DHCP Relay Agent
Course Contents
1. What Is a DHCP Relay Agent?
Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) simplifies IP address assignment.
But what happens when a DHCP server and a client reside on different subnets?
Normally, broadcast messages like DHCP requests do not cross routers.
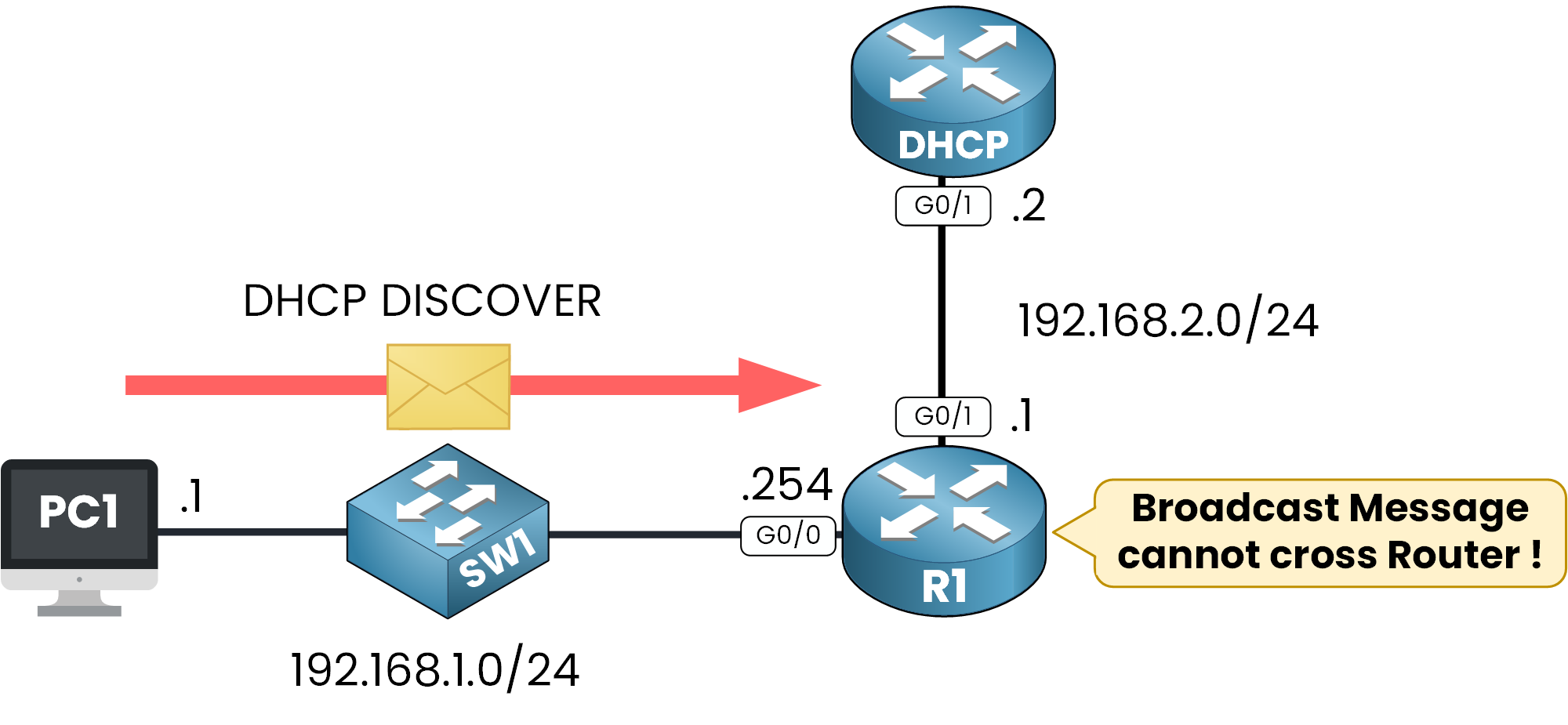
This creates a problem for DHCP clients in remote networks because they cannot communicate with the DHCP server to obtain an IP address.
