Duplex Speed Type Gi0/1 connected 1 auto auto unknown Gi0/2 connected 1 auto auto unknown Gi0/3 connected 1 auto auto unknownFine, all interfaces are up !
Next, let's take a look at the current MAC address table:SW1# show mac address-table dynamic Vlan Mac Address Type Ports ---- ----------- -------- -----As you can see, the MAC address table is empty.
No traffic has been seen yet, so the switch hasn’t learned anything.
Now let’s go through the MAC address learning process using the CLI.
From PC1, I try to ping PC3.
This creates an Ethernet frame with:Source MAC: PC1 MAC
Destination MAC: PC3 MAC
As you see, the switch is about to learn the MAC address of PC1 from this first frame.
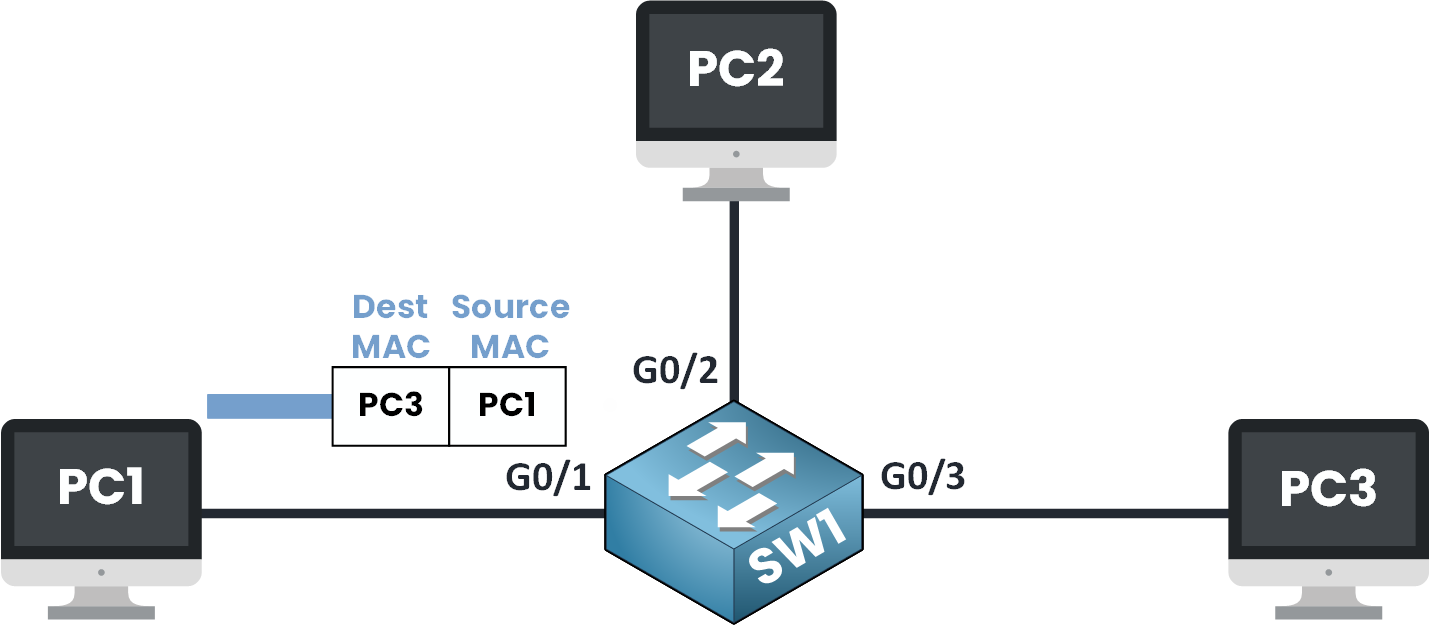
Figure 10 – Verifying MAC Learning on Cisco CLI
We can now verify on the CLI that the switch has learned PC1’s MAC address on G0/1 by using this command below
SW1# show mac address-table dynamic Mac Address Table ------------------------------------------- Vlan Mac Address Type Ports ---- ----------- -------- ----- 1 0011.22aa.33bb DYNAMIC Gi0/1 Total Mac Addresses for this criterion: 1Here we are, PC1 MAC address is learned 0011.22aa.33bb on G0/1 interface.
At this point the switch still doesn't know where (PC3 MAC) is, it floods the frame out of every port except the one it came from.