If you’re wondering what is a DHCP relay agent, it’s the component that solves exactly this problem. A relay agent intercepts DHCP requests from clients and forwards them to a DHCP server located in another subnet.
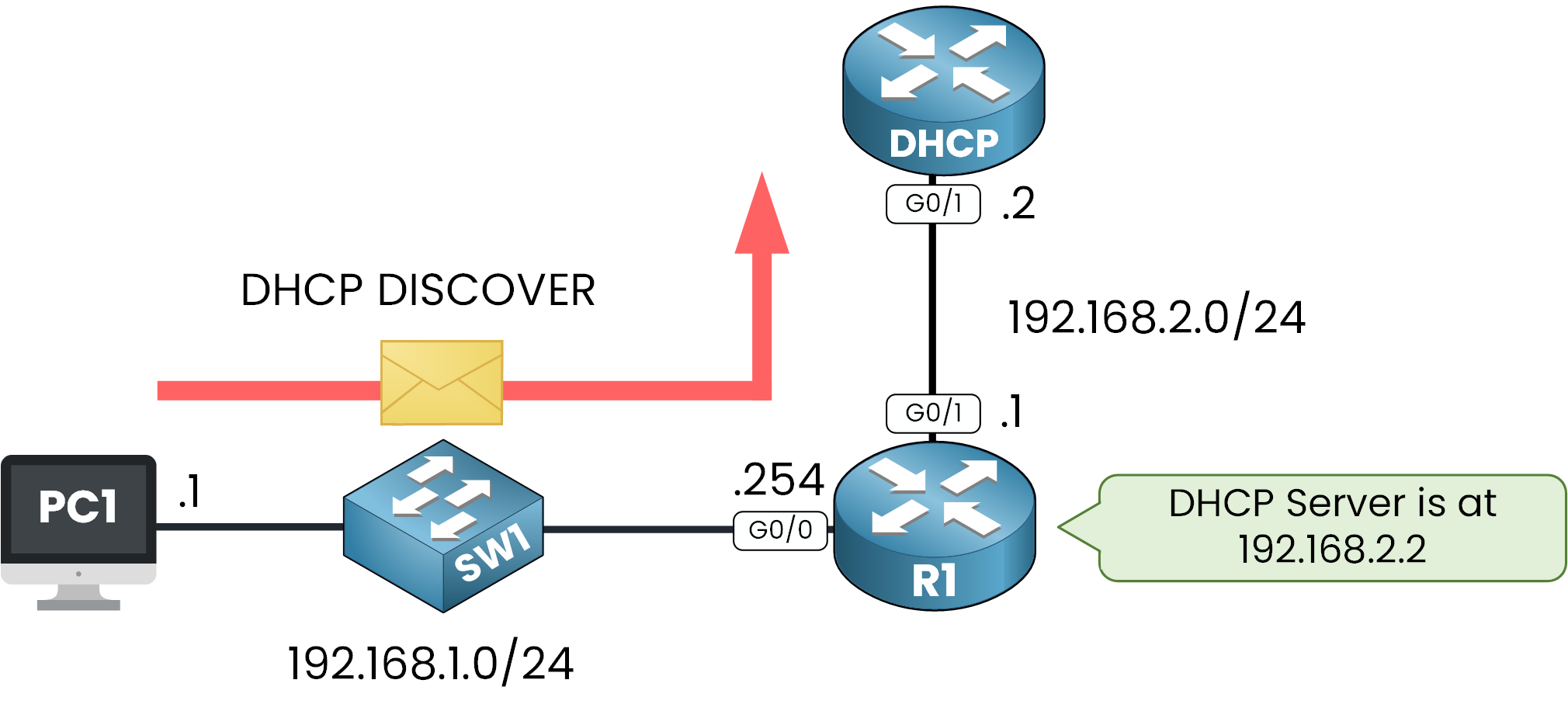
As you can see here, R1 is the DHCP Relay that sends the DHCP message to the DHCP Server located in another subnet.
Let’s take a closer look at why and how a DHCP Relay Agent can solve this challenge.