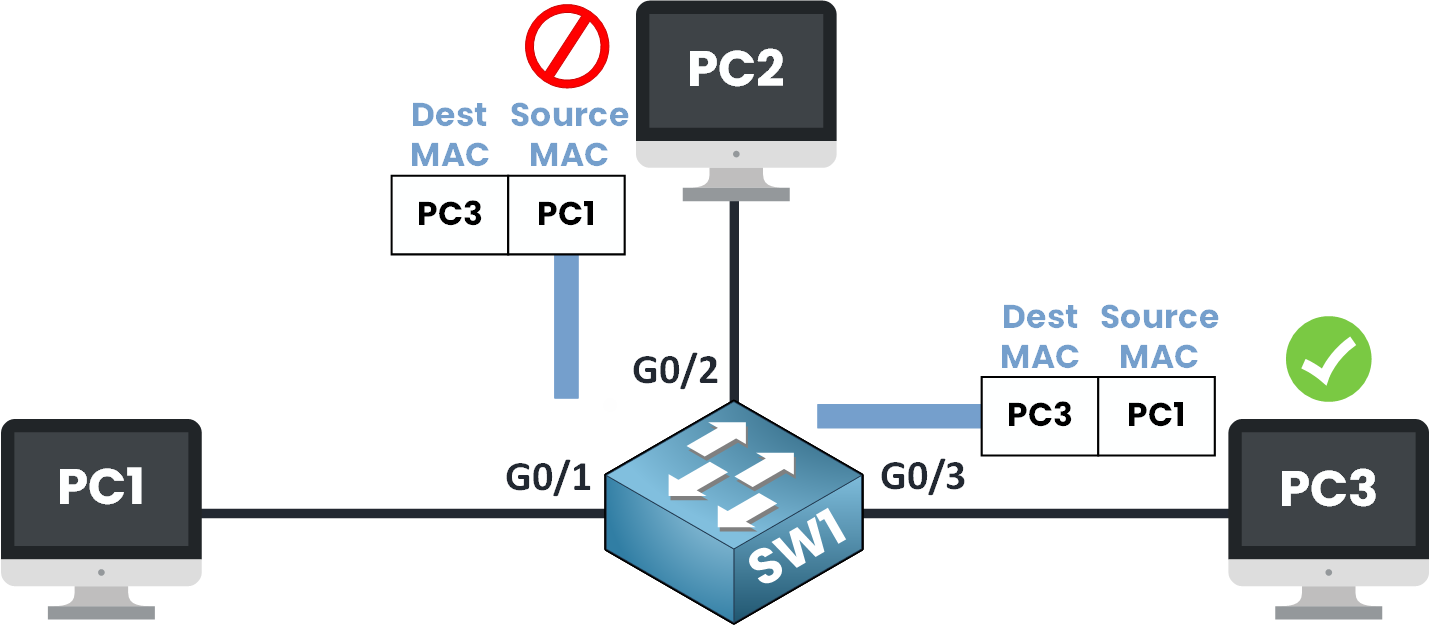
Figure 11 – Frame Flooding
PC3 receives the frame and sends back a reply.
That reply will allow the switch to learn PC3’s MAC address as well.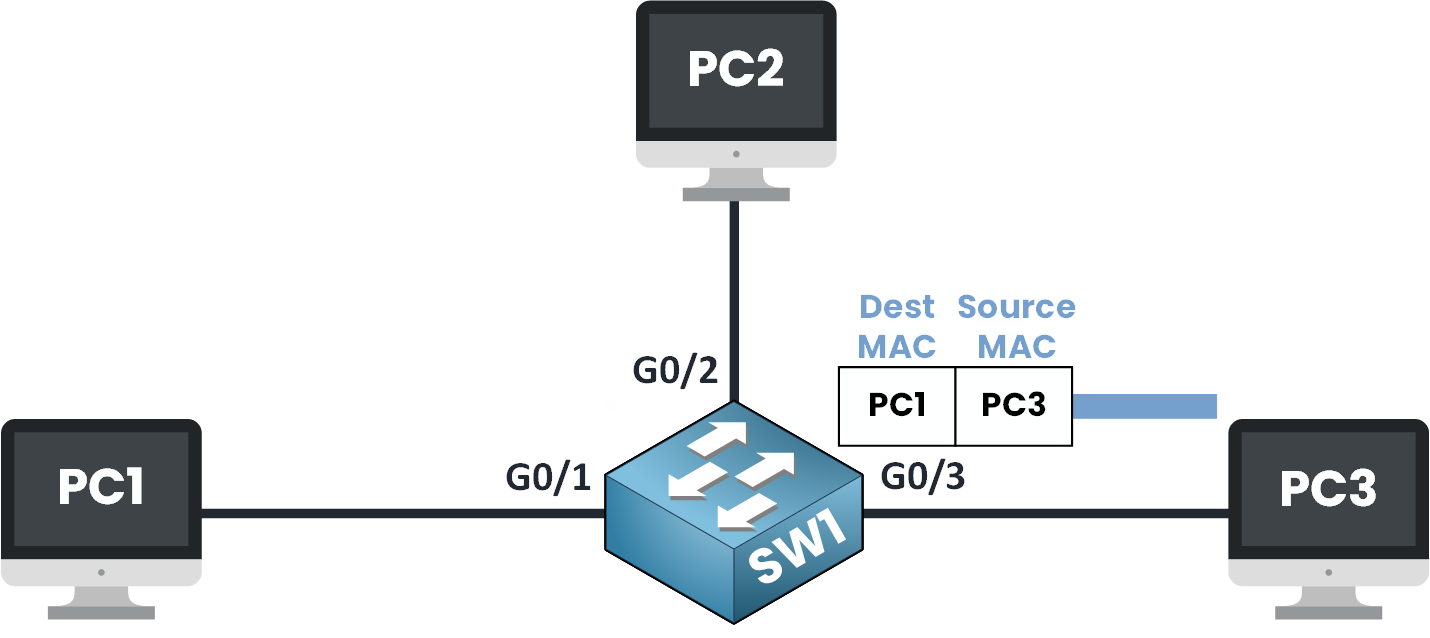
Figure 12 – PC3 Responds and the Switch Learns Its MAC
Let’s check the updated MAC address table:
SW1# show mac address-table dynamic Mac Address Table ------------------------------------------- Vlan Mac Address Type Ports ---- ----------- -------- ----- 1 0011.22aa.33bb DYNAMIC Gi0/1 1 0077.88ee.99ff DYNAMIC Gi0/3 Total Mac Addresses for this criterion: 2As you can see, the switch has now learned the mac address of PC3 which is 0077.88ee.99ff
The switch will now be able to forward the reply directly to PC1 using G0/1 interface.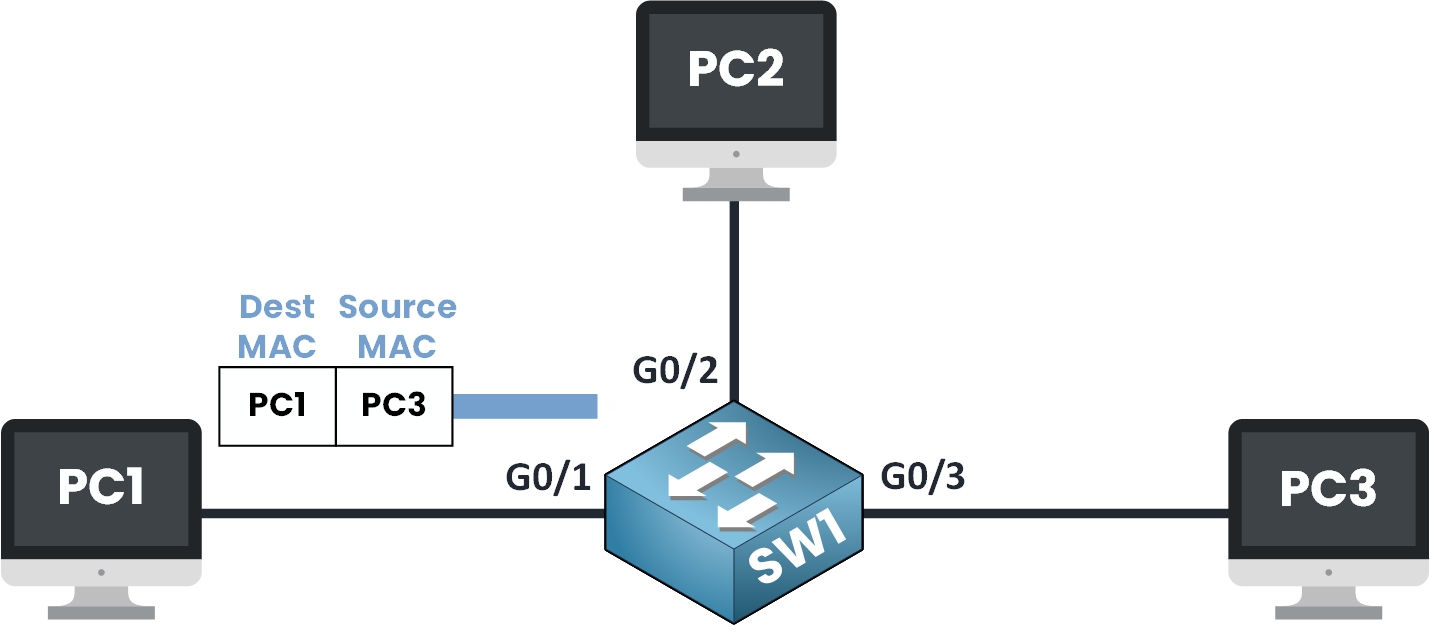
Figure 13 – Frame send to PC1
Keep in mind:
On a production network, you won’t be able to see the MAC addresses being learned one at a time like this.Since the ping exchange happens really fast, the switch learns both addresses almost instantly.
The key point to remember about how does a switch learn MAC addresses is that switches are intelligent devices that remember the source MAC address of the frame received on an interface.
Answer the question below
Which command shows the learned MAC addresses?
The switch doesn't keep MAC addresses forever in his mac address table.
Each MAC address it learns is remembered for 300 seconds (that’s 5 minutes) by default.
This is what we call the Aging Time.You can check it with the following command:
SW1# show mac address-table aging-time Global Aging Time: 300 Vlan Aging Time ---- ----------⏱️ By default, the aging time is set to 300 seconds but you can change it if needed depending on your network environment.
Answer the question below
What is the default aging time for MAC addresses on Cisco switches (in seconds)?