Why We Need a DHCP Relay Agent
Consider this scenario:

- A DHCP Client (PC1) in subnet 192.168.1.0/24 sends a DHCP DISCOVER broadcast message to obtain an IP address.
- The router (R1) receives the request but because broadcast traffic cannot traverse routers, the message does not reach the DHCP server in subnet 192.168.2.0/24.
Without a DHCP Relay Agent, PC1 would remain unconfigured and unable to connect to the network. By configuring R1 as a relay agent, the DHCP request is forwarded to the server and the server’s response is relayed back to the client.
Overview: What Is a DHCP Relay Agent and How It Works
A DHCP Relay Agent is a service configured on layer 3 devices such as routers or Layer 3 switches. It listens for DHCP requests and forwards them as unicast messages to the DHCP server.
Once the DHCP server responds, the relay agent ensures that the response is forwarded back to the client.
2. DHCP Relay Configuration
Now that we’ve answered the question what is a DHCP relay agent, let’s look at how to configure one on a Cisco router.
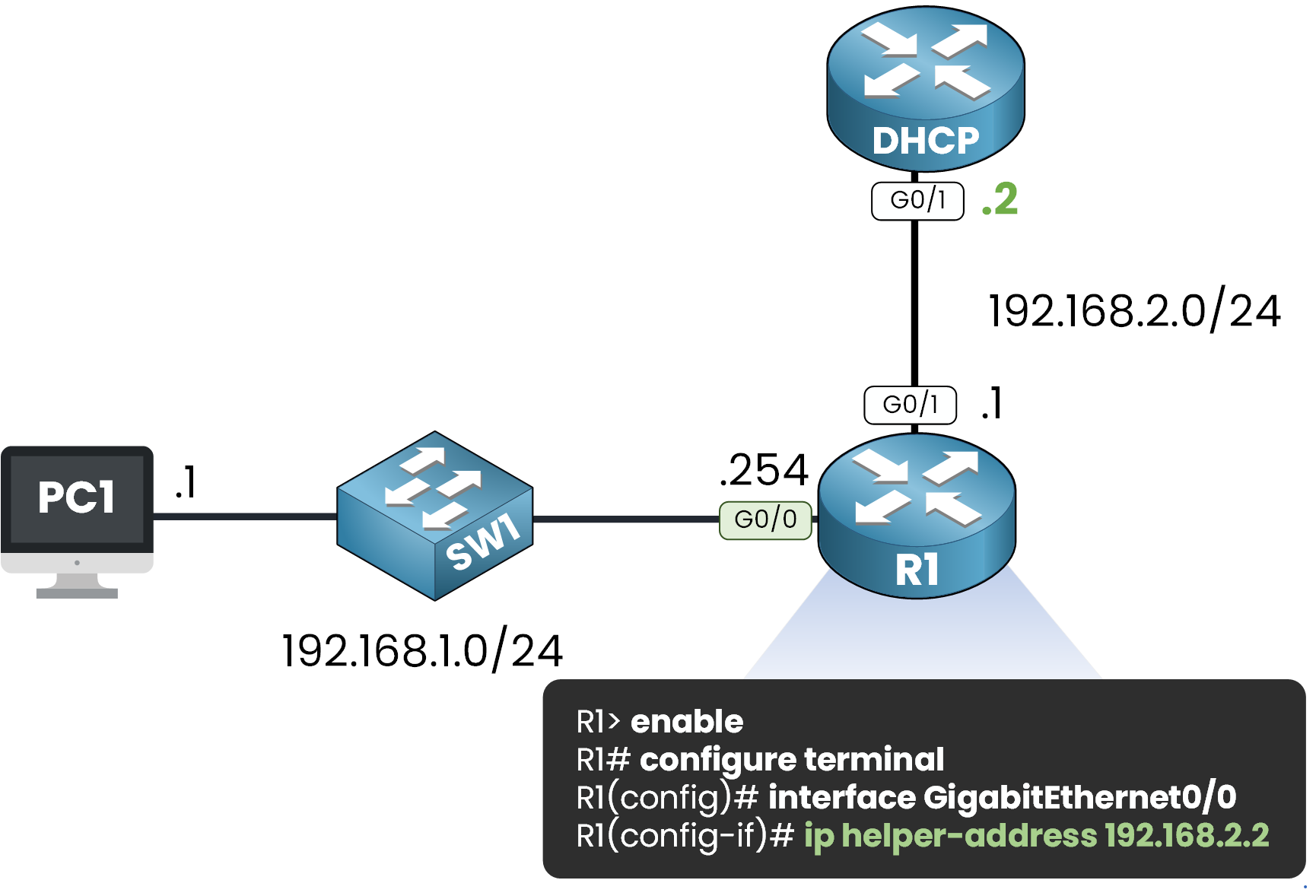
The configuration is straightforward.
Configuring a DHCP Relay Agent on Cisco Devices
- Access the router’s configuration mode:
R1> enable R1# configure terminal
2. Navigate to the interface connected to the local subnet (where the client resides):
R1(config)# interface GigabitEthernet0/0
3. Set the IP address of the DHCP server as the helper address:
R1(config-if)# ip helper-address 192.168.2.2
The ip helper-address command enables the router to forward DHCP requests received on the interface to the server at 192.168.2.2.
3. Verify DHCP Relay
After setting up your DHCP relay agent, it’s essential to verify that it’s functioning as expected.
Let’s explore how you can confirm your configuration and troubleshoot any issues.
Verifying the DHCP Relay Agent Configuration
To verify that your configuration is working correctly, use the show ip dhcp relay command.
R1# show ip dhcp relay
Interface Helper address VRF
---------------------------------------------------
GigabitEthernet0/0 192.168.2.2 global
Here we can view that the relay agent configured on GigabitEthernet0/0 will forward DHCP requests to the server at 192.168.2.2.
Monitor DHCP Events in Real-Time
You can monitor DHCP activity as the relay agent facilitates communication between the DHCP Client and DHCP Server. Let’s walk through the process using the debug ip dhcp events command:
R1# debug ip dhcp events *Mar 1 00:02:03.123: DHCPD: DHCPDISCOVER received from client 0100.1c42.4c39.91 on interface GigabitEthernet0/0 *Mar 1 00:02:03.124: DHCPD: Forwarding DHCPDISCOVER to helper address 192.168.2.2 *Mar 1 00:02:04.567: DHCPD: DHCPOFFER received from server 192.168.2.2 *Mar 1 00:02:04.568: DHCPD: Forwarding DHCPOFFER to client 0100.1c42.4c39.91 on interface GigabitEthernet0/0 *Mar 1 00:02:05.890: DHCPD: DHCPREQUEST received from client 0100.1c42.4c39.91 on interface GigabitEthernet0/0 *Mar 1 00:02:05.891: DHCPD: Forwarding DHCPREQUEST to helper address 192.168.2.2 *Mar 1 00:02:06.012: DHCPD: DHCPACK received from server 192.168.2.2 *Mar 1 00:02:06.013: DHCPD: Forwarding DHCPACK to client£ 0100.1c42.4c39.91 on interface GigabitEthernet0/0
This detailed output confirms that the entire DORA process (DISCOVER, OFFER, REQUEST, ACK) has been completed successfully.
DHCP Relay Process in Action
Let’s walk through how a DHCP relay agent facilitates IP address allocation.
Let’s break this down step by step:
STEP 1 – DHCP DISCOVER: The Client Searches for a DHCP Server
When the client sends a DHCPDISCOVER broadcast message, the relay agent intercepts it and forwards it as a unicast to the DHCP server (192.168.2.2).