Now imagine you have a MAC address table with over 100 MAC addresses entries,
You only want to check where one specific MAC address is located for example: 0077.88ee.99ff.You don't need to scroll through everything we can use filters to narrow it down.
To filter by MAC address, you can use:
SW1# show mac address-table dynamic address 0077.88ee.99ff Mac Address Table ------------------------------------------- Vlan Mac Address Type Ports ---- ----------- -------- ----- 1 0077.88ee.99ff DYNAMIC Gi0/3 Total Mac Addresses for this criterion: 1Or you can filter by interface directly:
SW1# show mac address-table dynamic interface Gi0/1 Mac Address Table ------------------------------------------- Vlan Mac Address Type Ports ---- ----------- -------- ----- 1 0011.22aa.33bb DYNAMIC Gi0/1 Total Mac Addresses for this criterion: 1Knowing how does a switch learn MAC addresses also means understanding how to clear them for troubleshooting.
You can delete all dynamic MAC entries from the table with this command:
SW1# clear mac address-table dynamicIf you run show mac address-table dynamic again right after,
you’ll see that the table is now completely empty:SW1# show mac address-table dynamic Mac Address Table ------------------------------------------- Vlan Mac Address Type Ports ---- ----------- -------- -----Answer the question below
Which command clears all dynamic MAC entries?
Now that we understand the basics of how does a switch learn MAC addresses per interface, let’s explore a more advanced case: learning multiple MACs on a single port.
So far, we’ve seen the switch learning one MAC address per port !
But did you know that a switch can actually learn multiple MAC addresses on the same port?
Let’s take a simple example.