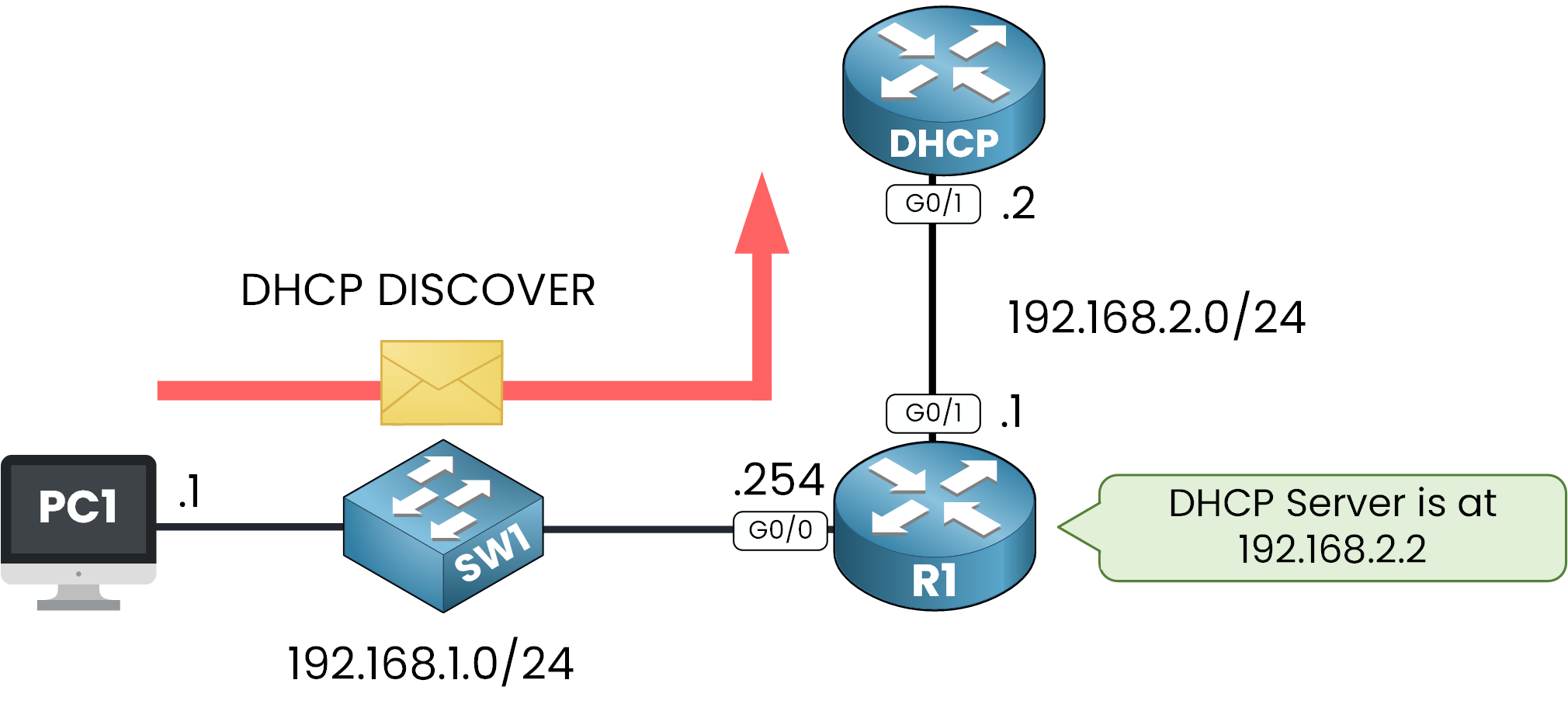
Since broadcast messages cannot cross routers, the relay agent ensures the request reaches the DHCP server.
STEP 2 – DHCP OFFER: The Server Makes an Offer
The DHCP server responds with a DHCPOFFER, providing the client with an available IP address and configuration details. The relay agent forwards this response to the client.
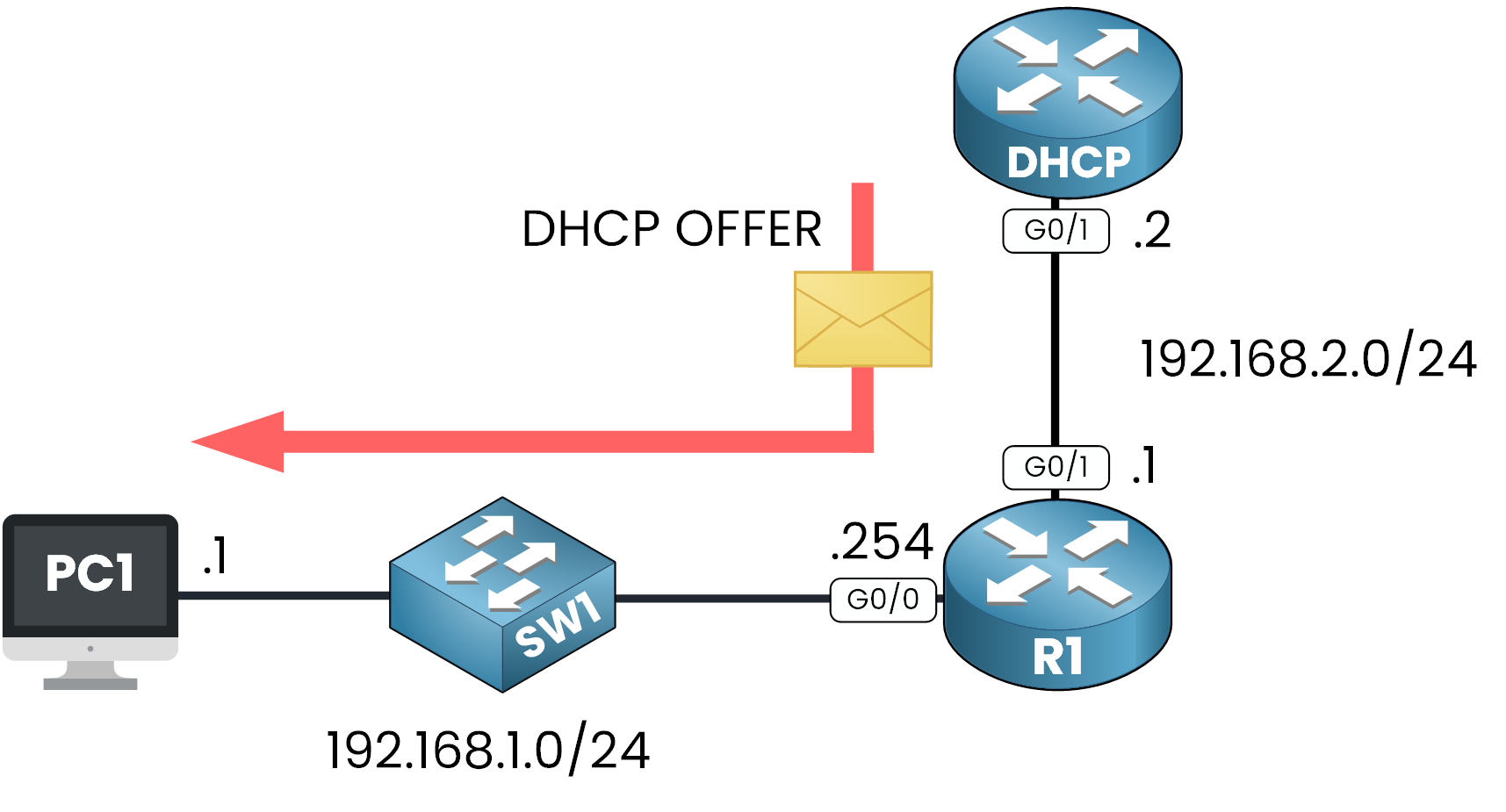
This is where the client gets its first look at the offered network settings.
STEP 3 – DHCP REQUEST: The Client Accepts the Offer
The client replies with a DHCPREQUEST message to indicate it accepts the offer. The relay agent forwards this message to the DHCP server.