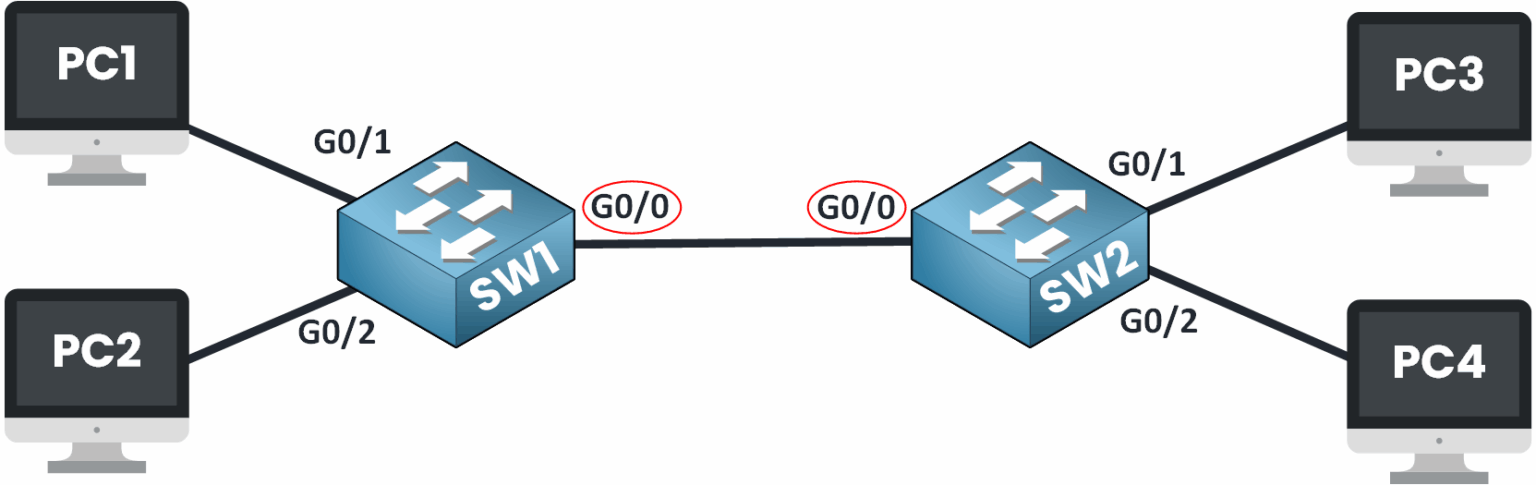
Figure 14 – Learning Multiple MAC Addresses on One Port
Imagine that SW1 is connected to another switch like SW2.
Now let’s take a look at the MAC address table of SW1:
SW1# show mac address-table dynamic Mac Address Table ------------------------------------------- Vlan Mac Address Type Ports ---- ----------- -------- ----- 1 fa16.3e12.a1b2 DYNAMIC Gi0/1 ← PC1 1 fa16.3e23.c3d4 DYNAMIC Gi0/2 ← PC2 1 fa16.3e34.e5f6 DYNAMIC Gi0/0 ← PC3 1 fa16.3e45.789a DYNAMIC Gi0/0 ← PC4 Total Mac Addresses for this criterion: 4You can see that two MAC addresses were learned on the same interface: g0/3
That's because both PC3 and PC4 are connected to SW2 and SW2 is connected to SW1 on g0/3.Since SW1 can reach PC3 and PC4 by using the G0/3, we can have multiple mac addresses learned on one interface.
Now let’s look at the opposite direction the MAC address table of SW2:
SW2# show mac address-table dynamic Mac Address Table ------------------------------------------- Vlan Mac Address Type Ports ---- ----------- -------- ----- 1 fa16.3e12.a1b2 DYNAMIC Gi0/0 ← PC1 1 fa16.3e23.c3d4 DYNAMIC Gi0/0 ← PC2 1 fa16.3e34.e5f6 DYNAMIC Gi0/1 ← PC3 1 fa16.3e45.789a DYNAMIC Gi0/2 ← PC4 Total Mac Addresses for this criterion: 4Same idea here !
SW2 sees both PC1 and PC2 behind Gi0/3 because SW2 it’s connected to SW1 through that port.
“To reach PC1 or PC2, I need to forward the frame out of Gi0/3.”
Answer the question below
Now that you’ve seen how does a switch learn MAC addresses , let’s highlight a few common misconceptions.
A quick recap of the most important things you should absolutely remember for your CCNA ! :)
Common Mistake
What You Really Need to Know
The switch learns the destination MAC address
🚫 False — it only learns the source MAC address
A port can only have one MAC address
🚫 False — a single port can learn multiple MACs, especially uplinks
The MAC address table keeps entries forever
🚫 False — entries expire after the aging-time (default: 300 sec)
Flooding means the switch is broken or misconfigured
🚫 False — flooding is normal when the destination MAC is unknown
Answer the question below