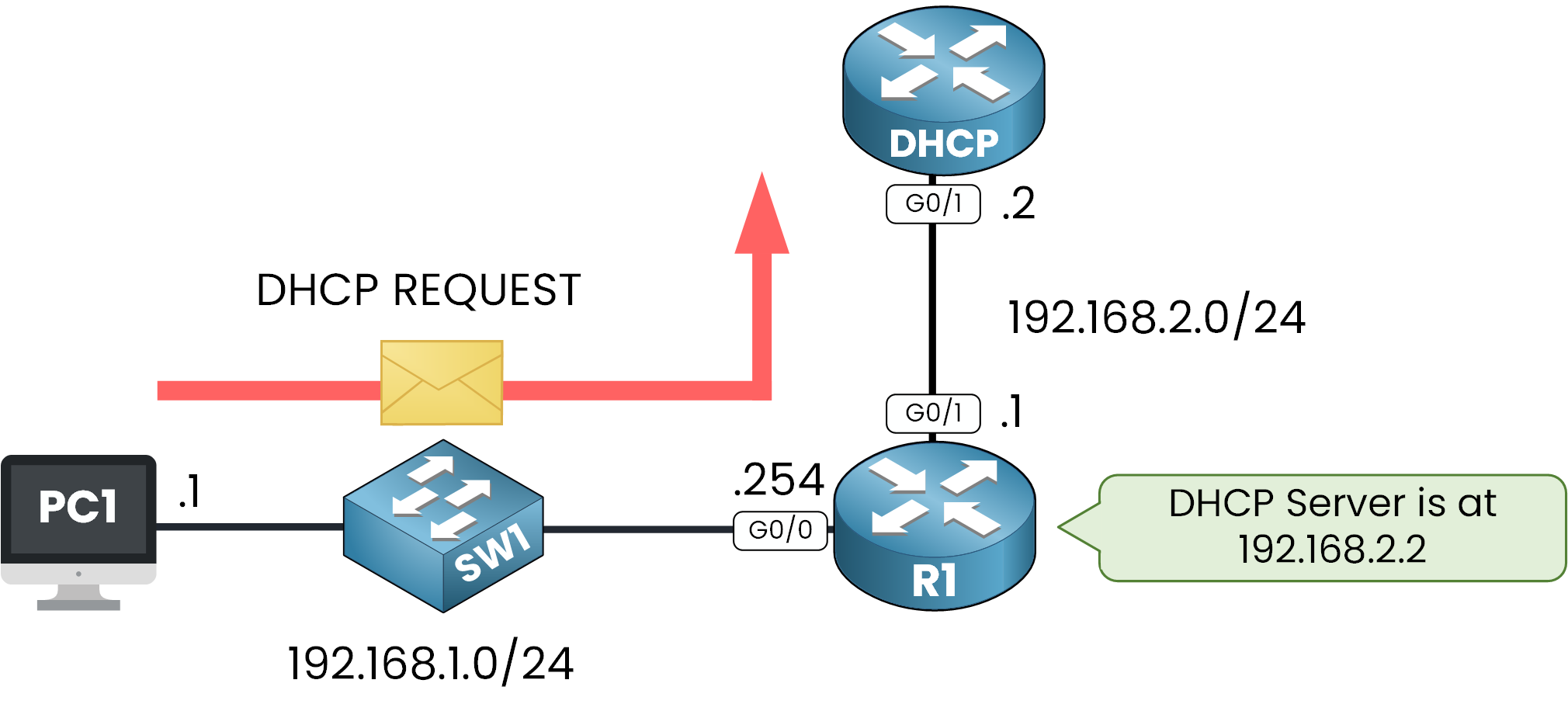
This step confirms that the client is ready to use the assigned IP address, along with the subnet mask, default gateway, DNS server and lease duration.
STEP 4 – DHCP ACK: The Server Confirms the Allocation
Finally, the server sends a DHCPACK message to confirm the IP address allocation and configuration. The relay agent ensures this message reaches the client.
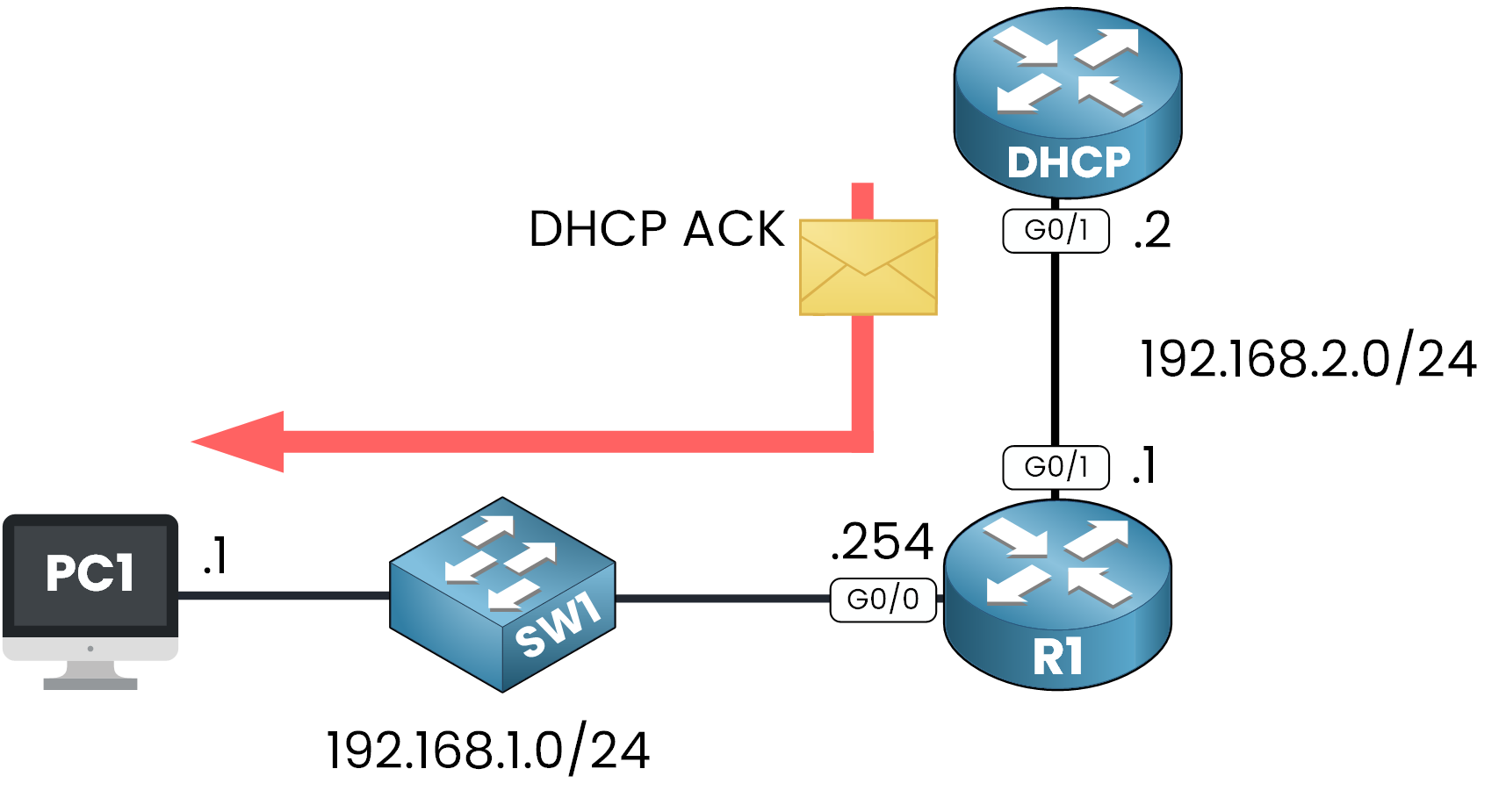
The client can now configure its network settings and begin communication on the network.
4. Conclusion
So, what is a DHCP relay agent really about? It’s a crucial component that makes dynamic IP assignment possible when clients and DHCP servers are located on different subnets.
Instead of allowing DHCP broadcast messages to fail at the router boundary, the relay agent captures and forwards them as unicast packets to the correct DHCP server, then brings the response back to the client.
Here’s what you’ve learned:
- How to configure it using the ip helper-address command on Cisco routers
- What happens during the full DORA exchange (Discover, Offer, Request, Acknowledgment)
- How to verify and debug the setup with real Cisco CLI commands
This mechanism may seem simple, but it’s a fundamental piece of scalable network design and it’s something you need to master for the CCNA exam and real-world implementation.
